James Traer
Finding Fallen Objects Via Asynchronous Audio-Visual Integration
Jul 07, 2022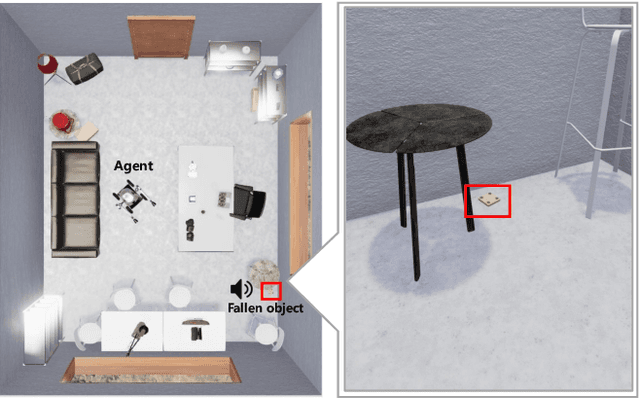
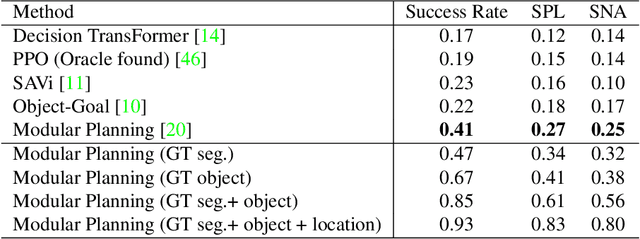
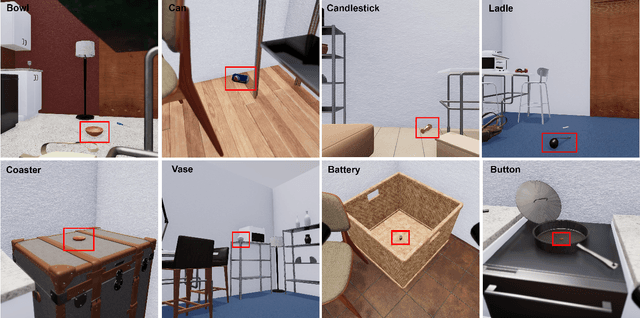
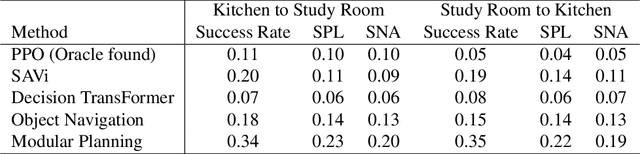
Abstract:The way an object looks and sounds provide complementary reflections of its physical properties. In many settings cues from vision and audition arrive asynchronously but must be integrated, as when we hear an object dropped on the floor and then must find it. In this paper, we introduce a setting in which to study multi-modal object localization in 3D virtual environments. An object is dropped somewhere in a room. An embodied robot agent, equipped with a camera and microphone, must determine what object has been dropped -- and where -- by combining audio and visual signals with knowledge of the underlying physics. To study this problem, we have generated a large-scale dataset -- the Fallen Objects dataset -- that includes 8000 instances of 30 physical object categories in 64 rooms. The dataset uses the ThreeDWorld platform which can simulate physics-based impact sounds and complex physical interactions between objects in a photorealistic setting. As a first step toward addressing this challenge, we develop a set of embodied agent baselines, based on imitation learning, reinforcement learning, and modular planning, and perform an in-depth analysis of the challenge of this new task.
Object-based synthesis of scraping and rolling sounds based on non-linear physical constraints
Dec 16, 2021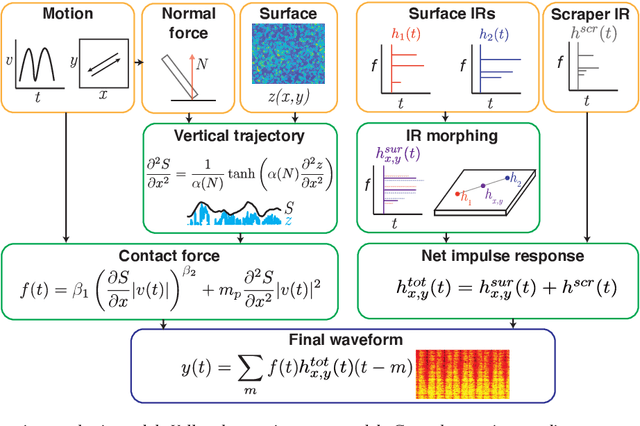
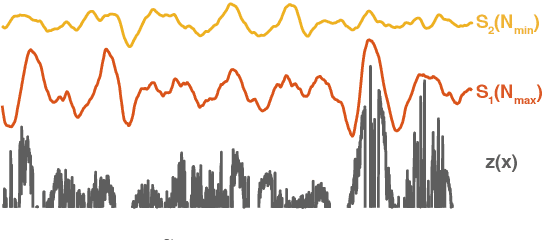
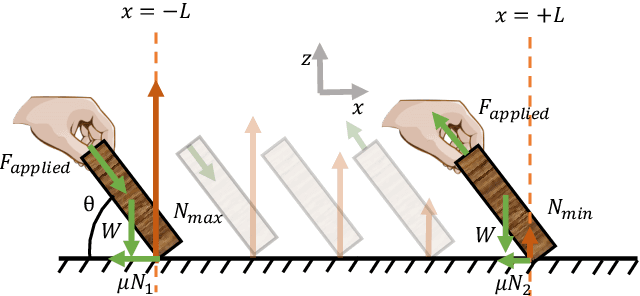
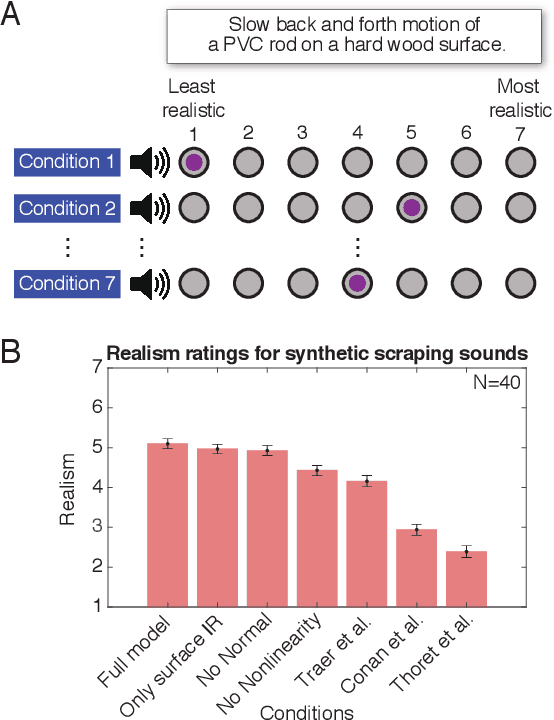
Abstract:Sustained contact interactions like scraping and rolling produce a wide variety of sounds. Previous studies have explored ways to synthesize these sounds efficiently and intuitively but could not fully mimic the rich structure of real instances of these sounds. We present a novel source-filter model for realistic synthesis of scraping and rolling sounds with physically and perceptually relevant controllable parameters constrained by principles of mechanics. Key features of our model include non-linearities to constrain the contact force, naturalistic normal force variation for different motions, and a method for morphing impulse responses within a material to achieve location-dependence. Perceptual experiments show that the presented model is able to synthesize realistic scraping and rolling sounds while conveying physical information similar to that in recorded sounds.
ThreeDWorld: A Platform for Interactive Multi-Modal Physical Simulation
Jul 09, 2020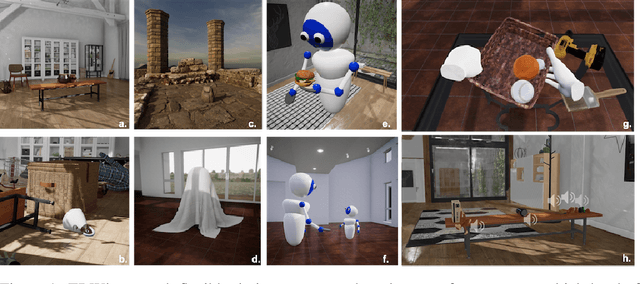
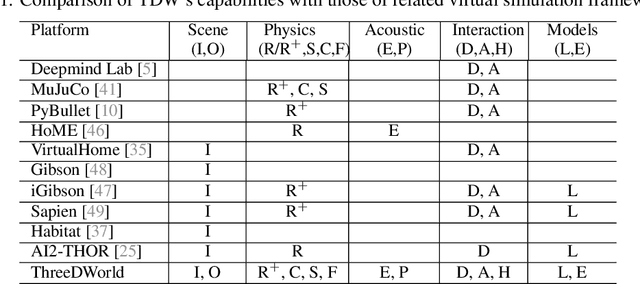

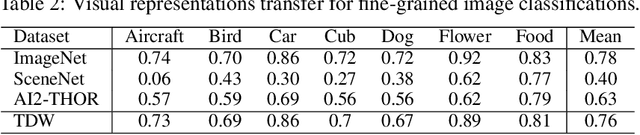
Abstract:We introduce ThreeDWorld (TDW), a platform for interactive multi-modal physical simulation. With TDW, users can simulate high-fidelity sensory data and physical interactions between mobile agents and objects in a wide variety of rich 3D environments. TDW has several unique properties: 1) realtime near photo-realistic image rendering quality; 2) a library of objects and environments with materials for high-quality rendering, and routines enabling user customization of the asset library; 3) generative procedures for efficiently building classes of new environments 4) high-fidelity audio rendering; 5) believable and realistic physical interactions for a wide variety of material types, including cloths, liquid, and deformable objects; 6) a range of "avatar" types that serve as embodiments of AI agents, with the option for user avatar customization; and 7) support for human interactions with VR devices. TDW also provides a rich API enabling multiple agents to interact within a simulation and return a range of sensor and physics data representing the state of the world. We present initial experiments enabled by the platform around emerging research directions in computer vision, machine learning, and cognitive science, including multi-modal physical scene understanding, multi-agent interactions, models that "learn like a child", and attention studies in humans and neural networks. The simulation platform will be made publicly available.
Machine learning in acoustics: a review
May 11, 2019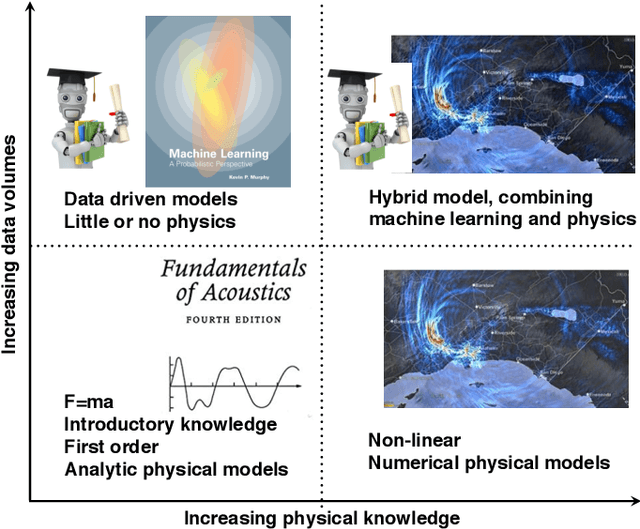
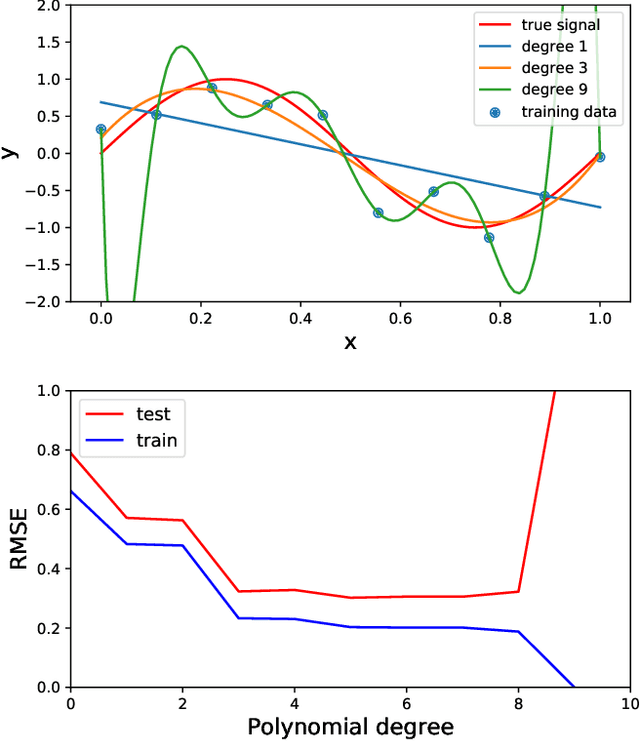
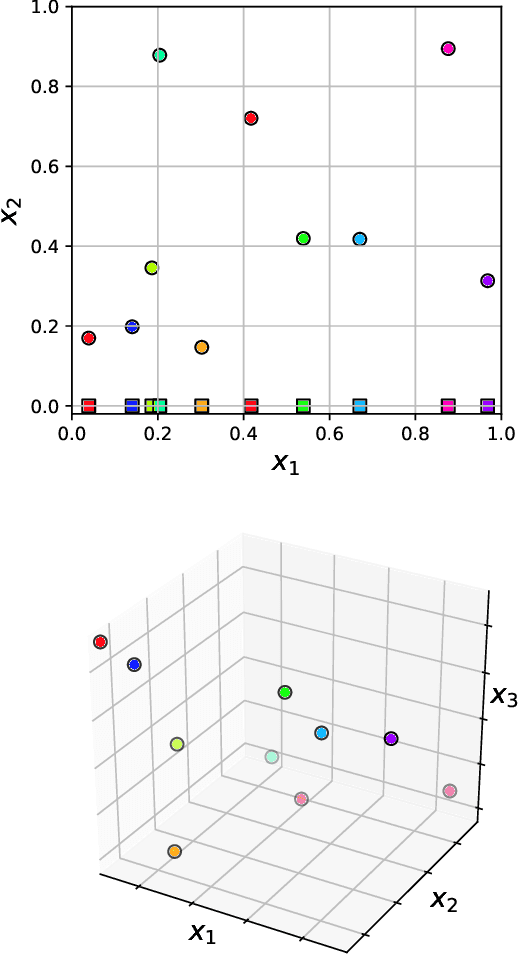
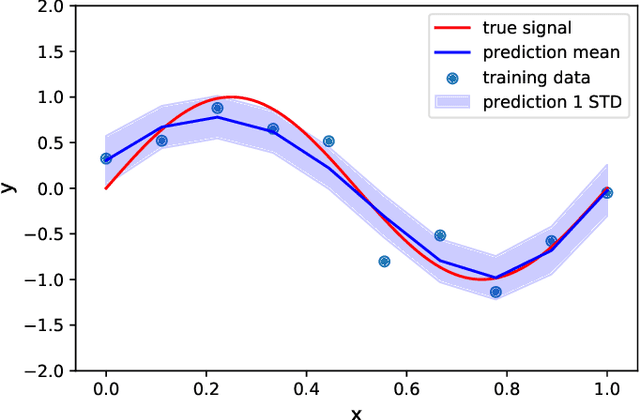
Abstract:Acoustic data provide scientific and engineering insights in fields ranging from biology and communications to ocean and Earth science. We survey the recent advances and transformative potential of machine learning (ML), including deep learning, in the field of acoustics. ML is a broad family of statistical techniques for automatically detecting and utilizing patterns in data. Relative to conventional acoustics and signal processing, ML is data-driven. Given sufficient training data, ML can discover complex relationships between features. With large volumes of training data, ML can discover models describing complex acoustic phenomena such as human speech and reverberation. ML in acoustics is rapidly developing with compelling results and significant future promise. We first introduce ML, then highlight ML developments in five acoustics research areas: source localization in speech processing, source localization in ocean acoustics, bioacoustics, seismic exploration, and environmental sounds in everyday scenes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge