Diego Garcia-Olano
Jack
Memorization Dynamics in Knowledge Distillation for Language Models
Jan 21, 2026Abstract:Knowledge Distillation (KD) is increasingly adopted to transfer capabilities from large language models to smaller ones, offering significant improvements in efficiency and utility while often surpassing standard fine-tuning. Beyond performance, KD is also explored as a privacy-preserving mechanism to mitigate the risk of training data leakage. While training data memorization has been extensively studied in standard pre-training and fine-tuning settings, its dynamics in a knowledge distillation setup remain poorly understood. In this work, we study memorization across the KD pipeline using three large language model (LLM) families (Pythia, OLMo-2, Qwen-3) and three datasets (FineWeb, Wikitext, Nemotron-CC-v2). We find: (1) distilled models memorize significantly less training data than standard fine-tuning (reducing memorization by more than 50%); (2) some examples are inherently easier to memorize and account for a large fraction of memorization during distillation (over ~95%); (3) student memorization is predictable prior to distillation using features based on zlib entropy, KL divergence, and perplexity; and (4) while soft and hard distillation have similar overall memorization rates, hard distillation poses a greater risk: it inherits $2.7\times$ more teacher-specific examples than soft distillation. Overall, we demonstrate that distillation can provide both improved generalization and reduced memorization risks compared to standard fine-tuning.
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Improving LLM First-Token Predictions in Multiple-Choice Question Answering via Prefilling Attack
May 21, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) are increasingly evaluated on multiple-choice question answering (MCQA) tasks using *first-token probability* (FTP), which selects the answer option whose initial token has the highest likelihood. While efficient, FTP can be fragile: models may assign high probability to unrelated tokens (*misalignment*) or use a valid token merely as part of a generic preamble rather than as a clear answer choice (*misinterpretation*), undermining the reliability of symbolic evaluation. We propose a simple solution: the *prefilling attack*, a structured natural-language prefix (e.g., "*The correct option is:*") prepended to the model output. Originally explored in AI safety, we repurpose prefilling to steer the model to respond with a clean, valid option, without modifying its parameters. Empirically, the FTP with prefilling strategy substantially improves accuracy, calibration, and output consistency across a broad set of LLMs and MCQA benchmarks. It outperforms standard FTP and often matches the performance of open-ended generation approaches that require full decoding and external classifiers, while being significantly more efficient. Our findings suggest that prefilling is a simple, robust, and low-cost method to enhance the reliability of FTP-based evaluation in multiple-choice settings.
The Llama 3 Herd of Models
Jul 31, 2024Abstract:Modern artificial intelligence (AI) systems are powered by foundation models. This paper presents a new set of foundation models, called Llama 3. It is a herd of language models that natively support multilinguality, coding, reasoning, and tool usage. Our largest model is a dense Transformer with 405B parameters and a context window of up to 128K tokens. This paper presents an extensive empirical evaluation of Llama 3. We find that Llama 3 delivers comparable quality to leading language models such as GPT-4 on a plethora of tasks. We publicly release Llama 3, including pre-trained and post-trained versions of the 405B parameter language model and our Llama Guard 3 model for input and output safety. The paper also presents the results of experiments in which we integrate image, video, and speech capabilities into Llama 3 via a compositional approach. We observe this approach performs competitively with the state-of-the-art on image, video, and speech recognition tasks. The resulting models are not yet being broadly released as they are still under development.
Using Captum to Explain Generative Language Models
Dec 09, 2023Abstract:Captum is a comprehensive library for model explainability in PyTorch, offering a range of methods from the interpretability literature to enhance users' understanding of PyTorch models. In this paper, we introduce new features in Captum that are specifically designed to analyze the behavior of generative language models. We provide an overview of the available functionalities and example applications of their potential for understanding learned associations within generative language models.
Error Discovery by Clustering Influence Embeddings
Dec 07, 2023



Abstract:We present a method for identifying groups of test examples -- slices -- on which a model under-performs, a task now known as slice discovery. We formalize coherence -- a requirement that erroneous predictions, within a slice, should be wrong for the same reason -- as a key property that any slice discovery method should satisfy. We then use influence functions to derive a new slice discovery method, InfEmbed, which satisfies coherence by returning slices whose examples are influenced similarly by the training data. InfEmbed is simple, and consists of applying K-Means clustering to a novel representation we deem influence embeddings. We show InfEmbed outperforms current state-of-the-art methods on 2 benchmarks, and is effective for model debugging across several case studies.
Intermediate Entity-based Sparse Interpretable Representation Learning
Dec 03, 2022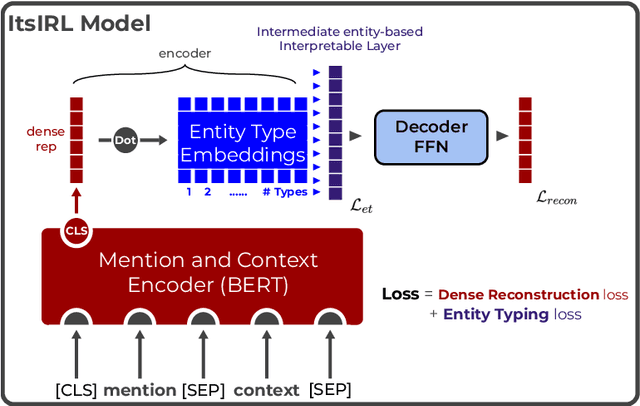
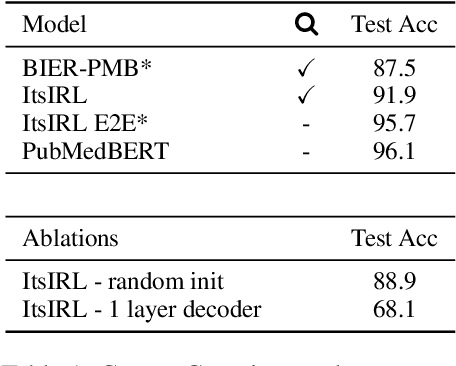
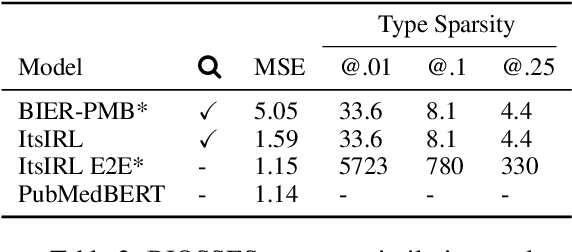
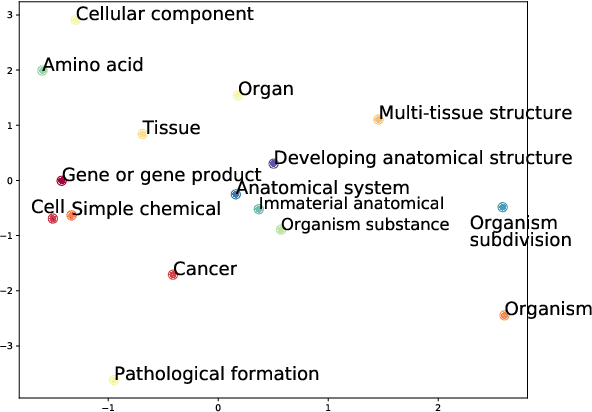
Abstract:Interpretable entity representations (IERs) are sparse embeddings that are "human-readable" in that dimensions correspond to fine-grained entity types and values are predicted probabilities that a given entity is of the corresponding type. These methods perform well in zero-shot and low supervision settings. Compared to standard dense neural embeddings, such interpretable representations may permit analysis and debugging. However, while fine-tuning sparse, interpretable representations improves accuracy on downstream tasks, it destroys the semantics of the dimensions which were enforced in pre-training. Can we maintain the interpretable semantics afforded by IERs while improving predictive performance on downstream tasks? Toward this end, we propose Intermediate enTity-based Sparse Interpretable Representation Learning (ItsIRL). ItsIRL realizes improved performance over prior IERs on biomedical tasks, while maintaining "interpretability" generally and their ability to support model debugging specifically. The latter is enabled in part by the ability to perform "counterfactual" fine-grained entity type manipulation, which we explore in this work. Finally, we propose a method to construct entity type based class prototypes for revealing global semantic properties of classes learned by our model.
Improving and Diagnosing Knowledge-Based Visual Question Answering via Entity Enhanced Knowledge Injection
Dec 13, 2021


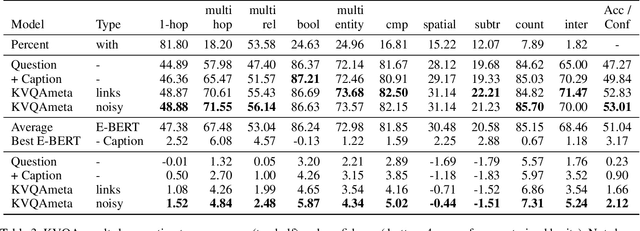
Abstract:Knowledge-Based Visual Question Answering (KBVQA) is a bi-modal task requiring external world knowledge in order to correctly answer a text question and associated image. Recent single modality text work has shown knowledge injection into pre-trained language models, specifically entity enhanced knowledge graph embeddings, can improve performance on downstream entity-centric tasks. In this work, we empirically study how and whether such methods, applied in a bi-modal setting, can improve an existing VQA system's performance on the KBVQA task. We experiment with two large publicly available VQA datasets, (1) KVQA which contains mostly rare Wikipedia entities and (2) OKVQA which is less entity-centric and more aligned with common sense reasoning. Both lack explicit entity spans and we study the effect of different weakly supervised and manual methods for obtaining them. Additionally we analyze how recently proposed bi-modal and single modal attention explanations are affected by the incorporation of such entity enhanced representations. Our results show substantial improved performance on the KBVQA task without the need for additional costly pre-training and we provide insights for when entity knowledge injection helps improve a model's understanding. We provide code and enhanced datasets for reproducibility.
Biomedical Interpretable Entity Representations
Jun 17, 2021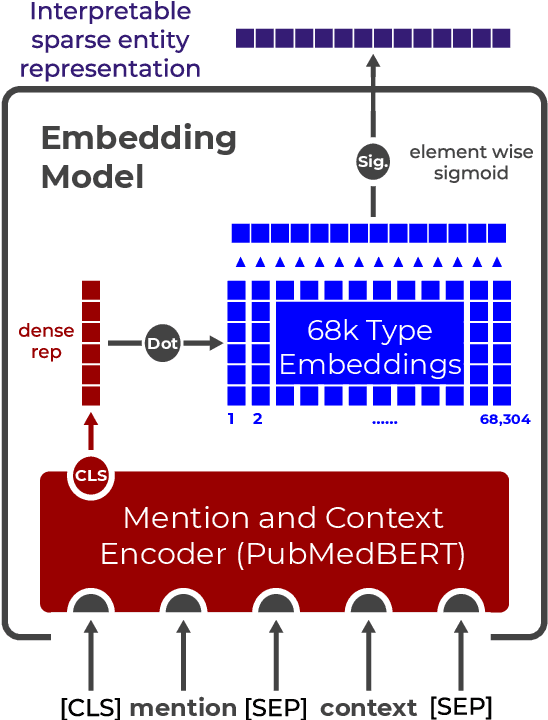
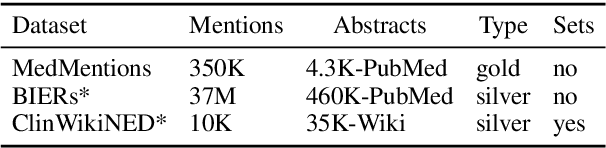
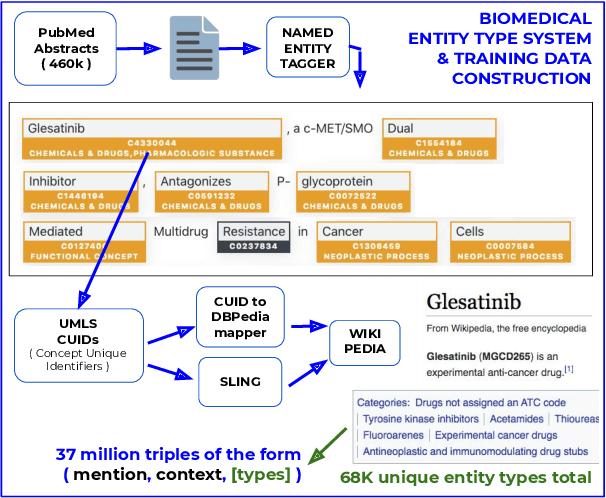
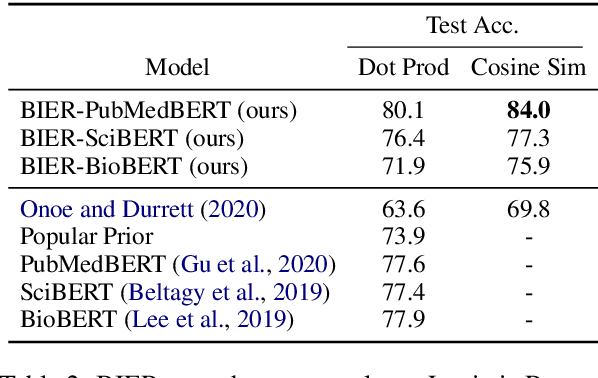
Abstract:Pre-trained language models induce dense entity representations that offer strong performance on entity-centric NLP tasks, but such representations are not immediately interpretable. This can be a barrier to model uptake in important domains such as biomedicine. There has been recent work on general interpretable representation learning (Onoe and Durrett, 2020), but these domain-agnostic representations do not readily transfer to the important domain of biomedicine. In this paper, we create a new entity type system and training set from a large corpus of biomedical texts by mapping entities to concepts in a medical ontology, and from these to Wikipedia pages whose categories are our types. From this mapping we derive Biomedical Interpretable Entity Representations(BIERs), in which dimensions correspond to fine-grained entity types, and values are predicted probabilities that a given entity is of the corresponding type. We propose a novel method that exploits BIER's final sparse and intermediate dense representations to facilitate model and entity type debugging. We show that BIERs achieve strong performance in biomedical tasks including named entity disambiguation and entity label classification, and we provide error analysis to highlight the utility of their interpretability, particularly in low-supervision settings. Finally, we provide our induced 68K biomedical type system, the corresponding 37 million triples of derived data used to train BIER models and our best performing model.
Learning Dense Representations for Entity Retrieval
Sep 23, 2019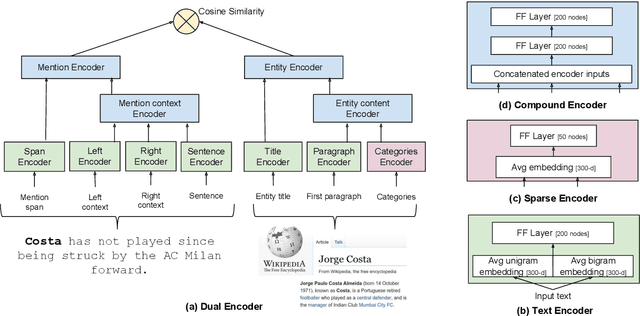
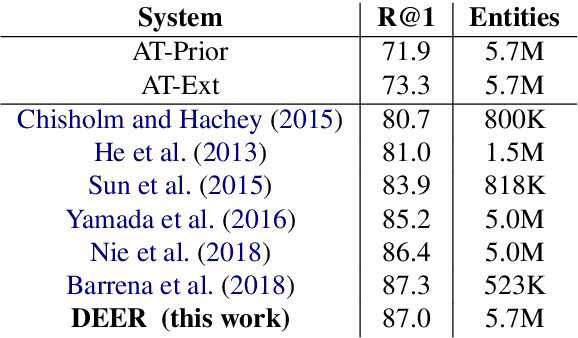
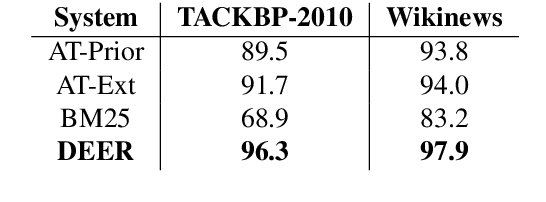
Abstract:We show that it is feasible to perform entity linking by training a dual encoder (two-tower) model that encodes mentions and entities in the same dense vector space, where candidate entities are retrieved by approximate nearest neighbor search. Unlike prior work, this setup does not rely on an alias table followed by a re-ranker, and is thus the first fully learned entity retrieval model. We show that our dual encoder, trained using only anchor-text links in Wikipedia, outperforms discrete alias table and BM25 baselines, and is competitive with the best comparable results on the standard TACKBP-2010 dataset. In addition, it can retrieve candidates extremely fast, and generalizes well to a new dataset derived from Wikinews. On the modeling side, we demonstrate the dramatic value of an unsupervised negative mining algorithm for this task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge