Ralf Steinberger
European Commission - Joint Research Centre
Observing Trends in Automated Multilingual Media Analysis
Mar 08, 2016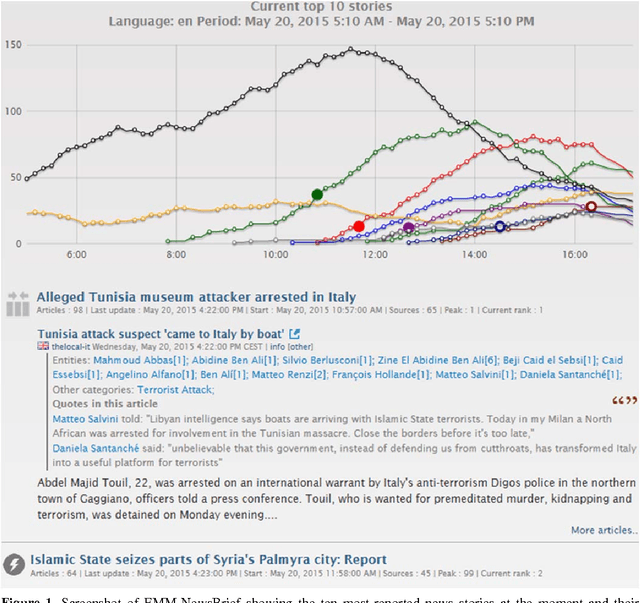
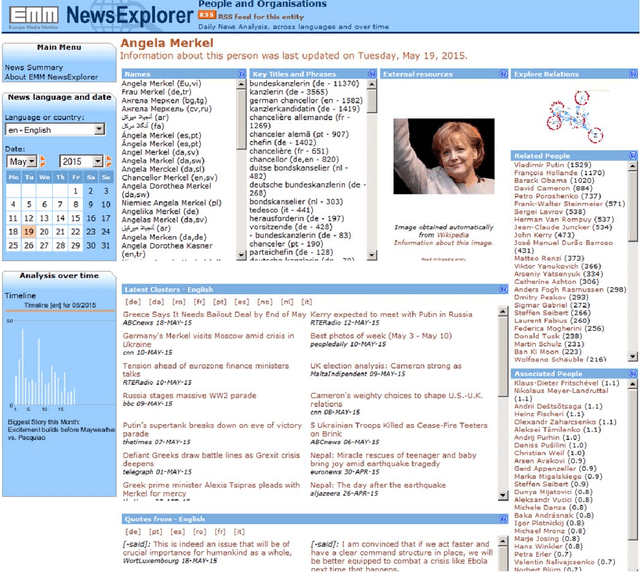
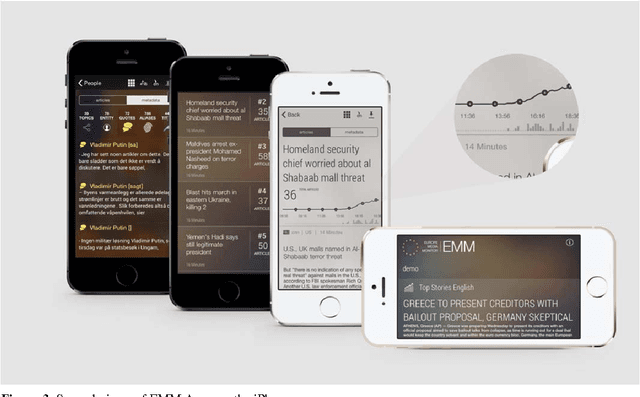
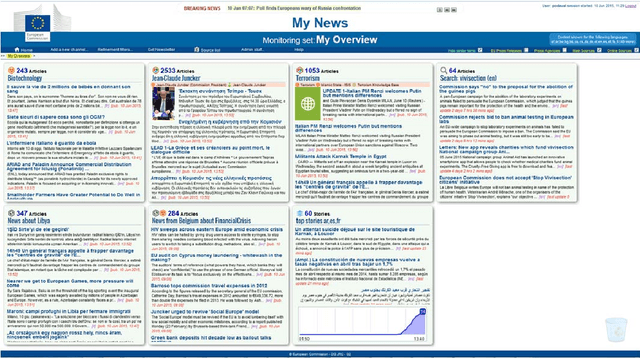
Abstract:Any large organisation, be it public or private, monitors the media for information to keep abreast of developments in their field of interest, and usually also to become aware of positive or negative opinions expressed towards them. At least for the written media, computer programs have become very efficient at helping the human analysts significantly in their monitoring task by gathering media reports, analysing them, detecting trends and - in some cases - even to issue early warnings or to make predictions of likely future developments. We present here trend recognition-related functionality of the Europe Media Monitor (EMM) system, which was developed by the European Commission's Joint Research Centre (JRC) for public administrations in the European Union (EU) and beyond. EMM performs large-scale media analysis in up to seventy languages and recognises various types of trends, some of them combining information from news articles written in different languages and from social media posts. EMM also lets users explore the huge amount of multilingual media data through interactive maps and graphs, allowing them to examine the data from various view points and according to multiple criteria. A lot of EMM's functionality is accessibly freely over the internet or via apps for hand-held devices.
Experiments to Improve Named Entity Recognition on Turkish Tweets
Oct 31, 2014



Abstract:Social media texts are significant information sources for several application areas including trend analysis, event monitoring, and opinion mining. Unfortunately, existing solutions for tasks such as named entity recognition that perform well on formal texts usually perform poorly when applied to social media texts. In this paper, we report on experiments that have the purpose of improving named entity recognition on Turkish tweets, using two different annotated data sets. In these experiments, starting with a baseline named entity recognition system, we adapt its recognition rules and resources to better fit Twitter language by relaxing its capitalization constraint and by diacritics-based expansion of its lexical resources, and we employ a simplistic normalization scheme on tweets to observe the effects of these on the overall named entity recognition performance on Turkish tweets. The evaluation results of the system with these different settings are provided with discussions of these results.
ONTS: "Optima" News Translation System
Jan 13, 2014

Abstract:We propose a real-time machine translation system that allows users to select a news category and to translate the related live news articles from Arabic, Czech, Danish, Farsi, French, German, Italian, Polish, Portuguese, Spanish and Turkish into English. The Moses-based system was optimised for the news domain and differs from other available systems in four ways: (1) News items are automatically categorised on the source side, before translation; (2) Named entity translation is optimised by recognising and extracting them on the source side and by re-inserting their translation in the target language, making use of a separate entity repository; (3) News titles are translated with a separate translation system which is optimised for the specific style of news titles; (4) The system was optimised for speed in order to cope with the large volume of daily news articles.
A survey of methods to ease the development of highly multilingual text mining applications
Jan 13, 2014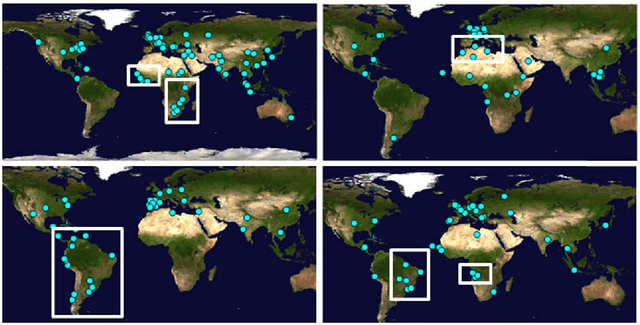

Abstract:Multilingual text processing is useful because the information content found in different languages is complementary, both regarding facts and opinions. While Information Extraction and other text mining software can, in principle, be developed for many languages, most text analysis tools have only been applied to small sets of languages because the development effort per language is large. Self-training tools obviously alleviate the problem, but even the effort of providing training data and of manually tuning the results is usually considerable. In this paper, we gather insights by various multilingual system developers on how to minimise the effort of developing natural language processing applications for many languages. We also explain the main guidelines underlying our own effort to develop complex text mining software for tens of languages. While these guidelines - most of all: extreme simplicity - can be very restrictive and limiting, we believe to have shown the feasibility of the approach through the development of the Europe Media Monitor (EMM) family of applications (http://emm.newsbrief.eu/overview.html). EMM is a set of complex media monitoring tools that process and analyse up to 100,000 online news articles per day in between twenty and fifty languages. We will also touch upon the kind of language resources that would make it easier for all to develop highly multilingual text mining applications. We will argue that - to achieve this - the most needed resources would be freely available, simple, parallel and uniform multilingual dictionaries, corpora and software tools.
* 22 pages. Published online on 12 October 2011
Sentiment Analysis in the News
Sep 24, 2013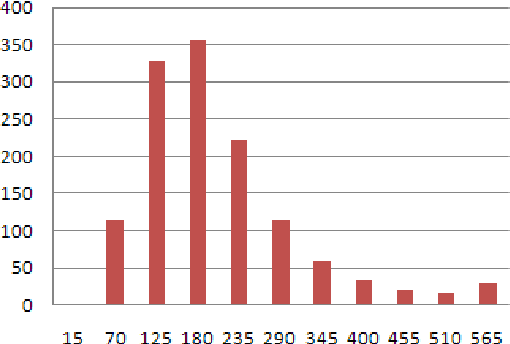
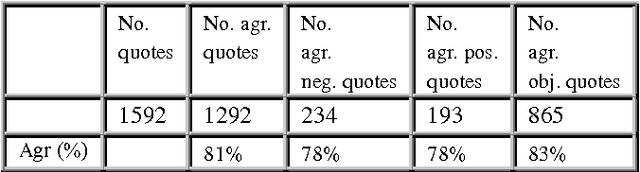
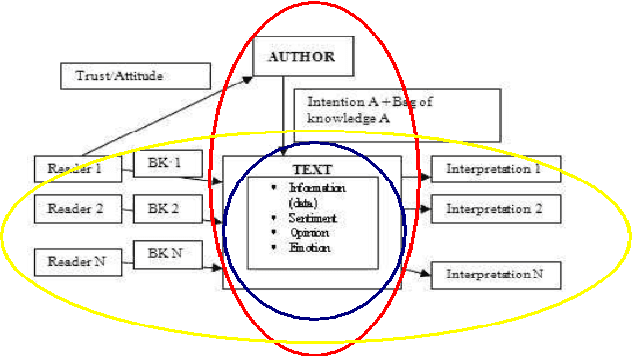
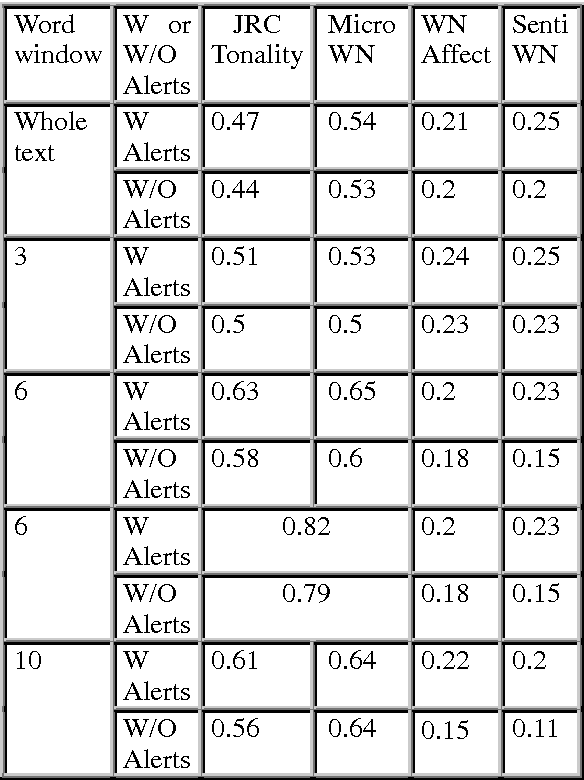
Abstract:Recent years have brought a significant growth in the volume of research in sentiment analysis, mostly on highly subjective text types (movie or product reviews). The main difference these texts have with news articles is that their target is clearly defined and unique across the text. Following different annotation efforts and the analysis of the issues encountered, we realised that news opinion mining is different from that of other text types. We identified three subtasks that need to be addressed: definition of the target; separation of the good and bad news content from the good and bad sentiment expressed on the target; and analysis of clearly marked opinion that is expressed explicitly, not needing interpretation or the use of world knowledge. Furthermore, we distinguish three different possible views on newspaper articles - author, reader and text, which have to be addressed differently at the time of analysing sentiment. Given these definitions, we present work on mining opinions about entities in English language news, in which (a) we test the relative suitability of various sentiment dictionaries and (b) we attempt to separate positive or negative opinion from good or bad news. In the experiments described here, we tested whether or not subject domain-defining vocabulary should be ignored. Results showed that this idea is more appropriate in the context of news opinion mining and that the approaches taking this into consideration produce a better performance.
Acronym recognition and processing in 22 languages
Sep 24, 2013



Abstract:We are presenting work on recognising acronyms of the form Long-Form (Short-Form) such as "International Monetary Fund (IMF)" in millions of news articles in twenty-two languages, as part of our more general effort to recognise entities and their variants in news text and to use them for the automatic analysis of the news, including the linking of related news across languages. We show how the acronym recognition patterns, initially developed for medical terms, needed to be adapted to the more general news domain and we present evaluation results. We describe our effort to automatically merge the numerous long-form variants referring to the same short-form, while keeping non-related long-forms separate. Finally, we provide extensive statistics on the frequency and the distribution of short-form/long-form pairs across languages.
JRC-Names: A freely available, highly multilingual named entity resource
Sep 24, 2013
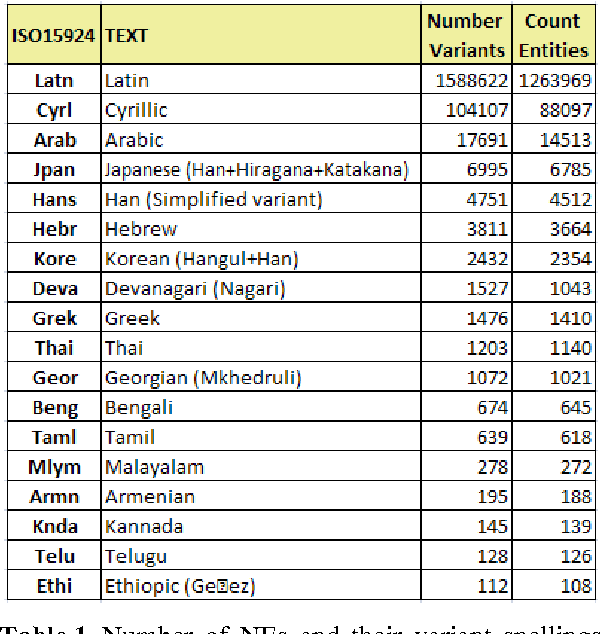
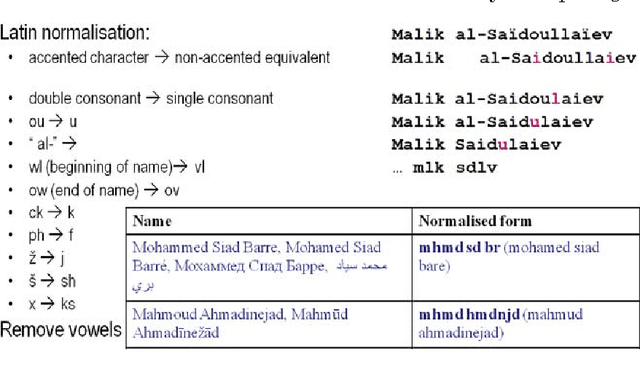
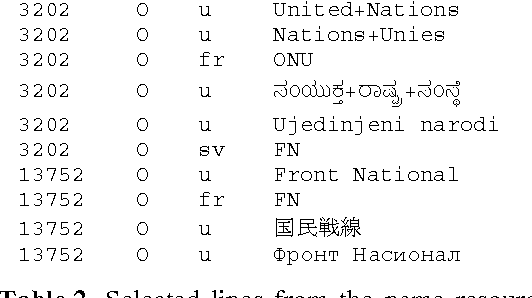
Abstract:This paper describes a new, freely available, highly multilingual named entity resource for person and organisation names that has been compiled over seven years of large-scale multilingual news analysis combined with Wikipedia mining, resulting in 205,000 per-son and organisation names plus about the same number of spelling variants written in over 20 different scripts and in many more languages. This resource, produced as part of the Europe Media Monitor activity (EMM, http://emm.newsbrief.eu/overview.html), can be used for a number of purposes. These include improving name search in databases or on the internet, seeding machine learning systems to learn named entity recognition rules, improve machine translation results, and more. We describe here how this resource was created; we give statistics on its current size; we address the issue of morphological inflection; and we give details regarding its functionality. Updates to this resource will be made available daily.
An introduction to the Europe Media Monitor family of applications
Sep 20, 2013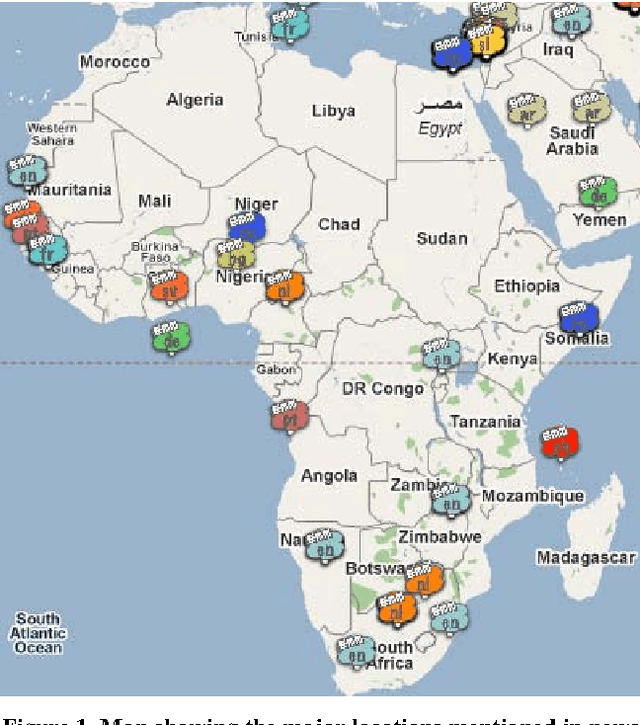
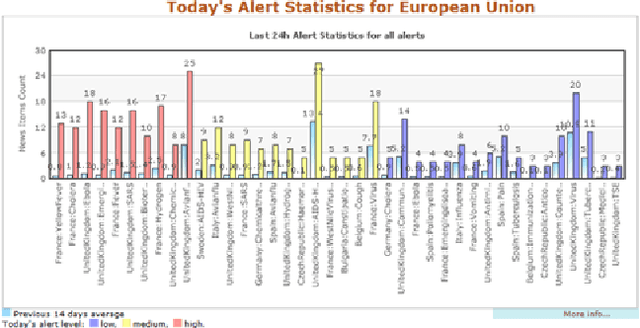
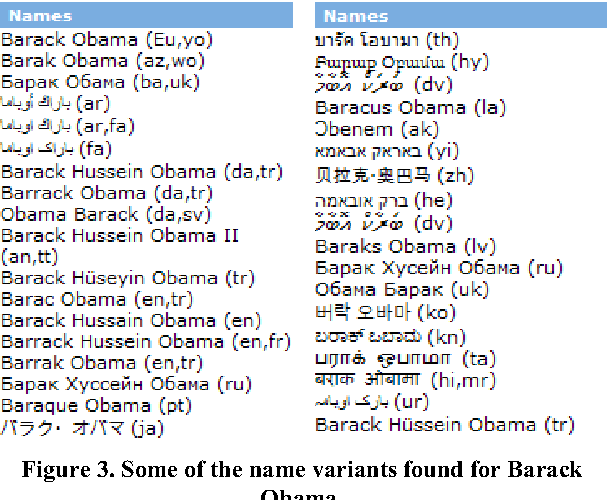
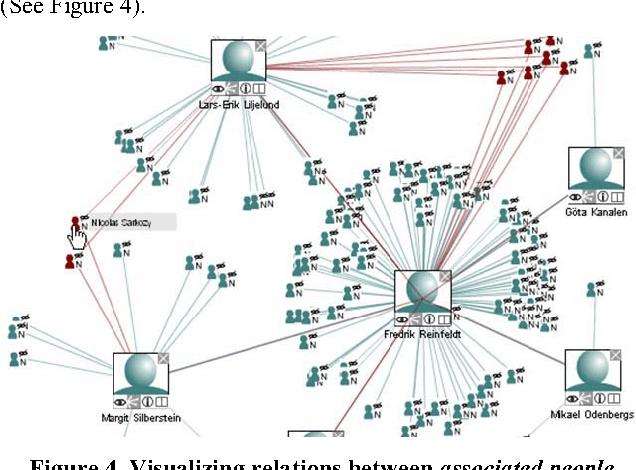
Abstract:Most large organizations have dedicated departments that monitor the media to keep up-to-date with relevant developments and to keep an eye on how they are represented in the news. Part of this media monitoring work can be automated. In the European Union with its 23 official languages, it is particularly important to cover media reports in many languages in order to capture the complementary news content published in the different countries. It is also important to be able to access the news content across languages and to merge the extracted information. We present here the four publicly accessible systems of the Europe Media Monitor (EMM) family of applications, which cover between 19 and 50 languages (see http://press.jrc.it/overview.html). We give an overview of their functionality and discuss some of the implications of the fact that they cover quite so many languages. We discuss design issues necessary to be able to achieve this high multilinguality, as well as the benefits of this multilinguality.
DGT-TM: A freely Available Translation Memory in 22 Languages
Sep 20, 2013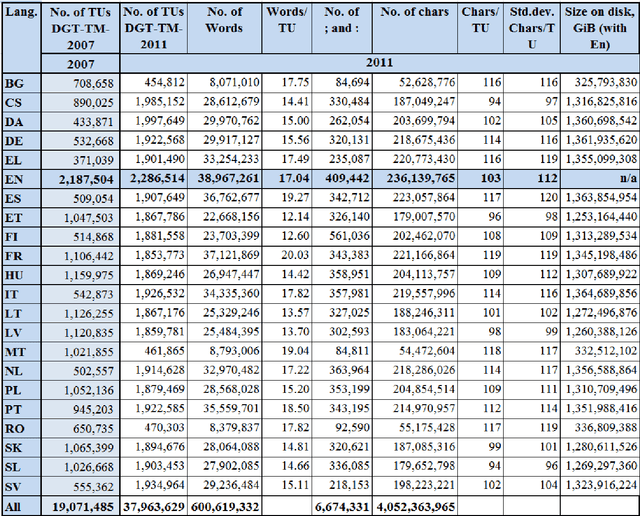
Abstract:The European Commission's (EC) Directorate General for Translation, together with the EC's Joint Research Centre, is making available a large translation memory (TM; i.e. sentences and their professionally produced translations) covering twenty-two official European Union (EU) languages and their 231 language pairs. Such a resource is typically used by translation professionals in combination with TM software to improve speed and consistency of their translations. However, this resource has also many uses for translation studies and for language technology applications, including Statistical Machine Translation (SMT), terminology extraction, Named Entity Recognition (NER), multilingual classification and clustering, and many more. In this reference paper for DGT-TM, we introduce this new resource, provide statistics regarding its size, and explain how it was produced and how to use it.
JRC EuroVoc Indexer JEX - A freely available multi-label categorisation tool
Sep 20, 2013



Abstract:EuroVoc (2012) is a highly multilingual thesaurus consisting of over 6,700 hierarchically organised subject domains used by European Institutions and many authorities in Member States of the European Union (EU) for the classification and retrieval of official documents. JEX is JRC-developed multi-label classification software that learns from manually labelled data to automatically assign EuroVoc descriptors to new documents in a profile-based category-ranking task. The JEX release consists of trained classifiers for 22 official EU languages, of parallel training data in the same languages, of an interface that allows viewing and amending the assignment results, and of a module that allows users to re-train the tool on their own document collections. JEX allows advanced users to change the document representation so as to possibly improve the categorisation result through linguistic pre-processing. JEX can be used as a tool for interactive EuroVoc descriptor assignment to increase speed and consistency of the human categorisation process, or it can be used fully automatically. The output of JEX is a language-independent EuroVoc feature vector lending itself also as input to various other Language Technology tasks, including cross-lingual clustering and classification, cross-lingual plagiarism detection, sentence selection and ranking, and more.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge