Vanni Zavarella
Triplètoile: Extraction of Knowledge from Microblogging Text
Aug 27, 2024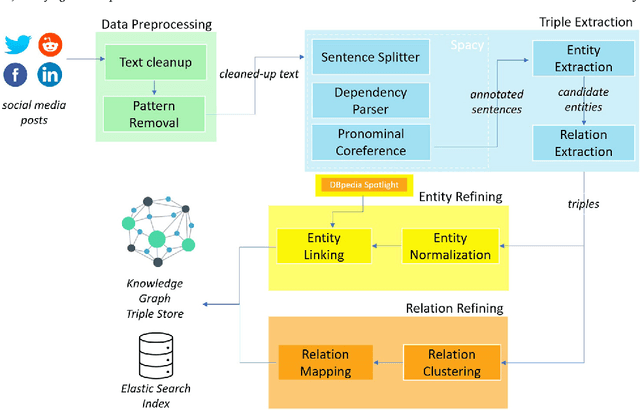



Abstract:Numerous methods and pipelines have recently emerged for the automatic extraction of knowledge graphs from documents such as scientific publications and patents. However, adapting these methods to incorporate alternative text sources like micro-blogging posts and news has proven challenging as they struggle to model open-domain entities and relations, typically found in these sources. In this paper, we propose an enhanced information extraction pipeline tailored to the extraction of a knowledge graph comprising open-domain entities from micro-blogging posts on social media platforms. Our pipeline leverages dependency parsing and classifies entity relations in an unsupervised manner through hierarchical clustering over word embeddings. We provide a use case on extracting semantic triples from a corpus of 100 thousand tweets about digital transformation and publicly release the generated knowledge graph. On the same dataset, we conduct two experimental evaluations, showing that the system produces triples with precision over 95% and outperforms similar pipelines of around 5% in terms of precision, while generating a comparatively higher number of triples.
* 42 pages, 6 figures
A Few-Shot Approach for Relation Extraction Domain Adaptation using Large Language Models
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:Knowledge graphs (KGs) have been successfully applied to the analysis of complex scientific and technological domains, with automatic KG generation methods typically building upon relation extraction models capturing fine-grained relations between domain entities in text. While these relations are fully applicable across scientific areas, existing models are trained on few domain-specific datasets such as SciERC and do not perform well on new target domains. In this paper, we experiment with leveraging in-context learning capabilities of Large Language Models to perform schema-constrained data annotation, collecting in-domain training instances for a Transformer-based relation extraction model deployed on titles and abstracts of research papers in the Architecture, Construction, Engineering and Operations (AECO) domain. By assessing the performance gain with respect to a baseline Deep Learning architecture trained on off-domain data, we show that by using a few-shot learning strategy with structured prompts and only minimal expert annotation the presented approach can potentially support domain adaptation of a science KG generation model.
Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from Text : Workshop and Shared Task Report
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:We provide a summary of the fifth edition of the CASE workshop that is held in the scope of EMNLP 2022. The workshop consists of regular papers, two keynotes, working papers of shared task participants, and task overview papers. This workshop has been bringing together all aspects of event information collection across technical and social science fields. In addition to the progress in depth, the submission and acceptance of multimodal approaches show the widening of this interdisciplinary research topic.
Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from News (AESPEN): Workshop and Shared Task Report
May 12, 2020

Abstract:We describe our effort on automated extraction of socio-political events from news in the scope of a workshop and a shared task we organized at Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC 2020). We believe the event extraction studies in computational linguistics and social and political sciences should further support each other in order to enable large scale socio-political event information collection across sources, countries, and languages. The event consists of regular research papers and a shared task, which is about event sentence coreference identification (ESCI), tracks. All submissions were reviewed by five members of the program committee. The workshop attracted research papers related to evaluation of machine learning methodologies, language resources, material conflict forecasting, and a shared task participation report in the scope of socio-political event information collection. It has shown us the volume and variety of both the data sources and event information collection approaches related to socio-political events and the need to fill the gap between automated text processing techniques and requirements of social and political sciences.
Observing Trends in Automated Multilingual Media Analysis
Mar 08, 2016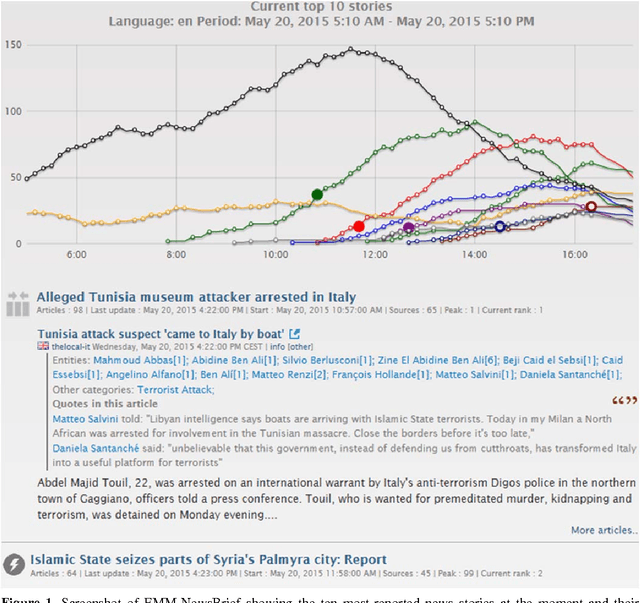
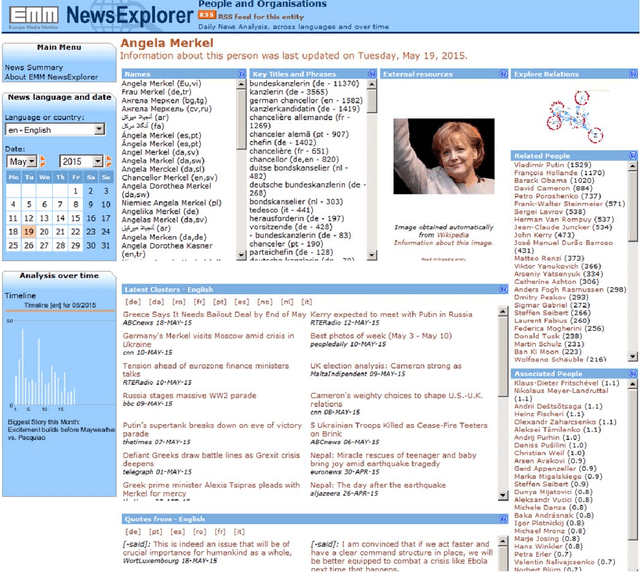
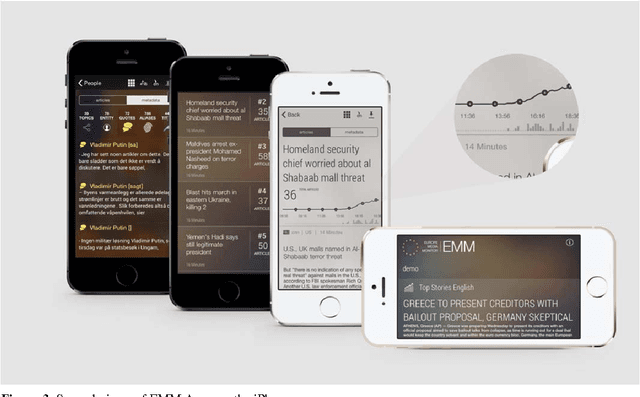
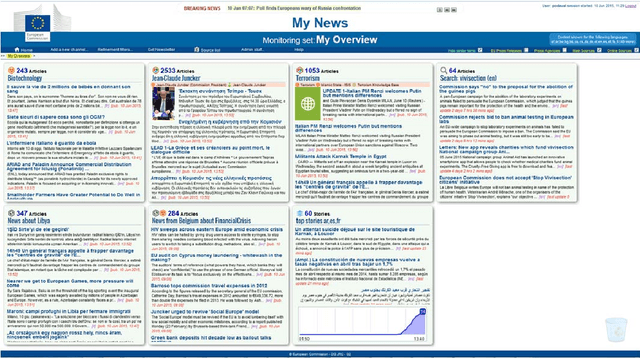
Abstract:Any large organisation, be it public or private, monitors the media for information to keep abreast of developments in their field of interest, and usually also to become aware of positive or negative opinions expressed towards them. At least for the written media, computer programs have become very efficient at helping the human analysts significantly in their monitoring task by gathering media reports, analysing them, detecting trends and - in some cases - even to issue early warnings or to make predictions of likely future developments. We present here trend recognition-related functionality of the Europe Media Monitor (EMM) system, which was developed by the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) for public administrations in the European Union (EU) and beyond. EMM performs large-scale media analysis in up to seventy languages and recognises various types of trends, some of them combining information from news articles written in different languages and from social media posts. EMM also lets users explore the huge amount of multilingual media data through interactive maps and graphs, allowing them to examine the data from various view points and according to multiple criteria. A lot of EMM's functionality is accessibly freely over the internet or via apps for hand-held devices.
Sentiment Analysis in the News
Sep 24, 2013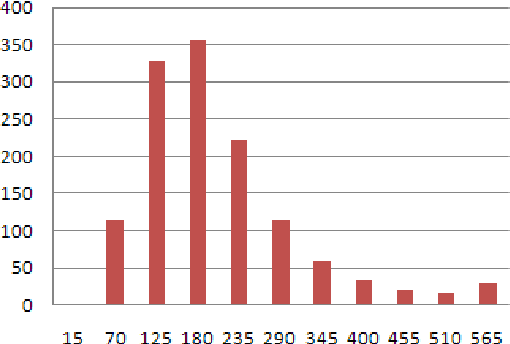
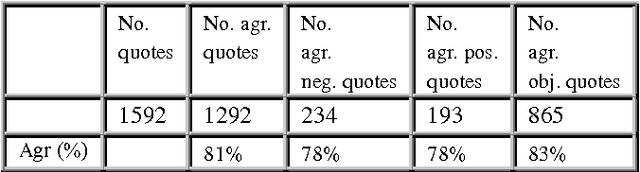
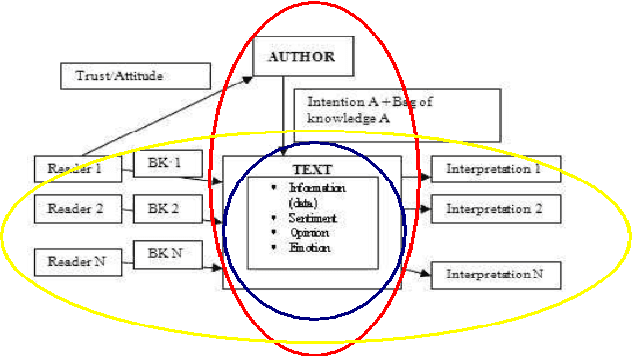
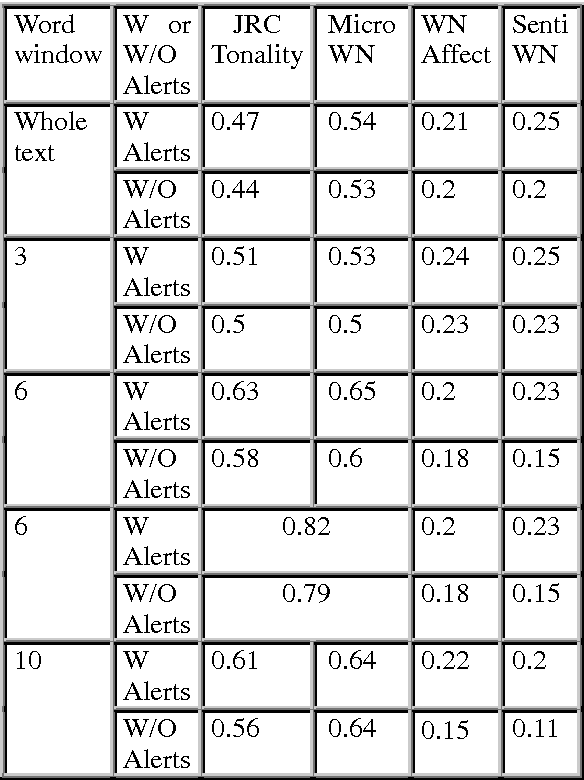
Abstract:Recent years have brought a significant growth in the volume of research in sentiment analysis, mostly on highly subjective text types (movie or product reviews). The main difference these texts have with news articles is that their target is clearly defined and unique across the text. Following different annotation efforts and the analysis of the issues encountered, we realised that news opinion mining is different from that of other text types. We identified three subtasks that need to be addressed: definition of the target; separation of the good and bad news content from the good and bad sentiment expressed on the target; and analysis of clearly marked opinion that is expressed explicitly, not needing interpretation or the use of world knowledge. Furthermore, we distinguish three different possible views on newspaper articles - author, reader and text, which have to be addressed differently at the time of analysing sentiment. Given these definitions, we present work on mining opinions about entities in English language news, in which (a) we test the relative suitability of various sentiment dictionaries and (b) we attempt to separate positive or negative opinion from good or bad news. In the experiments described here, we tested whether or not subject domain-defining vocabulary should be ignored. Results showed that this idea is more appropriate in the context of news opinion mining and that the approaches taking this into consideration produce a better performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge