L-WISE: Boosting Human Image Category Learning Through Model-Based Image Selection And Enhancement
Paper and Code
Dec 12, 2024


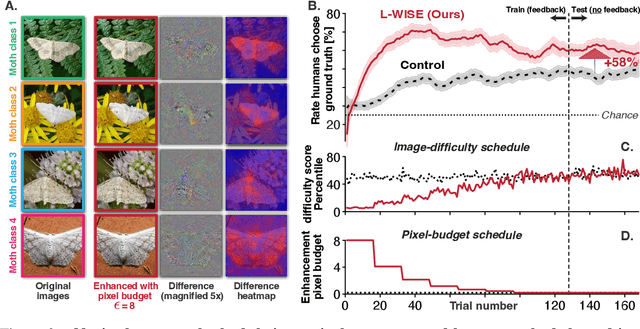
The currently leading artificial neural network (ANN) models of the visual ventral stream -- which are derived from a combination of performance optimization and robustification methods -- have demonstrated a remarkable degree of behavioral alignment with humans on visual categorization tasks. Extending upon previous work, we show that not only can these models guide image perturbations that change the induced human category percepts, but they also can enhance human ability to accurately report the original ground truth. Furthermore, we find that the same models can also be used out-of-the-box to predict the proportion of correct human responses to individual images, providing a simple, human-aligned estimator of the relative difficulty of each image. Motivated by these observations, we propose to augment visual learning in humans in a way that improves human categorization accuracy at test time. Our learning augmentation approach consists of (i) selecting images based on their model-estimated recognition difficulty, and (ii) using image perturbations that aid recognition for novice learners. We find that combining these model-based strategies gives rise to test-time categorization accuracy gains of 33-72% relative to control subjects without these interventions, despite using the same number of training feedback trials. Surprisingly, beyond the accuracy gain, the training time for the augmented learning group was also shorter by 20-23%. We demonstrate the efficacy of our approach in a fine-grained categorization task with natural images, as well as tasks in two clinically relevant image domains -- histology and dermoscopy -- where visual learning is notoriously challenging. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first application of ANNs to increase visual learning performance in humans by enhancing category-specific features.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge