Julian De Freitas
Anti Robot Speciesism
Mar 26, 2025

Abstract:Humanoid robots are a form of embodied artificial intelligence (AI) that looks and acts more and more like humans. Powered by generative AI and advances in robotics, humanoid robots can speak and interact with humans rather naturally but are still easily recognizable as robots. But how will we treat humanoids when they seem indistinguishable from humans in appearance and mind? We find a tendency (called "anti-robot" speciesism) to deny such robots humanlike capabilities, driven by motivations to accord members of the human species preferential treatment. Six experiments show that robots are denied humanlike attributes, simply because they are not biological beings and because humans want to avoid feelings of cognitive dissonance when utilizing such robots for unsavory tasks. Thus, people do not rationally attribute capabilities to perfectly humanlike robots but deny them capabilities as it suits them.
Lessons From an App Update at Replika AI: Identity Discontinuity in Human-AI Relationships
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Can consumers form especially deep emotional bonds with AI and be vested in AI identities over time? We leverage a natural app-update event at Replika AI, a popular US-based AI companion, to shed light on these questions. We find that, after the app removed its erotic role play (ERP) feature, preventing intimate interactions between consumers and chatbots that were previously possible, this event triggered perceptions in customers that their AI companion's identity had discontinued. This in turn predicted negative consumer welfare and marketing outcomes related to loss, including mourning the loss, and devaluing the "new" AI relative to the "original". Experimental evidence confirms these findings. Further experiments find that AI companions users feel closer to their AI companion than even their best human friend, and mourn a loss of their AI companion more than a loss of various other inanimate products. In short, consumers are forming human-level relationships with AI companions; disruptions to these relationships trigger real patterns of mourning as well as devaluation of the offering; and the degree of mourning and devaluation are explained by perceived discontinuity in the AIs identity. Our results illustrate that relationships with AI are truly personal, creating unique benefits and risks for consumers and firms alike.
Active World Model Learning with Progress Curiosity
Jul 15, 2020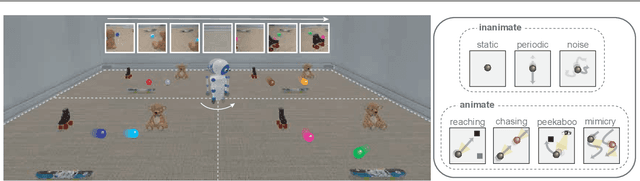
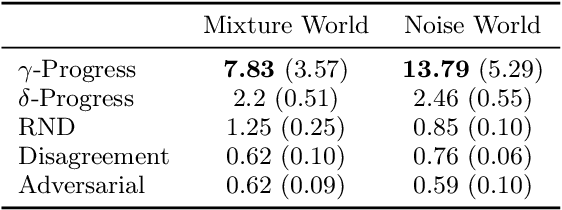
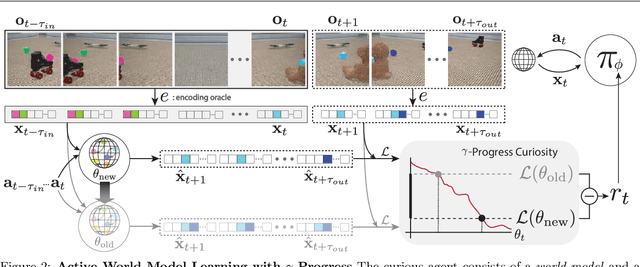
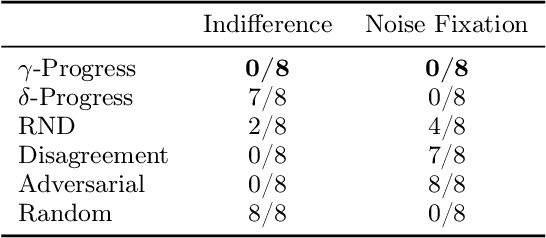
Abstract:World models are self-supervised predictive models of how the world evolves. Humans learn world models by curiously exploring their environment, in the process acquiring compact abstractions of high bandwidth sensory inputs, the ability to plan across long temporal horizons, and an understanding of the behavioral patterns of other agents. In this work, we study how to design such a curiosity-driven Active World Model Learning (AWML) system. To do so, we construct a curious agent building world models while visually exploring a 3D physical environment rich with distillations of representative real-world agents. We propose an AWML system driven by $\gamma$-Progress: a scalable and effective learning progress-based curiosity signal. We show that $\gamma$-Progress naturally gives rise to an exploration policy that directs attention to complex but learnable dynamics in a balanced manner, thus overcoming the "white noise problem". As a result, our $\gamma$-Progress-driven controller achieves significantly higher AWML performance than baseline controllers equipped with state-of-the-art exploration strategies such as Random Network Distillation and Model Disagreement.
ThreeDWorld: A Platform for Interactive Multi-Modal Physical Simulation
Jul 09, 2020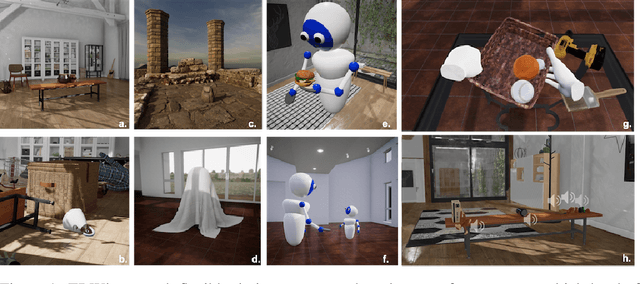
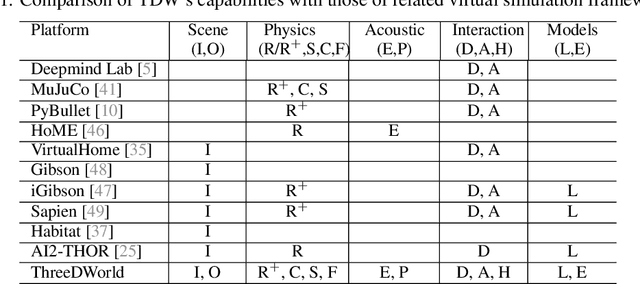

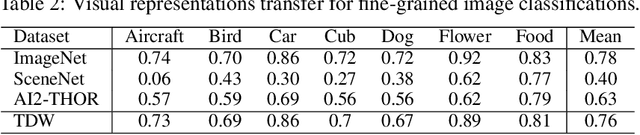
Abstract:We introduce ThreeDWorld (TDW), a platform for interactive multi-modal physical simulation. With TDW, users can simulate high-fidelity sensory data and physical interactions between mobile agents and objects in a wide variety of rich 3D environments. TDW has several unique properties: 1) realtime near photo-realistic image rendering quality; 2) a library of objects and environments with materials for high-quality rendering, and routines enabling user customization of the asset library; 3) generative procedures for efficiently building classes of new environments 4) high-fidelity audio rendering; 5) believable and realistic physical interactions for a wide variety of material types, including cloths, liquid, and deformable objects; 6) a range of "avatar" types that serve as embodiments of AI agents, with the option for user avatar customization; and 7) support for human interactions with VR devices. TDW also provides a rich API enabling multiple agents to interact within a simulation and return a range of sensor and physics data representing the state of the world. We present initial experiments enabled by the platform around emerging research directions in computer vision, machine learning, and cognitive science, including multi-modal physical scene understanding, multi-agent interactions, models that "learn like a child", and attention studies in humans and neural networks. The simulation platform will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge