Erdem Yörük
GLOCON Database: Design Decisions and User Manual (v1.0)
May 28, 2024
Abstract:GLOCON is a database of contentious events automatically extracted from national news sources from various countries in multiple languages. National news sources are utilized, and complete news archives are processed to create an event list for each source. Automation is achieved using a gold standard corpus sampled randomly from complete news archives (Y\"or\"uk et al. 2022) and all annotated by at least two domain experts based on the event definition provided in Duru\c{s}an et al. (2022).
Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from Text (CASE 2023): Workshop and Shared Task Report
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:We provide a summary of the sixth edition of the CASE workshop that is held in the scope of RANLP 2023. The workshop consists of regular papers, three keynotes, working papers of shared task participants, and shared task overview papers. This workshop series has been bringing together all aspects of event information collection across technical and social science fields. In addition to contributing to the progress in text based event extraction, the workshop provides a space for the organization of a multimodal event information collection task.
Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from Text : Workshop and Shared Task Report
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:We provide a summary of the fifth edition of the CASE workshop that is held in the scope of EMNLP 2022. The workshop consists of regular papers, two keynotes, working papers of shared task participants, and task overview papers. This workshop has been bringing together all aspects of event information collection across technical and social science fields. In addition to the progress in depth, the submission and acceptance of multimodal approaches show the widening of this interdisciplinary research topic.
Extended Multilingual Protest News Detection -- Shared Task 1, CASE 2021 and 2022
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:We report results of the CASE 2022 Shared Task 1 on Multilingual Protest Event Detection. This task is a continuation of CASE 2021 that consists of four subtasks that are i) document classification, ii) sentence classification, iii) event sentence coreference identification, and iv) event extraction. The CASE 2022 extension consists of expanding the test data with more data in previously available languages, namely, English, Hindi, Portuguese, and Spanish, and adding new test data in Mandarin, Turkish, and Urdu for Sub-task 1, document classification. The training data from CASE 2021 in English, Portuguese and Spanish were utilized. Therefore, predicting document labels in Hindi, Mandarin, Turkish, and Urdu occurs in a zero-shot setting. The CASE 2022 workshop accepts reports on systems developed for predicting test data of CASE 2021 as well. We observe that the best systems submitted by CASE 2022 participants achieve between 79.71 and 84.06 F1-macro for new languages in a zero-shot setting. The winning approaches are mainly ensembling models and merging data in multiple languages. The best two submissions on CASE 2021 data outperform submissions from last year for Subtask 1 and Subtask 2 in all languages. Only the following scenarios were not outperformed by new submissions on CASE 2021: Subtask 3 Portuguese \& Subtask 4 English.
Event Coreference Resolution for Contentious Politics Events
Mar 18, 2022



Abstract:We propose a dataset for event coreference resolution, which is based on random samples drawn from multiple sources, languages, and countries. Early scholarship on event information collection has not quantified the contribution of event coreference resolution. We prepared and analyzed a representative multilingual corpus and measured the performance and contribution of the state-of-the-art event coreference resolution approaches. We found that almost half of the event mentions in documents co-occur with other event mentions and this makes it inevitable to obtain erroneous or partial event information. We showed that event coreference resolution could help improving this situation. Our contribution sheds light on a challenge that has been overlooked or hard to study to date. Future event information collection studies can be designed based on the results we present in this report. The repository for this study is on https://github.com/emerging-welfare/ECR4-Contentious-Politics.
COVCOR20 at WNUT-2020 Task 2: An Attempt to Combine Deep Learning and Expert rules
Sep 07, 2020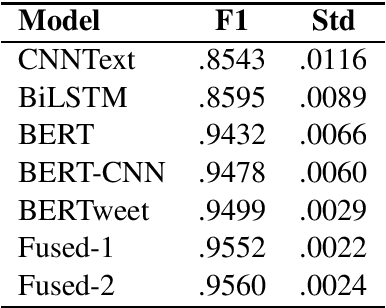
Abstract:In the scope of WNUT-2020 Task 2, we developed various text classification systems, using deep learning models and one using linguistically informed rules. While both of the deep learning systems outperformed the system using the linguistically informed rules, we found that through the integration of (the output of) the three systems a better performance could be achieved than the standalone performance of each approach in a cross-validation setting. However, on the test data the performance of the integration was slightly lower than our best performing deep learning model. These results hardly indicate any progress in line of integrating machine learning and expert rules driven systems. We expect that the release of the annotation manuals and gold labels of the test data after this workshop will shed light on these perplexing results.
Cross-context News Corpus for Protest Events related Knowledge Base Construction
Aug 01, 2020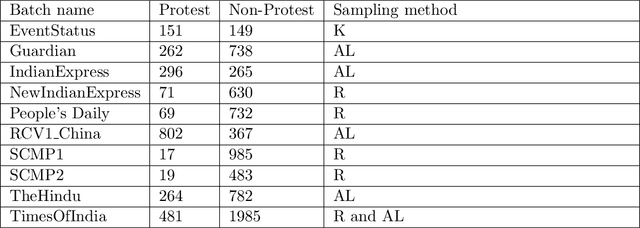
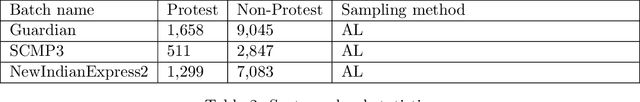
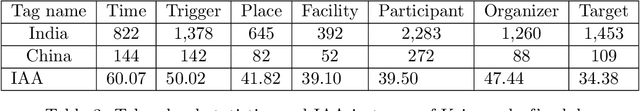
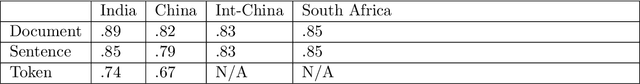
Abstract:We describe a gold standard corpus of protest events that comprise of various local and international sources from various countries in English. The corpus contains document, sentence, and token level annotations. This corpus facilitates creating machine learning models that automatically classify news articles and extract protest event-related information, constructing knowledge bases which enable comparative social and political science studies. For each news source, the annotation starts on random samples of news articles and continues with samples that are drawn using active learning. Each batch of samples was annotated by two social and political scientists, adjudicated by an annotation supervisor, and was improved by identifying annotation errors semi-automatically. We found that the corpus has the variety and quality to develop and benchmark text classification and event extraction systems in a cross-context setting, which contributes to the generalizability and robustness of automated text processing systems. This corpus and the reported results will set the currently lacking common ground in automated protest event collection studies.
Overview of CLEF 2019 Lab ProtestNews: Extracting Protests from News in a Cross-context Setting
Aug 01, 2020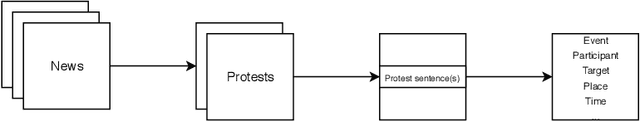
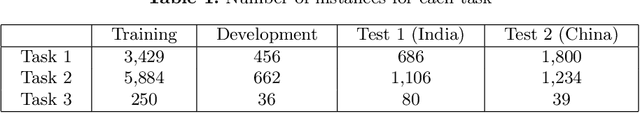

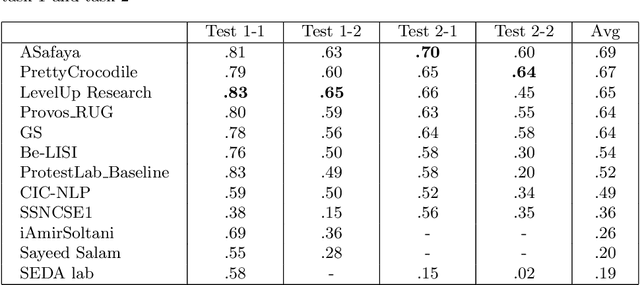
Abstract:We present an overview of the CLEF-2019 Lab ProtestNews on Extracting Protests from News in the context of generalizable natural language processing. The lab consists of document, sentence, and token level information classification and extraction tasks that were referred as task 1, task 2, and task 3 respectively in the scope of this lab. The tasks required the participants to identify protest relevant information from English local news at one or more aforementioned levels in a cross-context setting, which is cross-country in the scope of this lab. The training and development data were collected from India and test data was collected from India and China. The lab attracted 58 teams to participate in the lab. 12 and 9 of these teams submitted results and working notes respectively. We have observed neural networks yield the best results and the performance drops significantly for majority of the submissions in the cross-country setting, which is China.
Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from News (AESPEN): Workshop and Shared Task Report
May 12, 2020

Abstract:We describe our effort on automated extraction of socio-political events from news in the scope of a workshop and a shared task we organized at Language Resources and Evaluation Conference (LREC 2020). We believe the event extraction studies in computational linguistics and social and political sciences should further support each other in order to enable large scale socio-political event information collection across sources, countries, and languages. The event consists of regular research papers and a shared task, which is about event sentence coreference identification (ESCI), tracks. All submissions were reviewed by five members of the program committee. The workshop attracted research papers related to evaluation of machine learning methodologies, language resources, material conflict forecasting, and a shared task participation report in the scope of socio-political event information collection. It has shown us the volume and variety of both the data sources and event information collection approaches related to socio-political events and the need to fill the gap between automated text processing techniques and requirements of social and political sciences.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge