David Vázquez
XC-Cache: Cross-Attending to Cached Context for Efficient LLM Inference
Apr 23, 2024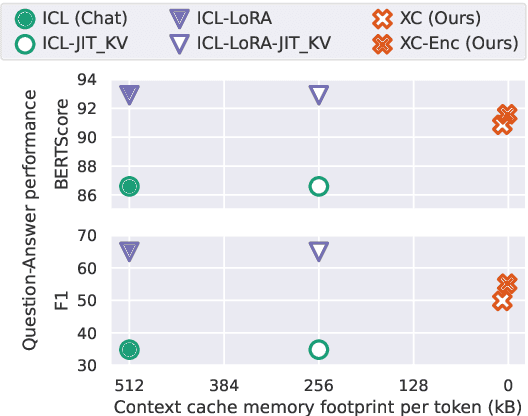
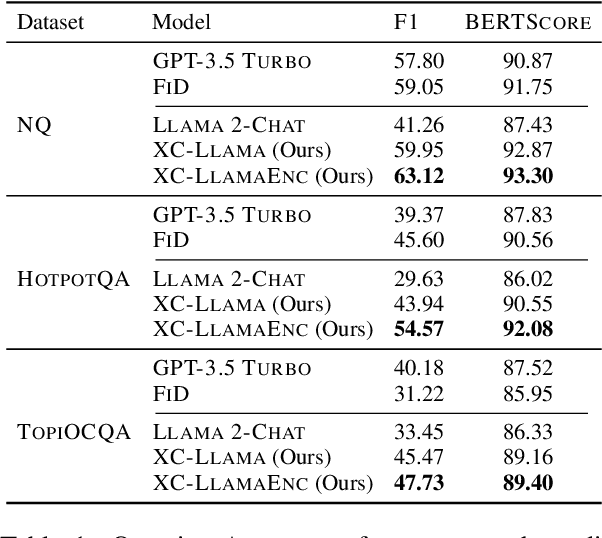
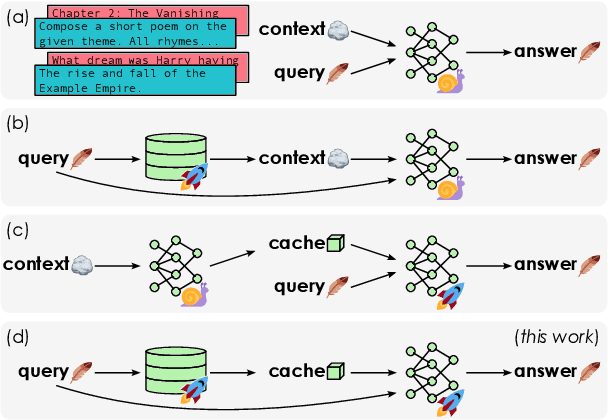
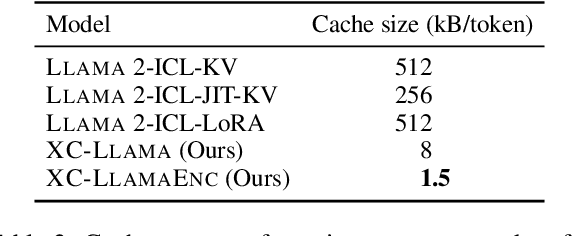
Abstract:In-context learning (ICL) approaches typically leverage prompting to condition decoder-only language model generation on reference information. Just-in-time processing of a context is inefficient due to the quadratic cost of self-attention operations, and caching is desirable. However, caching transformer states can easily require almost as much space as the model parameters. When the right context isn't known in advance, caching ICL can be challenging. This work addresses these limitations by introducing models that, inspired by the encoder-decoder architecture, use cross-attention to condition generation on reference text without the prompt. More precisely, we leverage pre-trained decoder-only models and only train a small number of added layers. We use Question-Answering (QA) as a testbed to evaluate the ability of our models to perform conditional generation and observe that they outperform ICL, are comparable to fine-tuned prompted LLMs, and drastically reduce the space footprint relative to standard KV caching by two orders of magnitude.
Automatic Data Augmentation Learning using Bilevel Optimization for Histopathological Images
Jul 21, 2023Abstract:Training a deep learning model to classify histopathological images is challenging, because of the color and shape variability of the cells and tissues, and the reduced amount of available data, which does not allow proper learning of those variations. Variations can come from the image acquisition process, for example, due to different cell staining protocols or tissue deformation. To tackle this challenge, Data Augmentation (DA) can be used during training to generate additional samples by applying transformations to existing ones, to help the model become invariant to those color and shape transformations. The problem with DA is that it is not only dataset-specific but it also requires domain knowledge, which is not always available. Without this knowledge, selecting the right transformations can only be done using heuristics or through a computationally demanding search. To address this, we propose an automatic DA learning method. In this method, the DA parameters, i.e. the transformation parameters needed to improve the model training, are considered learnable and are learned automatically using a bilevel optimization approach in a quick and efficient way using truncated backpropagation. We validated the method on six different datasets. Experimental results show that our model can learn color and affine transformations that are more helpful to train an image classifier than predefined DA transformations, which are also more expensive as they need to be selected before the training by grid search on a validation set. We also show that similarly to a model trained with RandAugment, our model has also only a few method-specific hyperparameters to tune but is performing better. This makes our model a good solution for learning the best DA parameters, especially in the context of histopathological images, where defining potentially useful transformation heuristically is not trivial.
Synbols: Probing Learning Algorithms with Synthetic Datasets
Sep 14, 2020



Abstract:Progress in the field of machine learning has been fueled by the introduction of benchmark datasets pushing the limits of existing algorithms. Enabling the design of datasets to test specific properties and failure modes of learning algorithms is thus a problem of high interest, as it has a direct impact on innovation in the field. In this sense, we introduce Synbols -- Synthetic Symbols -- a tool for rapidly generating new datasets with a rich composition of latent features rendered in low resolution images. Synbols leverages the large amount of symbols available in the Unicode standard and the wide range of artistic font provided by the open font community. Our tool's high-level interface provides a language for rapidly generating new distributions on the latent features, including various types of textures and occlusions. To showcase the versatility of Synbols, we use it to dissect the limitations and flaws in standard learning algorithms in various learning setups including supervised learning, active learning, out of distribution generalization, unsupervised representation learning, and object counting.
Slanted Stixels: Representing San Francisco's Steepest Streets
Jul 17, 2017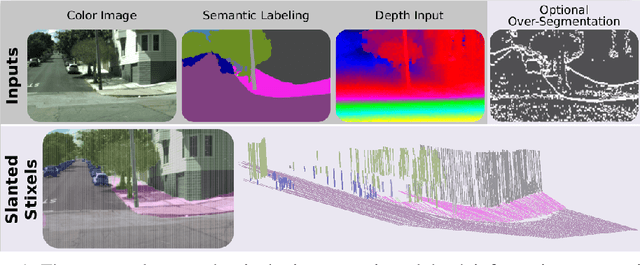
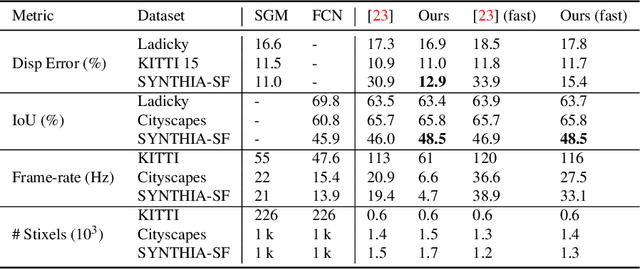
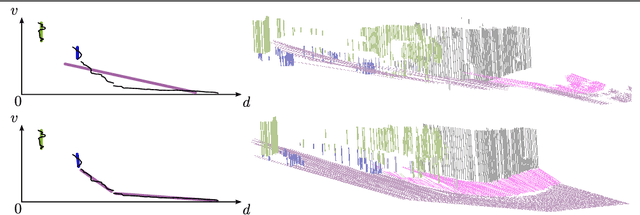
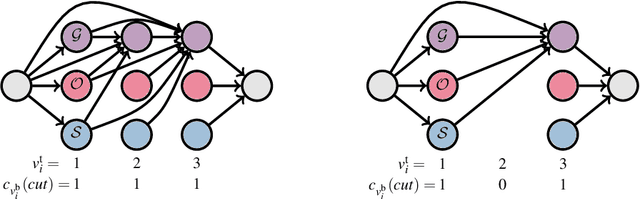
Abstract:In this work we present a novel compact scene representation based on Stixels that infers geometric and semantic information. Our approach overcomes the previous rather restrictive geometric assumptions for Stixels by introducing a novel depth model to account for non-flat roads and slanted objects. Both semantic and depth cues are used jointly to infer the scene representation in a sound global energy minimization formulation. Furthermore, a novel approximation scheme is introduced that uses an extremely efficient over-segmentation. In doing so, the computational complexity of the Stixel inference algorithm is reduced significantly, achieving real-time computation capabilities with only a slight drop in accuracy. We evaluate the proposed approach in terms of semantic and geometric accuracy as well as run-time on four publicly available benchmark datasets. Our approach maintains accuracy on flat road scene datasets while improving substantially on a novel non-flat road dataset.
A Benchmark for Endoluminal Scene Segmentation of Colonoscopy Images
Dec 02, 2016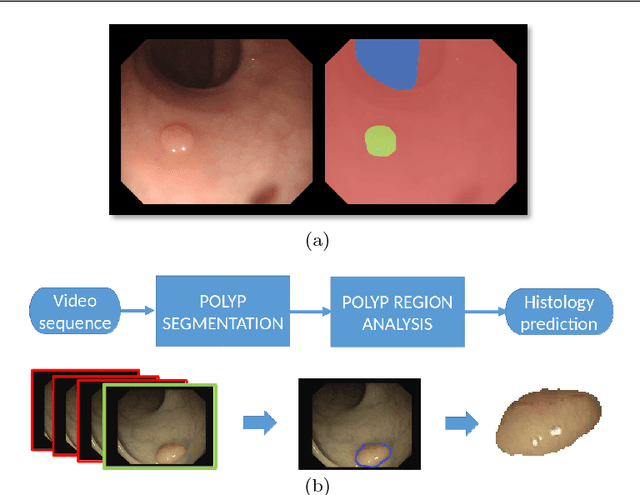
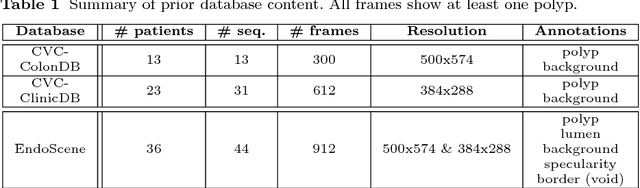

Abstract:Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third cause of cancer death worldwide. Currently, the standard approach to reduce CRC-related mortality is to perform regular screening in search for polyps and colonoscopy is the screening tool of choice. The main limitations of this screening procedure are polyp miss-rate and inability to perform visual assessment of polyp malignancy. These drawbacks can be reduced by designing Decision Support Systems (DSS) aiming to help clinicians in the different stages of the procedure by providing endoluminal scene segmentation. Thus, in this paper, we introduce an extended benchmark of colonoscopy image, with the hope of establishing a new strong benchmark for colonoscopy image analysis research. We provide new baselines on this dataset by training standard fully convolutional networks (FCN) for semantic segmentation and significantly outperforming, without any further post-processing, prior results in endoluminal scene segmentation.
GPU-based Pedestrian Detection for Autonomous Driving
Nov 05, 2016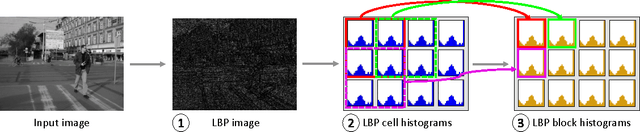
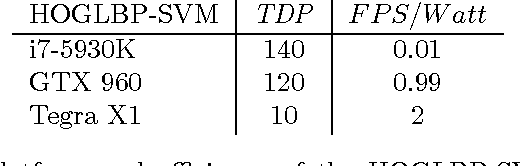
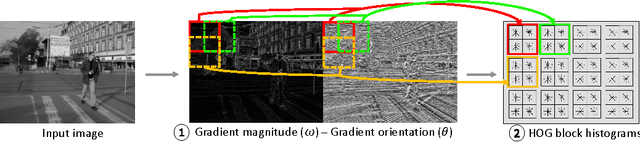
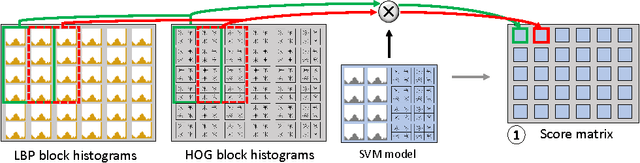
Abstract:We propose a real-time pedestrian detection system for the embedded Nvidia Tegra X1 GPU-CPU hybrid platform. The pipeline is composed by the following state-of-the-art algorithms: Histogram of Local Binary Patterns (LBP) and Histograms of Oriented Gradients (HOG) features extracted from the input image; Pyramidal Sliding Window technique for candidate generation; and Support Vector Machine (SVM) for classification. Results show a 8x speedup in the target Tegra X1 platform and a better performance/watt ratio than desktop CUDA platforms in study.
* 10 pages
GPU-accelerated real-time stixel computation
Oct 13, 2016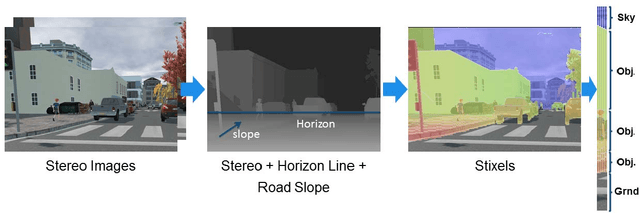

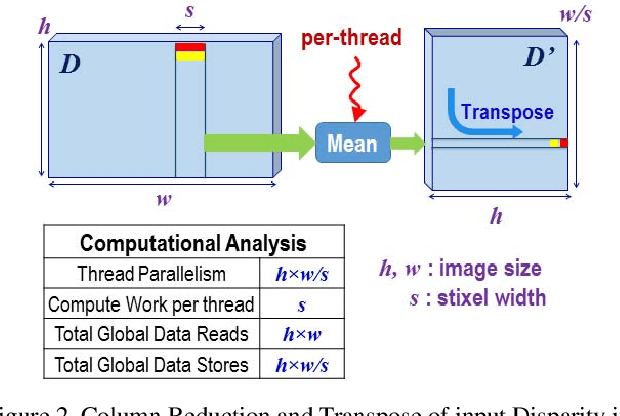
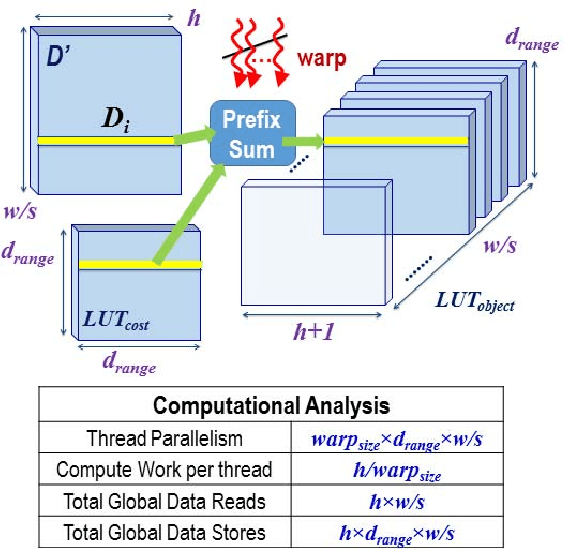
Abstract:The Stixel World is a medium-level, compact representation of road scenes that abstracts millions of disparity pixels into hundreds or thousands of stixels. The goal of this work is to implement and evaluate a complete multi-stixel estimation pipeline on an embedded, energy-efficient, GPU-accelerated device. This work presents a full GPU-accelerated implementation of stixel estimation that produces reliable results at 26 frames per second (real-time) on the Tegra X1 for disparity images of 1024x440 pixels and stixel widths of 5 pixels, and achieves more than 400 frames per second on a high-end Titan X GPU card.
Embedded real-time stereo estimation via Semi-Global Matching on the GPU
Oct 13, 2016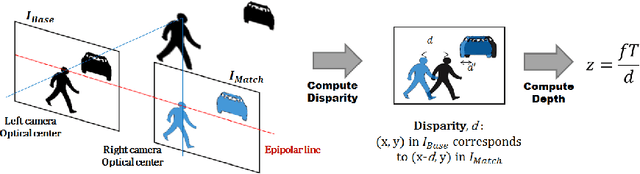
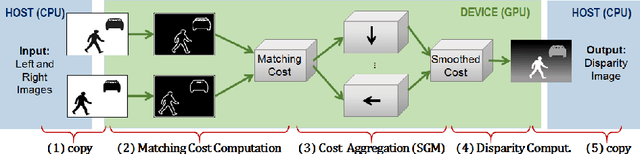
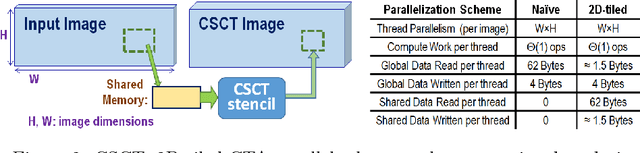
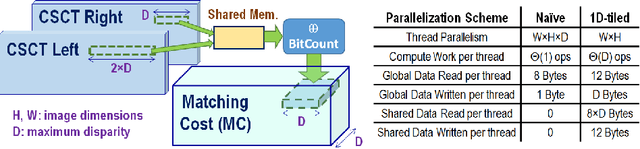
Abstract:Dense, robust and real-time computation of depth information from stereo-camera systems is a computationally demanding requirement for robotics, advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS) and autonomous vehicles. Semi-Global Matching (SGM) is a widely used algorithm that propagates consistency constraints along several paths across the image. This work presents a real-time system producing reliable disparity estimation results on the new embedded energy-efficient GPU devices. Our design runs on a Tegra X1 at 42 frames per second (fps) for an image size of 640x480, 128 disparity levels, and using 4 path directions for the SGM method.
Spatiotemporal Stacked Sequential Learning for Pedestrian Detection
Jul 14, 2014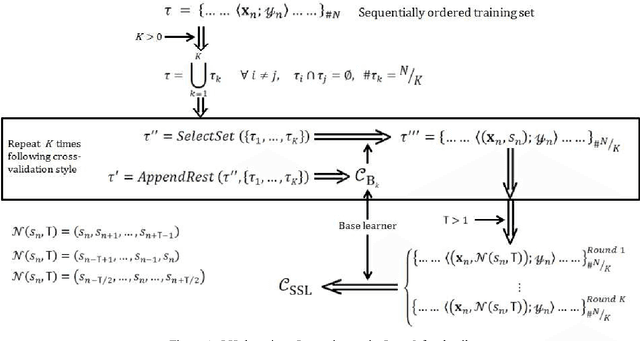
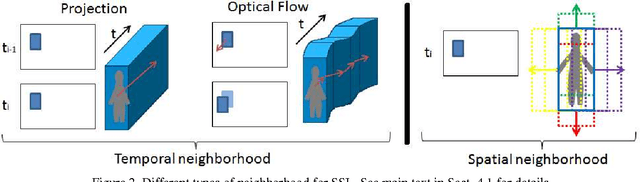
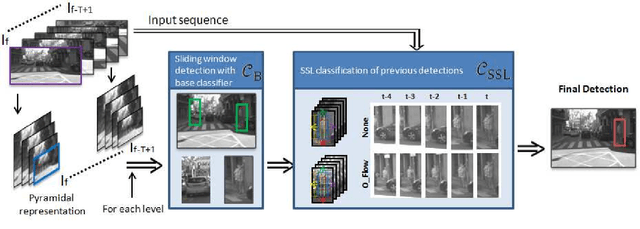
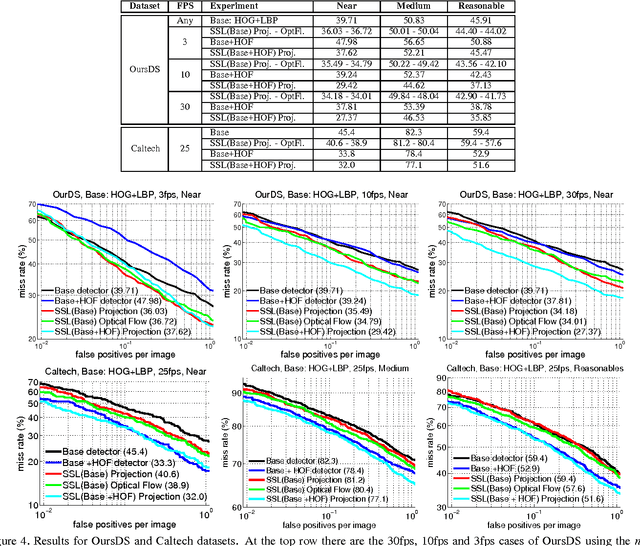
Abstract:Pedestrian classifiers decide which image windows contain a pedestrian. In practice, such classifiers provide a relatively high response at neighbor windows overlapping a pedestrian, while the responses around potential false positives are expected to be lower. An analogous reasoning applies for image sequences. If there is a pedestrian located within a frame, the same pedestrian is expected to appear close to the same location in neighbor frames. Therefore, such a location has chances of receiving high classification scores during several frames, while false positives are expected to be more spurious. In this paper we propose to exploit such correlations for improving the accuracy of base pedestrian classifiers. In particular, we propose to use two-stage classifiers which not only rely on the image descriptors required by the base classifiers but also on the response of such base classifiers in a given spatiotemporal neighborhood. More specifically, we train pedestrian classifiers using a stacked sequential learning (SSL) paradigm. We use a new pedestrian dataset we have acquired from a car to evaluate our proposal at different frame rates. We also test on a well known dataset: Caltech. The obtained results show that our SSL proposal boosts detection accuracy significantly with a minimal impact on the computational cost. Interestingly, SSL improves more the accuracy at the most dangerous situations, i.e. when a pedestrian is close to the camera.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge