Christian Cancedda
Faithful Path Language Modelling for Explainable Recommendation over Knowledge Graph
Oct 25, 2023


Abstract:Path reasoning methods over knowledge graphs have gained popularity for their potential to improve transparency in recommender systems. However, the resulting models still rely on pre-trained knowledge graph embeddings, fail to fully exploit the interdependence between entities and relations in the KG for recommendation, and may generate inaccurate explanations. In this paper, we introduce PEARLM, a novel approach that efficiently captures user behaviour and product-side knowledge through language modelling. With our approach, knowledge graph embeddings are directly learned from paths over the KG by the language model, which also unifies entities and relations in the same optimisation space. Constraints on the sequence decoding additionally guarantee path faithfulness with respect to the KG. Experiments on two datasets show the effectiveness of our approach compared to state-of-the-art baselines. Source code and datasets: AVAILABLE AFTER GETTING ACCEPTED.
Knowledge is Power, Understanding is Impact: Utility and Beyond Goals, Explanation Quality, and Fairness in Path Reasoning Recommendation
Jan 14, 2023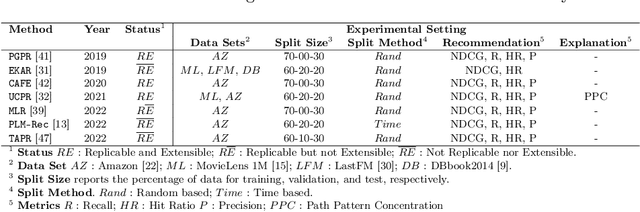



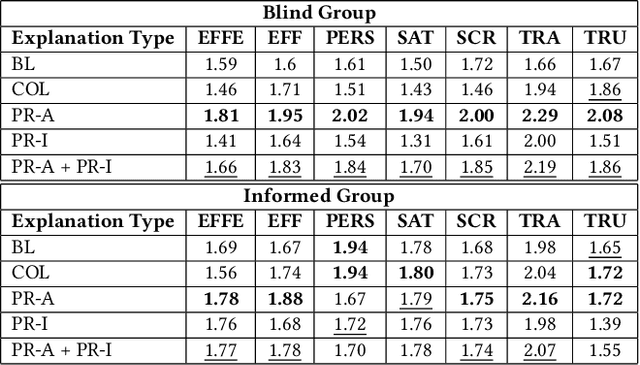
Abstract:Path reasoning is a notable recommendation approach that models high-order user-product relations, based on a Knowledge Graph (KG). This approach can extract reasoning paths between recommended products and already experienced products and, then, turn such paths into textual explanations for the user. Unfortunately, evaluation protocols in this field appear heterogeneous and limited, making it hard to contextualize the impact of the existing methods. In this paper, we replicated three state-of-the-art relevant path reasoning recommendation methods proposed in top-tier conferences. Under a common evaluation protocol, based on two public data sets and in comparison with other knowledge-aware methods, we then studied the extent to which they meet recommendation utility and beyond objectives, explanation quality, and consumer and provider fairness. Our study provides a picture of the progress in this field, highlighting open issues and future directions. Source code: \url{https://github.com/giacoballoccu/rep-path-reasoning-recsys}.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge