Ali Hürriyetoğlu
BrightCookies at SemEval-2025 Task 9: Exploring Data Augmentation for Food Hazard Classification
Apr 29, 2025Abstract:This paper presents our system developed for the SemEval-2025 Task 9: The Food Hazard Detection Challenge. The shared task's objective is to evaluate explainable classification systems for classifying hazards and products in two levels of granularity from food recall incident reports. In this work, we propose text augmentation techniques as a way to improve poor performance on minority classes and compare their effect for each category on various transformer and machine learning models. We explore three word-level data augmentation techniques, namely synonym replacement, random word swapping, and contextual word insertion. The results show that transformer models tend to have a better overall performance. None of the three augmentation techniques consistently improved overall performance for classifying hazards and products. We observed a statistically significant improvement (P < 0.05) in the fine-grained categories when using the BERT model to compare the baseline with each augmented model. Compared to the baseline, the contextual words insertion augmentation improved the accuracy of predictions for the minority hazard classes by 6%. This suggests that targeted augmentation of minority classes can improve the performance of transformer models.
A Cross-Validation Study of Turkish Sentiment Analysis Datasets and Tools
Dec 08, 2024Abstract:In recent years, sentiment analysis has gained increasing significance, prompting researchers to explore datasets in various languages, including Turkish. However, the limited availability of Turkish datasets has led to their multifaceted usage in different studies, yielding diverse outcomes. To overcome this challenge, a rigorous review was conducted of research articles published between 2012 and 2022. 31 studies were listed, and 23 Turkish datasets obtained from publicly available sources and email requests used in these studies were collected. We labeled these 31 studies using a taxonomy. We provide a map of sentiment analysis datasets according to this taxonomy in Turkish over 10 years. Moreover, we run state-of-the-art sentiment analysis tools on these datasets and analyzed performance across popular Turkish sentiment datasets. We observed that the performance of the sentiment analysis tools significantly depends on the characteristics of the target text. Our study fosters a more nuanced understanding of sentiment analysis in the Turkish language.
Federated learning in food research
Jun 10, 2024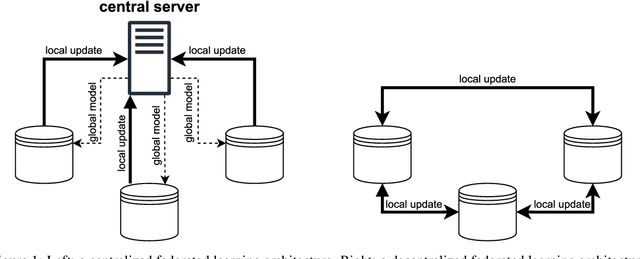
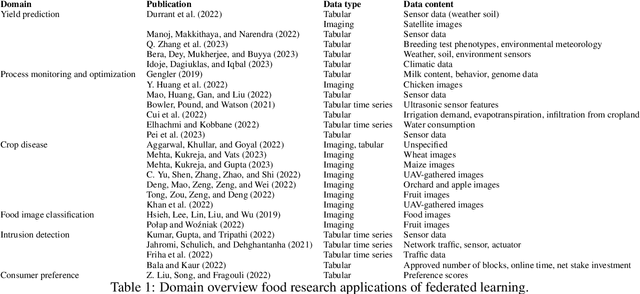
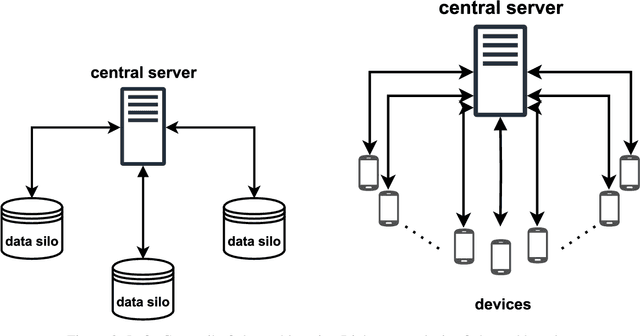
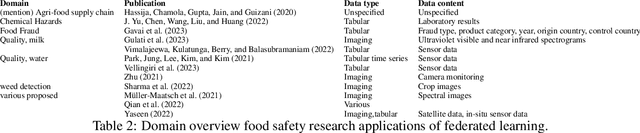
Abstract:Research in the food domain is at times limited due to data sharing obstacles, such as data ownership, privacy requirements, and regulations. While important, these obstacles can restrict data-driven methods such as machine learning. Federated learning, the approach of training models on locally kept data and only sharing the learned parameters, is a potential technique to alleviate data sharing obstacles. This systematic review investigates the use of federated learning within the food domain, structures included papers in a federated learning framework, highlights knowledge gaps, and discusses potential applications. A total of 41 papers were included in the review. The current applications include solutions to water and milk quality assessment, cybersecurity of water processing, pesticide residue risk analysis, weed detection, and fraud detection, focusing on centralized horizontal federated learning. One of the gaps found was the lack of vertical or transfer federated learning and decentralized architectures.
GLOCON Database: Design Decisions and User Manual (v1.0)
May 28, 2024
Abstract:GLOCON is a database of contentious events automatically extracted from national news sources from various countries in multiple languages. National news sources are utilized, and complete news archives are processed to create an event list for each source. Automation is achieved using a gold standard corpus sampled randomly from complete news archives (Y\"or\"uk et al. 2022) and all annotated by at least two domain experts based on the event definition provided in Duru\c{s}an et al. (2022).
Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from Text (CASE 2023): Workshop and Shared Task Report
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:We provide a summary of the sixth edition of the CASE workshop that is held in the scope of RANLP 2023. The workshop consists of regular papers, three keynotes, working papers of shared task participants, and shared task overview papers. This workshop series has been bringing together all aspects of event information collection across technical and social science fields. In addition to contributing to the progress in text based event extraction, the workshop provides a space for the organization of a multimodal event information collection task.
Event Causality Identification with Causal News Corpus -- Shared Task 3, CASE 2022
Nov 22, 2022



Abstract:The Event Causality Identification Shared Task of CASE 2022 involved two subtasks working on the Causal News Corpus. Subtask 1 required participants to predict if a sentence contains a causal relation or not. This is a supervised binary classification task. Subtask 2 required participants to identify the Cause, Effect and Signal spans per causal sentence. This could be seen as a supervised sequence labeling task. For both subtasks, participants uploaded their predictions for a held-out test set, and ranking was done based on binary F1 and macro F1 scores for Subtask 1 and 2, respectively. This paper summarizes the work of the 17 teams that submitted their results to our competition and 12 system description papers that were received. The best F1 scores achieved for Subtask 1 and 2 were 86.19% and 54.15%, respectively. All the top-performing approaches involved pre-trained language models fine-tuned to the targeted task. We further discuss these approaches and analyze errors across participants' systems in this paper.
Challenges and Applications of Automated Extraction of Socio-political Events from Text : Workshop and Shared Task Report
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:We provide a summary of the fifth edition of the CASE workshop that is held in the scope of EMNLP 2022. The workshop consists of regular papers, two keynotes, working papers of shared task participants, and task overview papers. This workshop has been bringing together all aspects of event information collection across technical and social science fields. In addition to the progress in depth, the submission and acceptance of multimodal approaches show the widening of this interdisciplinary research topic.
Extended Multilingual Protest News Detection -- Shared Task 1, CASE 2021 and 2022
Nov 21, 2022



Abstract:We report results of the CASE 2022 Shared Task 1 on Multilingual Protest Event Detection. This task is a continuation of CASE 2021 that consists of four subtasks that are i) document classification, ii) sentence classification, iii) event sentence coreference identification, and iv) event extraction. The CASE 2022 extension consists of expanding the test data with more data in previously available languages, namely, English, Hindi, Portuguese, and Spanish, and adding new test data in Mandarin, Turkish, and Urdu for Sub-task 1, document classification. The training data from CASE 2021 in English, Portuguese and Spanish were utilized. Therefore, predicting document labels in Hindi, Mandarin, Turkish, and Urdu occurs in a zero-shot setting. The CASE 2022 workshop accepts reports on systems developed for predicting test data of CASE 2021 as well. We observe that the best systems submitted by CASE 2022 participants achieve between 79.71 and 84.06 F1-macro for new languages in a zero-shot setting. The winning approaches are mainly ensembling models and merging data in multiple languages. The best two submissions on CASE 2021 data outperform submissions from last year for Subtask 1 and Subtask 2 in all languages. Only the following scenarios were not outperformed by new submissions on CASE 2021: Subtask 3 Portuguese \& Subtask 4 English.
Zero-Shot Ranking Socio-Political Texts with Transformer Language Models to Reduce Close Reading Time
Oct 17, 2022


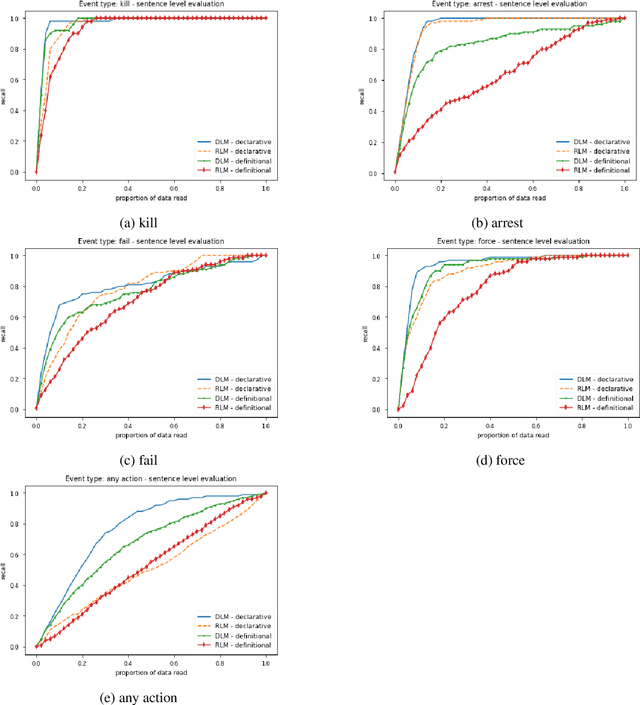
Abstract:We approach the classification problem as an entailment problem and apply zero-shot ranking to socio-political texts. Documents that are ranked at the top can be considered positively classified documents and this reduces the close reading time for the information extraction process. We use Transformer Language Models to get the entailment probabilities and investigate different types of queries. We find that DeBERTa achieves higher mean average precision scores than RoBERTa and when declarative form of the class label is used as a query, it outperforms dictionary definition of the class label. We show that one can reduce the close reading time by taking some percentage of the ranked documents that the percentage depends on how much recall they want to achieve. However, our findings also show that percentage of the documents that should be read increases as the topic gets broader.
The Causal News Corpus: Annotating Causal Relations in Event Sentences from News
Apr 25, 2022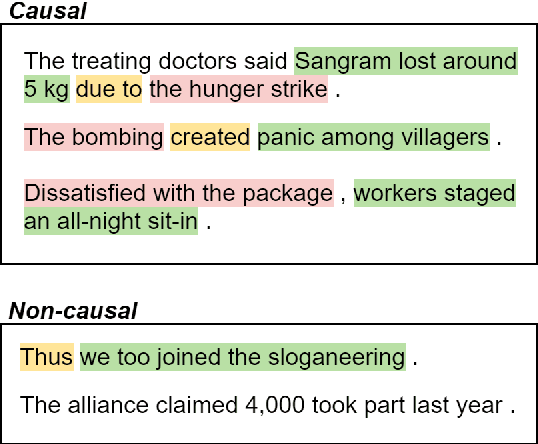
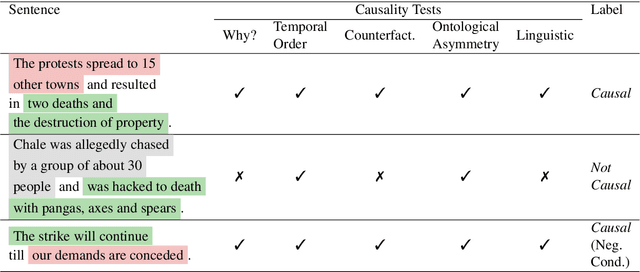
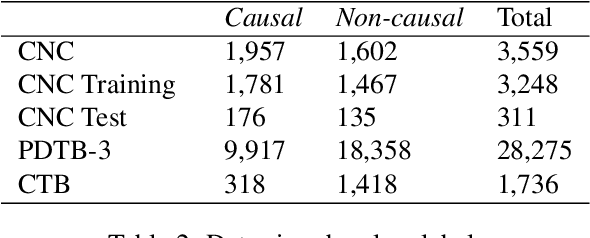
Abstract:Despite the importance of understanding causality, corpora addressing causal relations are limited. There is a discrepancy between existing annotation guidelines of event causality and conventional causality corpora that focus more on linguistics. Many guidelines restrict themselves to include only explicit relations or clause-based arguments. Therefore, we propose an annotation schema for event causality that addresses these concerns. We annotated 3,559 event sentences from protest event news with labels on whether it contains causal relations or not. Our corpus is known as the Causal News Corpus (CNC). A neural network built upon a state-of-the-art pre-trained language model performed well with 81.20% F1 score on test set, and 83.46% in 5-folds cross-validation. CNC is transferable across two external corpora: CausalTimeBank (CTB) and Penn Discourse Treebank (PDTB). Leveraging each of these external datasets for training, we achieved up to approximately 64% F1 on the CNC test set without additional fine-tuning. CNC also served as an effective training and pre-training dataset for the two external corpora. Lastly, we demonstrate the difficulty of our task to the layman in a crowd-sourced annotation exercise. Our annotated corpus is publicly available, providing a valuable resource for causal text mining researchers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge