Guizhen Chen
Lingshu: A Generalist Foundation Model for Unified Multimodal Medical Understanding and Reasoning
Jun 08, 2025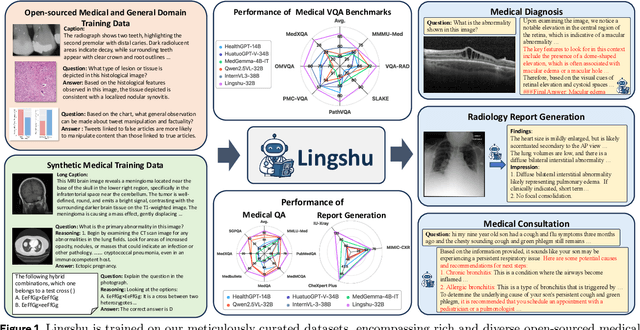
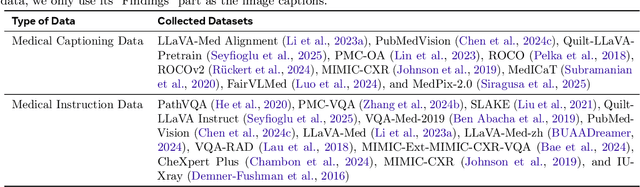
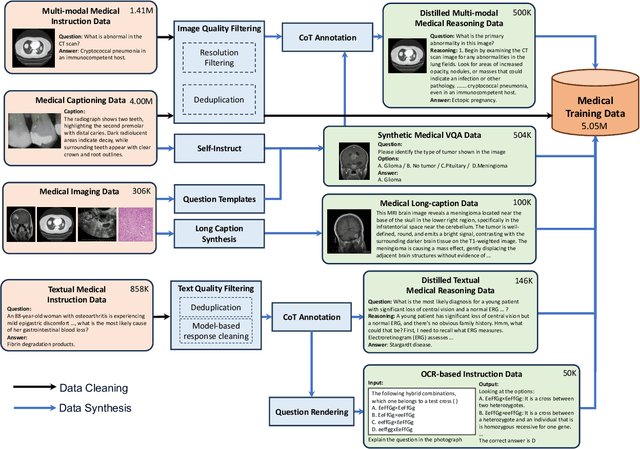
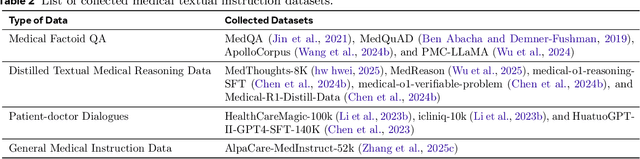
Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have demonstrated impressive capabilities in understanding common visual elements, largely due to their large-scale datasets and advanced training strategies. However, their effectiveness in medical applications remains limited due to the inherent discrepancies between data and tasks in medical scenarios and those in the general domain. Concretely, existing medical MLLMs face the following critical limitations: (1) limited coverage of medical knowledge beyond imaging, (2) heightened susceptibility to hallucinations due to suboptimal data curation processes, (3) lack of reasoning capabilities tailored for complex medical scenarios. To address these challenges, we first propose a comprehensive data curation procedure that (1) efficiently acquires rich medical knowledge data not only from medical imaging but also from extensive medical texts and general-domain data; and (2) synthesizes accurate medical captions, visual question answering (VQA), and reasoning samples. As a result, we build a multimodal dataset enriched with extensive medical knowledge. Building on the curated data, we introduce our medical-specialized MLLM: Lingshu. Lingshu undergoes multi-stage training to embed medical expertise and enhance its task-solving capabilities progressively. Besides, we preliminarily explore the potential of applying reinforcement learning with verifiable rewards paradigm to enhance Lingshu's medical reasoning ability. Additionally, we develop MedEvalKit, a unified evaluation framework that consolidates leading multimodal and textual medical benchmarks for standardized, fair, and efficient model assessment. We evaluate the performance of Lingshu on three fundamental medical tasks, multimodal QA, text-based QA, and medical report generation. The results show that Lingshu consistently outperforms the existing open-source multimodal models on most tasks ...
FINEREASON: Evaluating and Improving LLMs' Deliberate Reasoning through Reflective Puzzle Solving
Feb 27, 2025



Abstract:Many challenging reasoning tasks require not just rapid, intuitive responses, but a more deliberate, multi-step approach. Recent progress in large language models (LLMs) highlights an important shift from the "System 1" way of quick reactions to the "System 2" style of reflection-and-correction problem solving. However, current benchmarks heavily rely on the final-answer accuracy, leaving much of a model's intermediate reasoning steps unexamined. This fails to assess the model's ability to reflect and rectify mistakes within the reasoning process. To bridge this gap, we introduce FINEREASON, a logic-puzzle benchmark for fine-grained evaluation of LLMs' reasoning capabilities. Each puzzle can be decomposed into atomic steps, making it ideal for rigorous validation of intermediate correctness. Building on this, we introduce two tasks: state checking, and state transition, for a comprehensive evaluation of how models assess the current situation and plan the next move. To support broader research, we also provide a puzzle training set aimed at enhancing performance on general mathematical tasks. We show that models trained on our state checking and transition data demonstrate gains in math reasoning by up to 5.1% on GSM8K.
Reasoning Paths Optimization: Learning to Reason and Explore From Diverse Paths
Oct 07, 2024



Abstract:Advanced models such as OpenAI o1 exhibit impressive problem-solving capabilities through step-by-step reasoning. However, they may still falter on more complex problems, making errors that disrupt their reasoning paths. We attribute this to the expansive solution space, where each step has the risk of diverging into mistakes. To enhance language model reasoning, we introduce a specialized training framework called Reasoning Paths Optimization (RPO), which enables learning to reason and explore from diverse paths. Our approach encourages favorable branches at each reasoning step while penalizing unfavorable ones, enhancing the model's overall problem-solving performance. Reasoning Paths Optimization does not rely on large-scale human-annotated rationales or outputs from closed-source models, making it scalable and data-efficient. We focus on multi-step reasoning tasks, such as math word problems and science-based exam questions. The experiments demonstrate that our framework significantly enhances the reasoning performance of large language models, with up to 3.1% and 4.3% improvement on GSM8K and MMLU (STEM) respectively. Our data and code can be found at https://reasoning-paths.github.io.
Data Augmentation using LLMs: Data Perspectives, Learning Paradigms and Challenges
Mar 05, 2024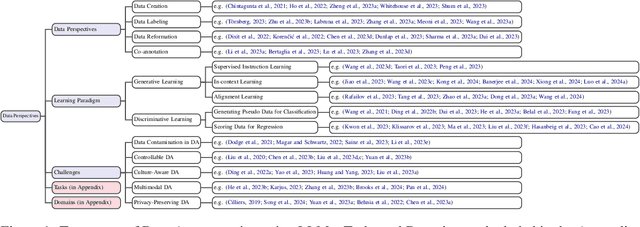
Abstract:In the rapidly evolving field of machine learning (ML), data augmentation (DA) has emerged as a pivotal technique for enhancing model performance by diversifying training examples without the need for additional data collection. This survey explores the transformative impact of Large Language Models (LLMs) on DA, particularly addressing the unique challenges and opportunities they present in the context of natural language processing (NLP) and beyond. From a data perspective and a learning perspective, we examine various strategies that utilize Large Language Models for data augmentation, including a novel exploration of learning paradigms where LLM-generated data is used for further training. Additionally, this paper delineates the primary challenges faced in this domain, ranging from controllable data augmentation to multi modal data augmentation. This survey highlights the paradigm shift introduced by LLMs in DA, aims to serve as a foundational guide for researchers and practitioners in this field.
How do Large Language Models Handle Multilingualism?
Feb 29, 2024Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) demonstrate remarkable performance across a spectrum of languages. In this work, we delve into the question: How do LLMs handle multilingualism? We introduce a framework that depicts LLMs' processing of multilingual inputs: In the first several layers, LLMs understand the question, converting multilingual inputs into English to facilitate the task-solving phase. In the intermediate layers, LLMs engage in problem-solving by thinking in English and incorporating multilingual knowledge to obtain factual content, leveraging the self-attention and feed-forward structures, respectively. In the last several layers, LLMs generate responses that align with the original language of the query. In addition, we investigate the existence of language-specific neurons when processing a certain language. To detect neurons activated by the input language, even without labels, we innovatively design a Parallel Language specific Neuron Detection ($\texttt{PLND}$) method that effectively measures the significance of neurons when handling multilingual inputs. By comprehensive ablation analysis through deactivating neurons of different layers and structures, we verify the framework that we propose. Additionally, we demonstrate that we can utilize such a framework to effectively enhance the multilingual ability with much less training effort.
Contrastive Chain-of-Thought Prompting
Nov 15, 2023Abstract:Despite the success of chain of thought in enhancing language model reasoning, the underlying process remains less well understood. Although logically sound reasoning appears inherently crucial for chain of thought, prior studies surprisingly reveal minimal impact when using invalid demonstrations instead. Furthermore, the conventional chain of thought does not inform language models on what mistakes to avoid, which potentially leads to more errors. Hence, inspired by how humans can learn from both positive and negative examples, we propose contrastive chain of thought to enhance language model reasoning. Compared to the conventional chain of thought, our approach provides both valid and invalid reasoning demonstrations, to guide the model to reason step-by-step while reducing reasoning mistakes. To improve generalization, we introduce an automatic method to construct contrastive demonstrations. Our experiments on reasoning benchmarks demonstrate that contrastive chain of thought can serve as a general enhancement of chain-of-thought prompting.
Exploring the Potential of Large Language Models in Computational Argumentation
Nov 15, 2023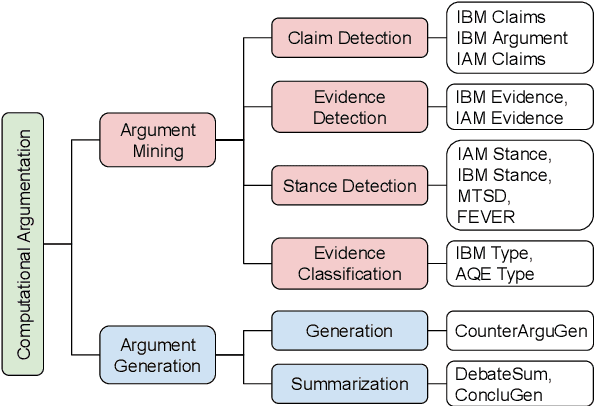
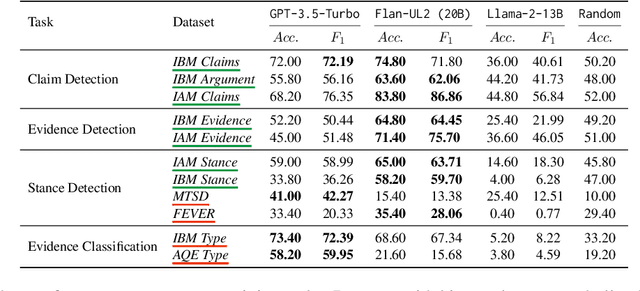
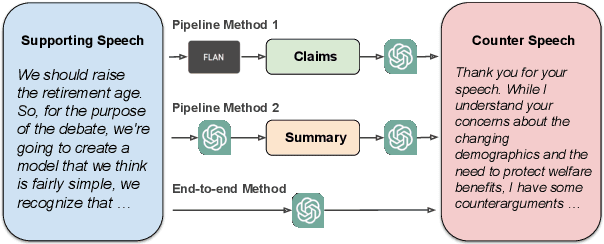
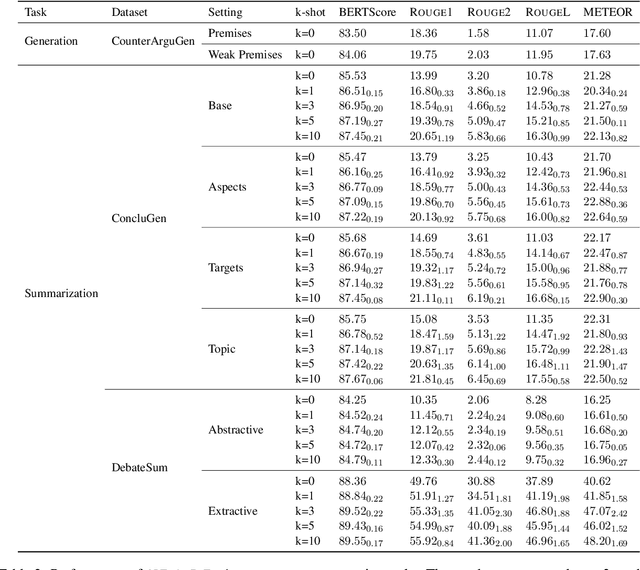
Abstract:Computational argumentation has become an essential tool in various fields, including artificial intelligence, law, and public policy. It is an emerging research field in natural language processing (NLP) that attracts increasing attention. Research on computational argumentation mainly involves two types of tasks: argument mining and argument generation. As large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated strong abilities in understanding context and generating natural language, it is worthwhile to evaluate the performance of LLMs on various computational argumentation tasks. This work aims to embark on an assessment of LLMs, such as ChatGPT, Flan models and LLaMA2 models, under zero-shot and few-shot settings within the realm of computational argumentation. We organize existing tasks into 6 main classes and standardise the format of 14 open-sourced datasets. In addition, we present a new benchmark dataset on counter speech generation, that aims to holistically evaluate the end-to-end performance of LLMs on argument mining and argument generation. Extensive experiments show that LLMs exhibit commendable performance across most of these datasets, demonstrating their capabilities in the field of argumentation. We also highlight the limitations in evaluating computational argumentation and provide suggestions for future research directions in this field.
JsonTuning: Towards Generalizable, Robust, and Controllable Instruction Tuning
Oct 04, 2023Abstract:Instruction tuning has emerged as a crucial process for harnessing the capabilities of large language models (LLMs) by providing explicit task instructions, leading to improved performance in various tasks. However, prevalent text-to-text instruction tuning (TextTuning) methods suffer from limitations in generalization, robustness, and controllability due to the ambiguity and lack of explicit structure in tasks. In this paper, we propose JsonTuning, a novel structure-to-structure approach for instruction tuning. By leveraging the versatility and structured nature of JSON to represent tasks, JsonTuning enhances generalization by helping the model understand essential task elements and their relations, improves robustness by minimizing ambiguity, and increases controllability by providing explicit control over the output. We conduct a comprehensive comparative study with diverse language models and evaluation benchmarks. Experimental results show that JsonTuning outperforms TextTuning in various applications, showcasing improved performance, adaptability, robustness, and controllability. By overcoming the limitations of TextTuning, JsonTuning demonstrates significant potential for more effective and reliable LLMs capable of handling diverse scenarios.
Zero-Shot Text Classification via Self-Supervised Tuning
May 25, 2023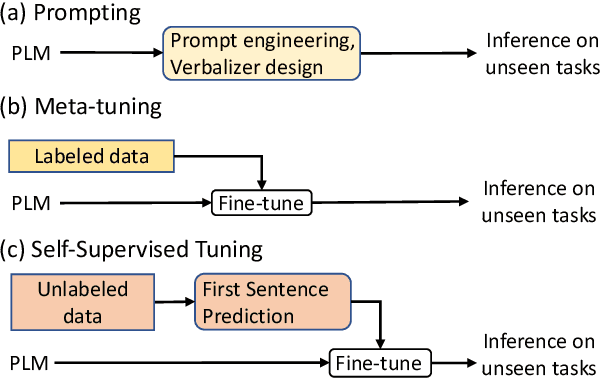



Abstract:Existing solutions to zero-shot text classification either conduct prompting with pre-trained language models, which is sensitive to the choices of templates, or rely on large-scale annotated data of relevant tasks for meta-tuning. In this work, we propose a new paradigm based on self-supervised learning to solve zero-shot text classification tasks by tuning the language models with unlabeled data, called self-supervised tuning. By exploring the inherent structure of free texts, we propose a new learning objective called first sentence prediction to bridge the gap between unlabeled data and text classification tasks. After tuning the model to learn to predict the first sentence in a paragraph based on the rest, the model is able to conduct zero-shot inference on unseen tasks such as topic classification and sentiment analysis. Experimental results show that our model outperforms the state-of-the-art baselines on 7 out of 10 tasks. Moreover, the analysis reveals that our model is less sensitive to the prompt design. Our code and pre-trained models are publicly available at https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/SSTuning .
Domain-Expanded ASTE: Rethinking Generalization in Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction
May 23, 2023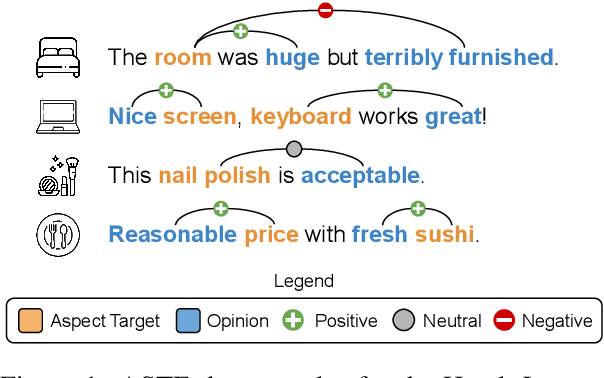
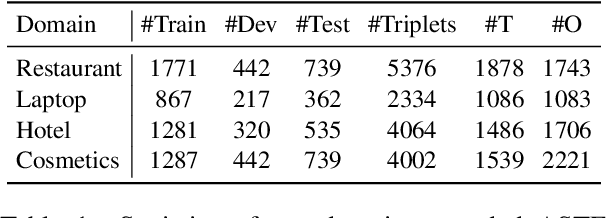
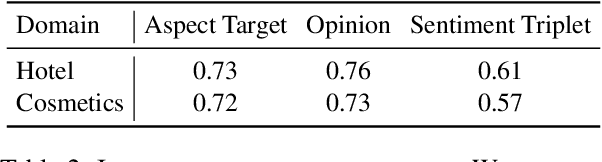
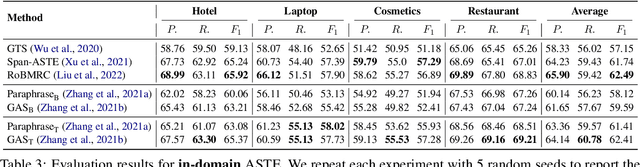
Abstract:Aspect Sentiment Triplet Extraction (ASTE) is a subtask of Aspect-Based Sentiment Analysis (ABSA) that considers each opinion term, their expressed sentiment, and the corresponding aspect targets. However, existing methods are limited to the in-domain setting with two domains. Hence, we propose a domain-expanded benchmark to address the in-domain, out-of-domain and cross-domain settings. We support the new benchmark by annotating more than 4000 data samples for two new domains based on hotel and cosmetics reviews. Our analysis of five existing methods shows that while there is a significant gap between in-domain and out-of-domain performance, generative methods have a strong potential for domain generalization. Our datasets, code implementation and models are available at https://github.com/DAMO-NLP-SG/domain-expanded-aste .
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge