Biomedical Interpretable Entity Representations
Paper and Code
Jun 17, 2021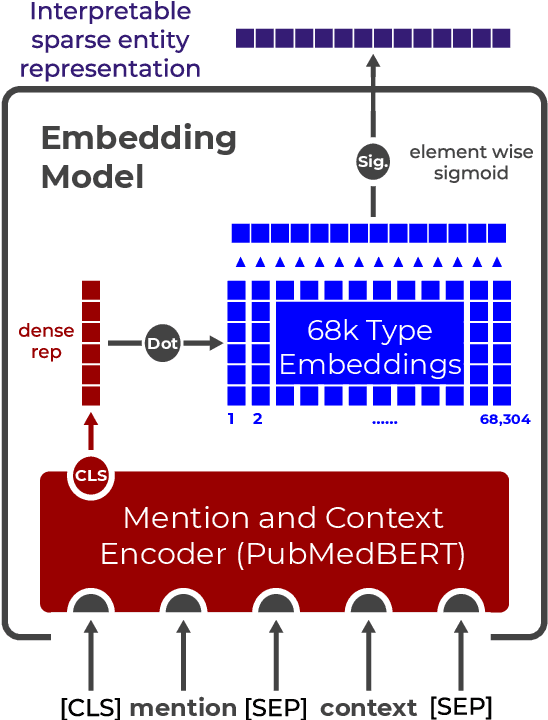
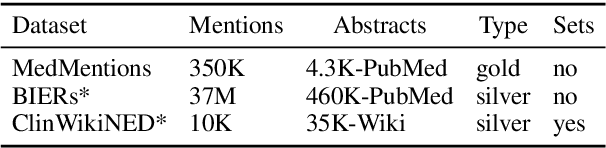
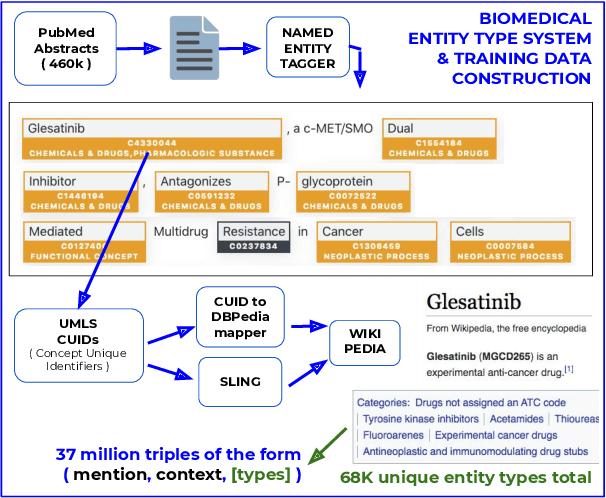
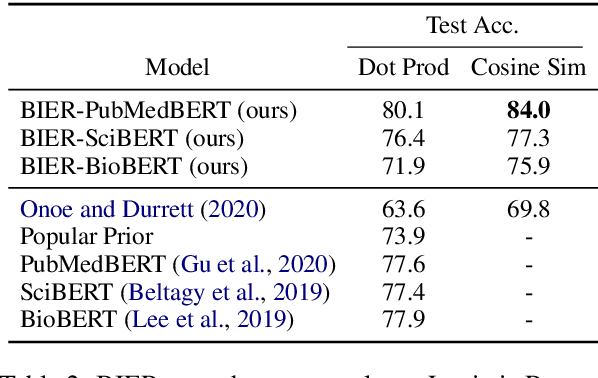
Pre-trained language models induce dense entity representations that offer strong performance on entity-centric NLP tasks, but such representations are not immediately interpretable. This can be a barrier to model uptake in important domains such as biomedicine. There has been recent work on general interpretable representation learning (Onoe and Durrett, 2020), but these domain-agnostic representations do not readily transfer to the important domain of biomedicine. In this paper, we create a new entity type system and training set from a large corpus of biomedical texts by mapping entities to concepts in a medical ontology, and from these to Wikipedia pages whose categories are our types. From this mapping we derive Biomedical Interpretable Entity Representations(BIERs), in which dimensions correspond to fine-grained entity types, and values are predicted probabilities that a given entity is of the corresponding type. We propose a novel method that exploits BIER's final sparse and intermediate dense representations to facilitate model and entity type debugging. We show that BIERs achieve strong performance in biomedical tasks including named entity disambiguation and entity label classification, and we provide error analysis to highlight the utility of their interpretability, particularly in low-supervision settings. Finally, we provide our induced 68K biomedical type system, the corresponding 37 million triples of derived data used to train BIER models and our best performing model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge