Gianni Fenu
A Comparative Study of Task Adaptation Techniques of Large Language Models for Identifying Sustainable Development Goals
Jun 18, 2025Abstract:In 2012, the United Nations introduced 17 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) aimed at creating a more sustainable and improved future by 2030. However, tracking progress toward these goals is difficult because of the extensive scale and complexity of the data involved. Text classification models have become vital tools in this area, automating the analysis of vast amounts of text from a variety of sources. Additionally, large language models (LLMs) have recently proven indispensable for many natural language processing tasks, including text classification, thanks to their ability to recognize complex linguistic patterns and semantics. This study analyzes various proprietary and open-source LLMs for a single-label, multi-class text classification task focused on the SDGs. Then, it also evaluates the effectiveness of task adaptation techniques (i.e., in-context learning approaches), namely Zero-Shot and Few-Shot Learning, as well as Fine-Tuning within this domain. The results reveal that smaller models, when optimized through prompt engineering, can perform on par with larger models like OpenAI's GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer).
Second FRCSyn-onGoing: Winning Solutions and Post-Challenge Analysis to Improve Face Recognition with Synthetic Data
Dec 02, 2024Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing popularity for face recognition technologies, mainly due to the privacy concerns and challenges associated with obtaining real data, including diverse scenarios, quality, and demographic groups, among others. It also offers some advantages over real data, such as the large amount of data that can be generated or the ability to customize it to adapt to specific problem-solving needs. To effectively use such data, face recognition models should also be specifically designed to exploit synthetic data to its fullest potential. In order to promote the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and investigate the application of synthetic data to better train face recognition systems, we introduce the 2nd FRCSyn-onGoing challenge, based on the 2nd Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn), originally launched at CVPR 2024. This is an ongoing challenge that provides researchers with an accessible platform to benchmark i) the proposal of novel Generative AI methods and synthetic data, and ii) novel face recognition systems that are specifically proposed to take advantage of synthetic data. We focus on exploring the use of synthetic data both individually and in combination with real data to solve current challenges in face recognition such as demographic bias, domain adaptation, and performance constraints in demanding situations, such as age disparities between training and testing, changes in the pose, or occlusions. Very interesting findings are obtained in this second edition, including a direct comparison with the first one, in which synthetic databases were restricted to DCFace and GANDiffFace.
LIMBA: An Open-Source Framework for the Preservation and Valorization of Low-Resource Languages using Generative Models
Nov 20, 2024

Abstract:Minority languages are vital to preserving cultural heritage, yet they face growing risks of extinction due to limited digital resources and the dominance of artificial intelligence models trained on high-resource languages. This white paper proposes a framework to generate linguistic tools for low-resource languages, focusing on data creation to support the development of language models that can aid in preservation efforts. Sardinian, an endangered language, serves as the case study to demonstrate the framework's effectiveness. By addressing the data scarcity that hinders intelligent applications for such languages, we contribute to promoting linguistic diversity and support ongoing efforts in language standardization and revitalization through modern technologies.
The Impact of Balancing Real and Synthetic Data on Accuracy and Fairness in Face Recognition
Sep 04, 2024Abstract:Over the recent years, the advancements in deep face recognition have fueled an increasing demand for large and diverse datasets. Nevertheless, the authentic data acquired to create those datasets is typically sourced from the web, which, in many cases, can lead to significant privacy issues due to the lack of explicit user consent. Furthermore, obtaining a demographically balanced, large dataset is even more difficult because of the natural imbalance in the distribution of images from different demographic groups. In this paper, we investigate the impact of demographically balanced authentic and synthetic data, both individually and in combination, on the accuracy and fairness of face recognition models. Initially, several generative methods were used to balance the demographic representations of the corresponding synthetic datasets. Then a state-of-the-art face encoder was trained and evaluated using (combinations of) synthetic and authentic images. Our findings emphasized two main points: (i) the increased effectiveness of training data generated by diffusion-based models in enhancing accuracy, whether used alone or combined with subsets of authentic data, and (ii) the minimal impact of incorporating balanced data from pre-trained generative methods on fairness (in nearly all tested scenarios using combined datasets, fairness scores remained either unchanged or worsened, even when compared to unbalanced authentic datasets). Source code and data are available at \url{https://cutt.ly/AeQy1K5G} for reproducibility.
Triplètoile: Extraction of Knowledge from Microblogging Text
Aug 27, 2024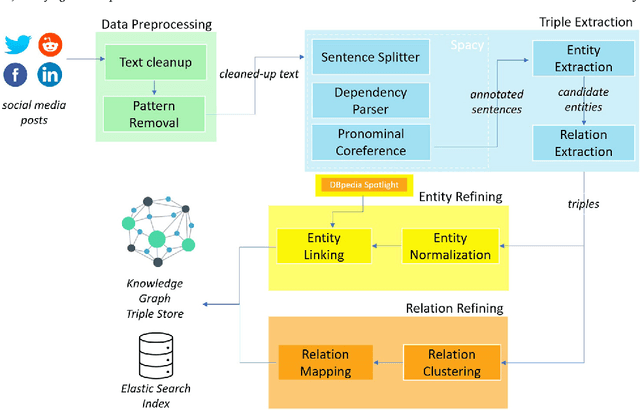



Abstract:Numerous methods and pipelines have recently emerged for the automatic extraction of knowledge graphs from documents such as scientific publications and patents. However, adapting these methods to incorporate alternative text sources like micro-blogging posts and news has proven challenging as they struggle to model open-domain entities and relations, typically found in these sources. In this paper, we propose an enhanced information extraction pipeline tailored to the extraction of a knowledge graph comprising open-domain entities from micro-blogging posts on social media platforms. Our pipeline leverages dependency parsing and classifies entity relations in an unsupervised manner through hierarchical clustering over word embeddings. We provide a use case on extracting semantic triples from a corpus of 100 thousand tweets about digital transformation and publicly release the generated knowledge graph. On the same dataset, we conduct two experimental evaluations, showing that the system produces triples with precision over 95% and outperforms similar pipelines of around 5% in terms of precision, while generating a comparatively higher number of triples.
* 42 pages, 6 figures
Fair Augmentation for Graph Collaborative Filtering
Aug 22, 2024Abstract:Recent developments in recommendation have harnessed the collaborative power of graph neural networks (GNNs) in learning users' preferences from user-item networks. Despite emerging regulations addressing fairness of automated systems, unfairness issues in graph collaborative filtering remain underexplored, especially from the consumer's perspective. Despite numerous contributions on consumer unfairness, only a few of these works have delved into GNNs. A notable gap exists in the formalization of the latest mitigation algorithms, as well as in their effectiveness and reliability on cutting-edge models. This paper serves as a solid response to recent research highlighting unfairness issues in graph collaborative filtering by reproducing one of the latest mitigation methods. The reproduced technique adjusts the system fairness level by learning a fair graph augmentation. Under an experimental setup based on 11 GNNs, 5 non-GNN models, and 5 real-world networks across diverse domains, our investigation reveals that fair graph augmentation is consistently effective on high-utility models and large datasets. Experiments on the transferability of the fair augmented graph open new issues for future recommendation studies. Source code: https://github.com/jackmedda/FA4GCF.
Second Edition FRCSyn Challenge at CVPR 2024: Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data
Apr 16, 2024



Abstract:Synthetic data is gaining increasing relevance for training machine learning models. This is mainly motivated due to several factors such as the lack of real data and intra-class variability, time and errors produced in manual labeling, and in some cases privacy concerns, among others. This paper presents an overview of the 2nd edition of the Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn) organized at CVPR 2024. FRCSyn aims to investigate the use of synthetic data in face recognition to address current technological limitations, including data privacy concerns, demographic biases, generalization to novel scenarios, and performance constraints in challenging situations such as aging, pose variations, and occlusions. Unlike the 1st edition, in which synthetic data from DCFace and GANDiffFace methods was only allowed to train face recognition systems, in this 2nd edition we propose new sub-tasks that allow participants to explore novel face generative methods. The outcomes of the 2nd FRCSyn Challenge, along with the proposed experimental protocol and benchmarking contribute significantly to the application of synthetic data to face recognition.
* arXiv admin note: text overlap with arXiv:2311.10476
If It's Not Enough, Make It So: Reducing Authentic Data Demand in Face Recognition through Synthetic Faces
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Recent advances in deep face recognition have spurred a growing demand for large, diverse, and manually annotated face datasets. Acquiring authentic, high-quality data for face recognition has proven to be a challenge, primarily due to privacy concerns. Large face datasets are primarily sourced from web-based images, lacking explicit user consent. In this paper, we examine whether and how synthetic face data can be used to train effective face recognition models with reduced reliance on authentic images, thereby mitigating data collection concerns. First, we explored the performance gap among recent state-of-the-art face recognition models, trained with synthetic data only and authentic (scarce) data only. Then, we deepened our analysis by training a state-of-the-art backbone with various combinations of synthetic and authentic data, gaining insights into optimizing the limited use of the latter for verification accuracy. Finally, we assessed the effectiveness of data augmentation approaches on synthetic and authentic data, with the same goal in mind. Our results highlighted the effectiveness of FR trained on combined datasets, particularly when combined with appropriate augmentation techniques.
Robustness in Fairness against Edge-level Perturbations in GNN-based Recommendation
Jan 26, 2024Abstract:Efforts in the recommendation community are shifting from the sole emphasis on utility to considering beyond-utility factors, such as fairness and robustness. Robustness of recommendation models is typically linked to their ability to maintain the original utility when subjected to attacks. Limited research has explored the robustness of a recommendation model in terms of fairness, e.g., the parity in performance across groups, under attack scenarios. In this paper, we aim to assess the robustness of graph-based recommender systems concerning fairness, when exposed to attacks based on edge-level perturbations. To this end, we considered four different fairness operationalizations, including both consumer and provider perspectives. Experiments on three datasets shed light on the impact of perturbations on the targeted fairness notion, uncovering key shortcomings in existing evaluation protocols for robustness. As an example, we observed perturbations affect consumer fairness on a higher extent than provider fairness, with alarming unfairness for the former. Source code: https://github.com/jackmedda/CPFairRobust
FRCSyn Challenge at WACV 2024:Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data
Nov 17, 2023



Abstract:Despite the widespread adoption of face recognition technology around the world, and its remarkable performance on current benchmarks, there are still several challenges that must be covered in more detail. This paper offers an overview of the Face Recognition Challenge in the Era of Synthetic Data (FRCSyn) organized at WACV 2024. This is the first international challenge aiming to explore the use of synthetic data in face recognition to address existing limitations in the technology. Specifically, the FRCSyn Challenge targets concerns related to data privacy issues, demographic biases, generalization to unseen scenarios, and performance limitations in challenging scenarios, including significant age disparities between enrollment and testing, pose variations, and occlusions. The results achieved in the FRCSyn Challenge, together with the proposed benchmark, contribute significantly to the application of synthetic data to improve face recognition technology.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge