Benjamin Morrell
Jet Propulsion Lab., California Institute of Technology and
An Addendum to NeBula: Towards Extending TEAM CoSTAR's Solution to Larger Scale Environments
Apr 18, 2025Abstract:This paper presents an appendix to the original NeBula autonomy solution developed by the TEAM CoSTAR (Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Robots), participating in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Specifically, this paper presents extensions to NeBula's hardware, software, and algorithmic components that focus on increasing the range and scale of the exploration environment. From the algorithmic perspective, we discuss the following extensions to the original NeBula framework: (i) large-scale geometric and semantic environment mapping; (ii) an adaptive positioning system; (iii) probabilistic traversability analysis and local planning; (iv) large-scale POMDP-based global motion planning and exploration behavior; (v) large-scale networking and decentralized reasoning; (vi) communication-aware mission planning; and (vii) multi-modal ground-aerial exploration solutions. We demonstrate the application and deployment of the presented systems and solutions in various large-scale underground environments, including limestone mine exploration scenarios as well as deployment in the DARPA Subterranean challenge.
Present and Future of SLAM in Extreme Underground Environments
Aug 02, 2022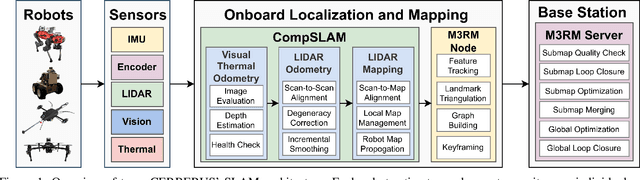
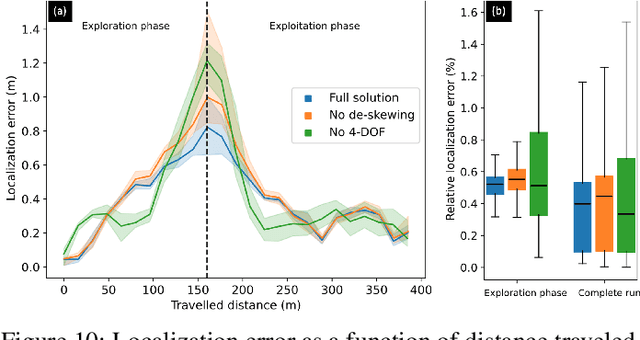
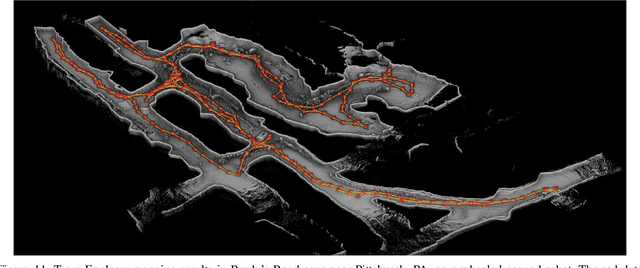
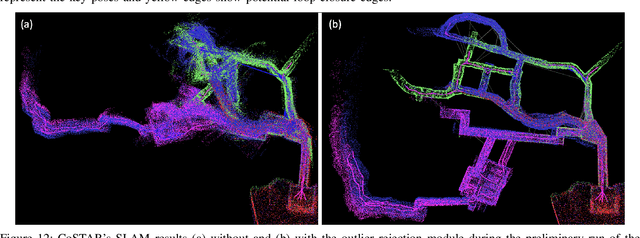
Abstract:This paper reports on the state of the art in underground SLAM by discussing different SLAM strategies and results across six teams that participated in the three-year-long SubT competition. In particular, the paper has four main goals. First, we review the algorithms, architectures, and systems adopted by the teams; particular emphasis is put on lidar-centric SLAM solutions (the go-to approach for virtually all teams in the competition), heterogeneous multi-robot operation (including both aerial and ground robots), and real-world underground operation (from the presence of obscurants to the need to handle tight computational constraints). We do not shy away from discussing the dirty details behind the different SubT SLAM systems, which are often omitted from technical papers. Second, we discuss the maturity of the field by highlighting what is possible with the current SLAM systems and what we believe is within reach with some good systems engineering. Third, we outline what we believe are fundamental open problems, that are likely to require further research to break through. Finally, we provide a list of open-source SLAM implementations and datasets that have been produced during the SubT challenge and related efforts, and constitute a useful resource for researchers and practitioners.
LAMP 2.0: A Robust Multi-Robot SLAM System for Operation in Challenging Large-Scale Underground Environments
May 31, 2022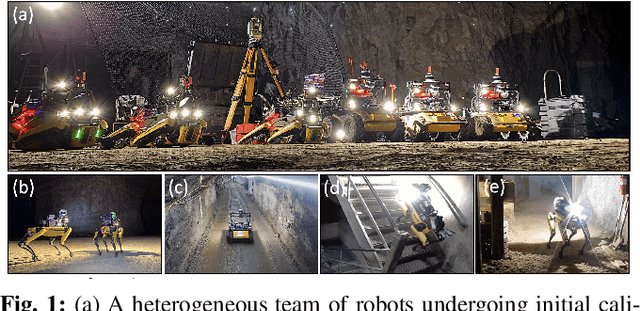
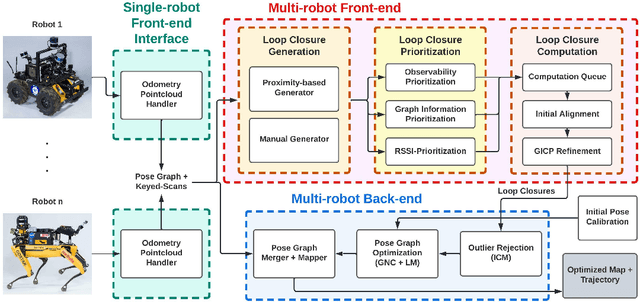
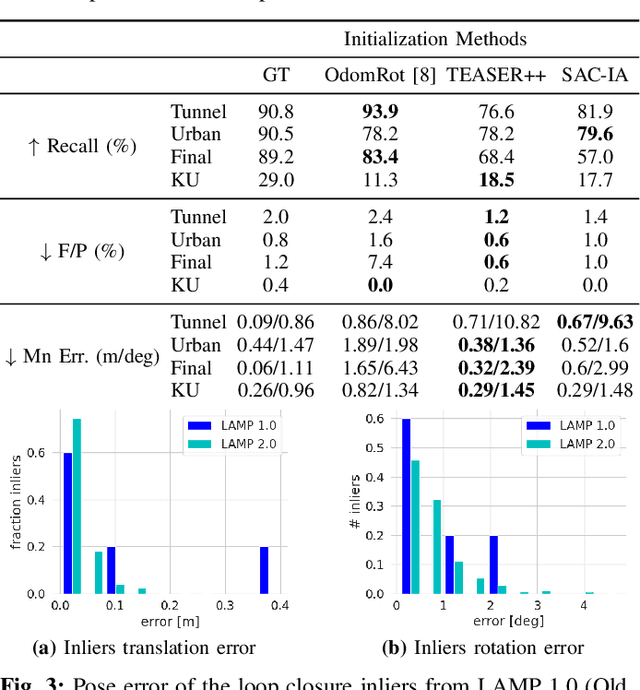
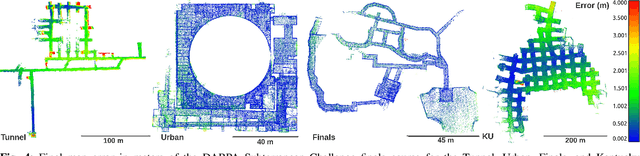
Abstract:Search and rescue with a team of heterogeneous mobile robots in unknown and large-scale underground environments requires high-precision localization and mapping. This crucial requirement is faced with many challenges in complex and perceptually-degraded subterranean environments, as the onboard perception system is required to operate in off-nominal conditions (poor visibility due to darkness and dust, rugged and muddy terrain, and the presence of self-similar and ambiguous scenes). In a disaster response scenario and in the absence of prior information about the environment, robots must rely on noisy sensor data and perform Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) to build a 3D map of the environment and localize themselves and potential survivors. To that end, this paper reports on a multi-robot SLAM system developed by team CoSTAR in the context of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. We extend our previous work, LAMP, by incorporating a single-robot front-end interface that is adaptable to different odometry sources and lidar configurations, a scalable multi-robot front-end to support inter- and intra-robot loop closure detection for large scale environments and multi-robot teams, and a robust back-end equipped with an outlier-resilient pose graph optimization based on Graduated Non-Convexity. We provide a detailed ablation study on the multi-robot front-end and back-end, and assess the overall system performance in challenging real-world datasets collected across mines, power plants, and caves in the United States. We also release our multi-robot back-end datasets (and the corresponding ground truth), which can serve as challenging benchmarks for large-scale underground SLAM.
Loop Closure Prioritization for Efficient and Scalable Multi-Robot SLAM
May 24, 2022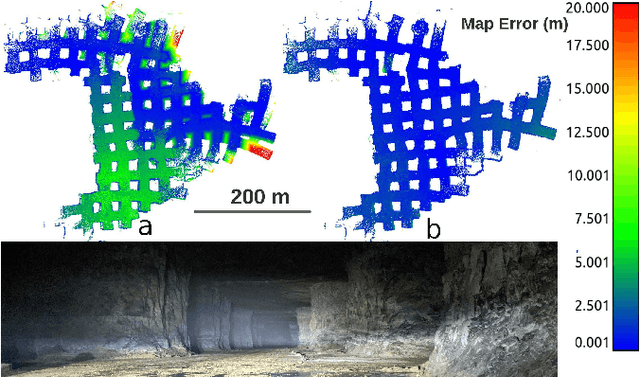
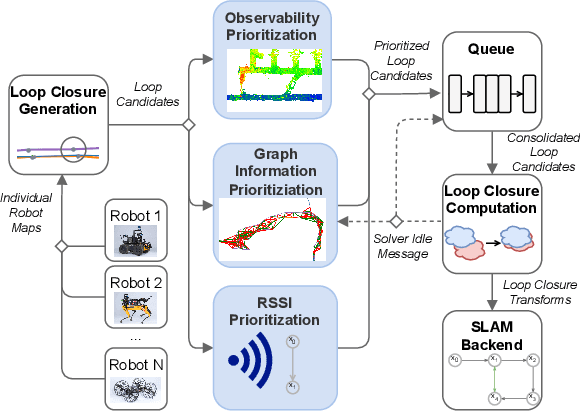
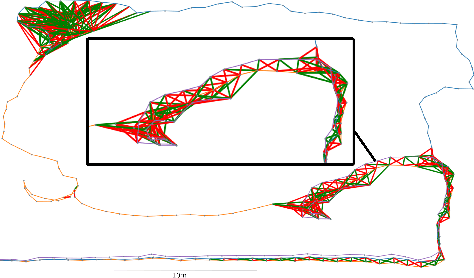
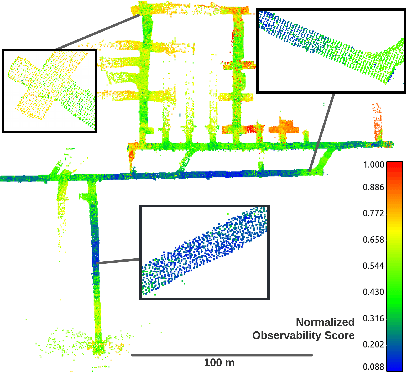
Abstract:Multi-robot SLAM systems in GPS-denied environments require loop closures to maintain a drift-free centralized map. With an increasing number of robots and size of the environment, checking and computing the transformation for all the loop closure candidates becomes computationally infeasible. In this work, we describe a loop closure module that is able to prioritize which loop closures to compute based on the underlying pose graph, the proximity to known beacons, and the characteristics of the point clouds. We validate this system in the context of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge and on numerous challenging underground datasets and demonstrate the ability of this system to generate and maintain a map with low error. We find that our proposed techniques are able to select effective loop closures which results in 51% mean reduction in median error when compared to an odometric solution and 75% mean reduction in median error when compared to a baseline version of this system with no prioritization. We also find our proposed system is able to find a lower error in the mission time of one hour when compared to a system that processes every possible loop closure in four and a half hours.
LOCUS 2.0: Robust and Computationally Efficient Lidar Odometry for Real-Time Underground 3D Mapping
May 24, 2022
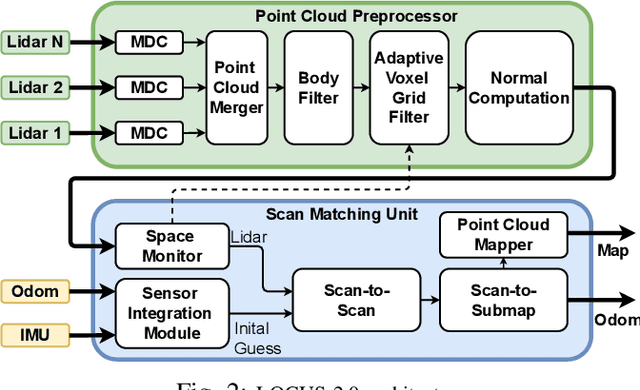
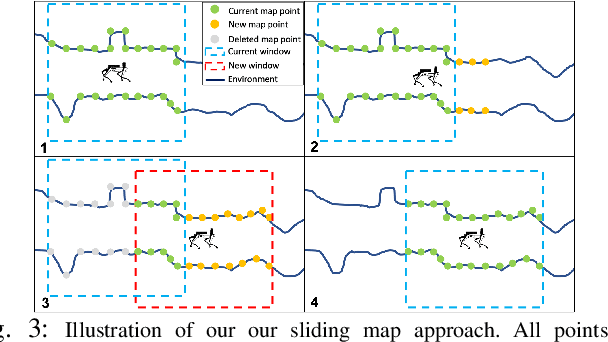
Abstract:Lidar odometry has attracted considerable attention as a robust localization method for autonomous robots operating in complex GNSS-denied environments. However, achieving reliable and efficient performance on heterogeneous platforms in large-scale environments remains an open challenge due to the limitations of onboard computation and memory resources needed for autonomous operation. In this work, we present LOCUS 2.0, a robust and computationally-efficient \lidar odometry system for real-time underground 3D mapping. LOCUS 2.0 includes a novel normals-based \morrell{Generalized Iterative Closest Point (GICP)} formulation that reduces the computation time of point cloud alignment, an adaptive voxel grid filter that maintains the desired computation load regardless of the environment's geometry, and a sliding-window map approach that bounds the memory consumption. The proposed approach is shown to be suitable to be deployed on heterogeneous robotic platforms involved in large-scale explorations under severe computation and memory constraints. We demonstrate LOCUS 2.0, a key element of the CoSTAR team's entry in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge, across various underground scenarios. We release LOCUS 2.0 as an open-source library and also release a \lidar-based odometry dataset in challenging and large-scale underground environments. The dataset features legged and wheeled platforms in multiple environments including fog, dust, darkness, and geometrically degenerate surroundings with a total of $11~h$ of operations and $16~km$ of distance traveled.
Exploring Event Camera-based Odometry for Planetary Robots
Apr 12, 2022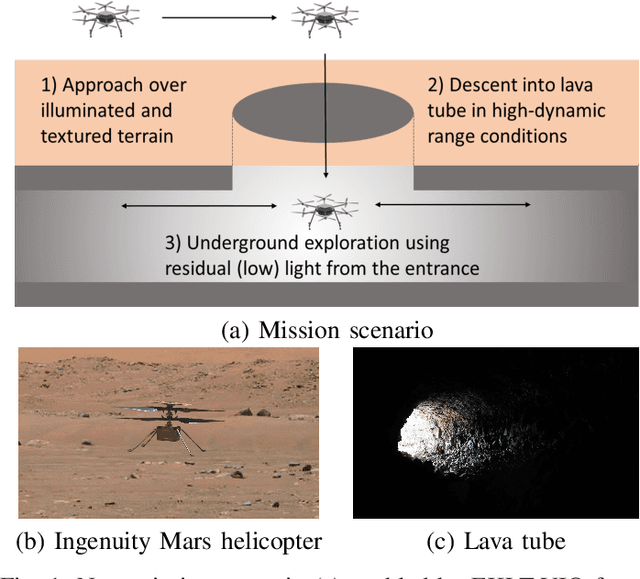
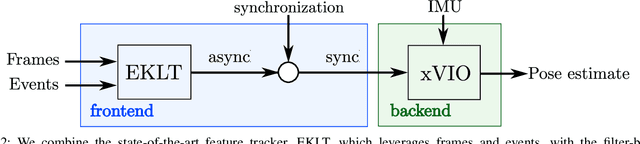
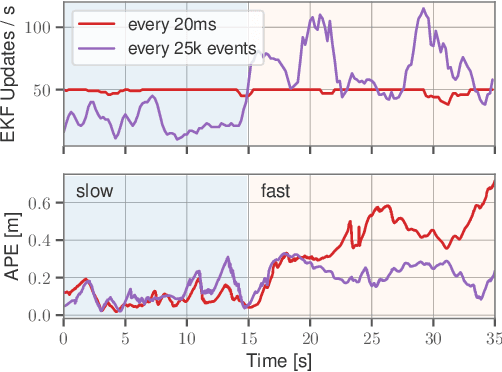
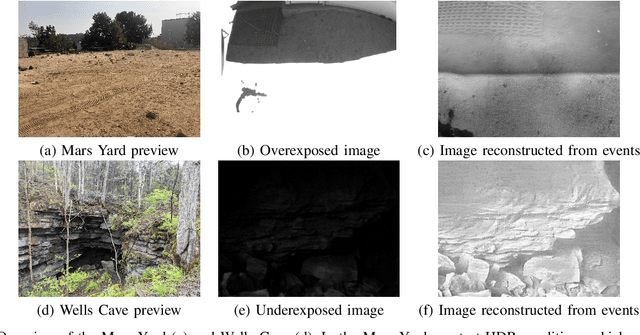
Abstract:Due to their resilience to motion blur and high robustness in low-light and high dynamic range conditions, event cameras are poised to become enabling sensors for vision-based exploration on future Mars helicopter missions. However, existing event-based visual-inertial odometry (VIO) algorithms either suffer from high tracking errors or are brittle, since they cannot cope with significant depth uncertainties caused by an unforeseen loss of tracking or other effects. In this work, we introduce EKLT-VIO, which addresses both limitations by combining a state-of-the-art event-based frontend with a filter-based backend. This makes it both accurate and robust to uncertainties, outperforming event- and frame-based VIO algorithms on challenging benchmarks by 32%. In addition, we demonstrate accurate performance in hover-like conditions (outperforming existing event-based methods) as well as high robustness in newly collected Mars-like and high-dynamic-range sequences, where existing frame-based methods fail. In doing so, we show that event-based VIO is the way forward for vision-based exploration on Mars.
NeBula: Quest for Robotic Autonomy in Challenging Environments; TEAM CoSTAR at the DARPA Subterranean Challenge
Mar 28, 2021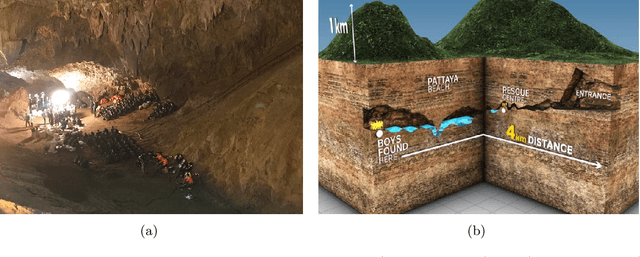
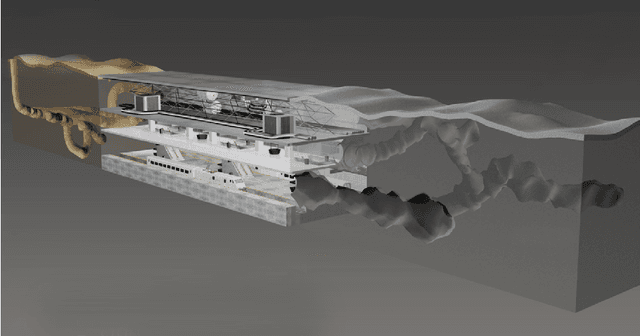
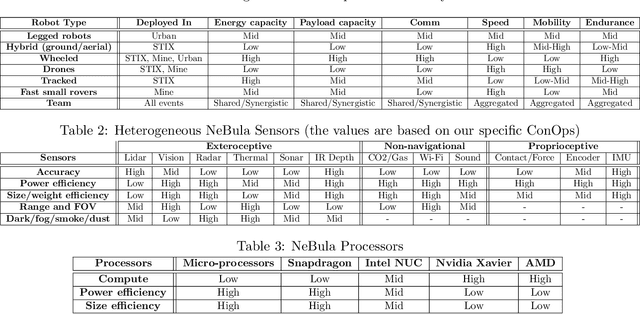
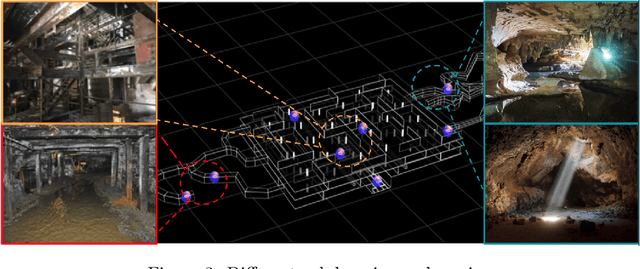
Abstract:This paper presents and discusses algorithms, hardware, and software architecture developed by the TEAM CoSTAR (Collaborative SubTerranean Autonomous Robots), competing in the DARPA Subterranean Challenge. Specifically, it presents the techniques utilized within the Tunnel (2019) and Urban (2020) competitions, where CoSTAR achieved 2nd and 1st place, respectively. We also discuss CoSTAR's demonstrations in Martian-analog surface and subsurface (lava tubes) exploration. The paper introduces our autonomy solution, referred to as NeBula (Networked Belief-aware Perceptual Autonomy). NeBula is an uncertainty-aware framework that aims at enabling resilient and modular autonomy solutions by performing reasoning and decision making in the belief space (space of probability distributions over the robot and world states). We discuss various components of the NeBula framework, including: (i) geometric and semantic environment mapping; (ii) a multi-modal positioning system; (iii) traversability analysis and local planning; (iv) global motion planning and exploration behavior; (i) risk-aware mission planning; (vi) networking and decentralized reasoning; and (vii) learning-enabled adaptation. We discuss the performance of NeBula on several robot types (e.g. wheeled, legged, flying), in various environments. We discuss the specific results and lessons learned from fielding this solution in the challenging courses of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge competition.
Unsupervised Deep Persistent Monocular Visual Odometry and Depth Estimation in Extreme Environments
Oct 31, 2020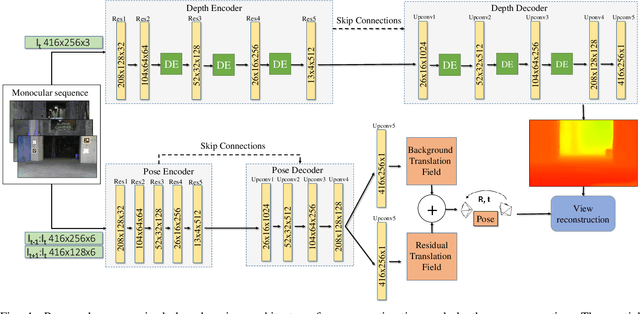
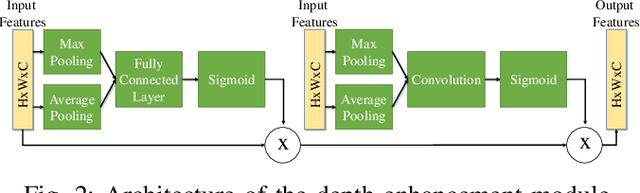
Abstract:In recent years, unsupervised deep learning approaches have received significant attention to estimate the depth and visual odometry (VO) from unlabelled monocular image sequences. However, their performance is limited in challenging environments due to perceptual degradation, occlusions and rapid motions. Moreover, the existing unsupervised methods suffer from the lack of scale-consistency constraints across frames, which causes that the VO estimators fail to provide persistent trajectories over long sequences. In this study, we propose an unsupervised monocular deep VO framework that predicts six-degrees-of-freedom pose camera motion and depth map of the scene from unlabelled RGB image sequences. We provide detailed quantitative and qualitative evaluations of the proposed framework on a) a challenging dataset collected during the DARPA Subterranean challenge; and b) the benchmark KITTI and Cityscapes datasets. The proposed approach outperforms both traditional and state-of-the-art unsupervised deep VO methods providing better results for both pose estimation and depth recovery. The presented approach is part of the solution used by the COSTAR team participating at the DARPA Subterranean Challenge.
Towards Resilient Autonomous Navigation of Drones
Aug 21, 2020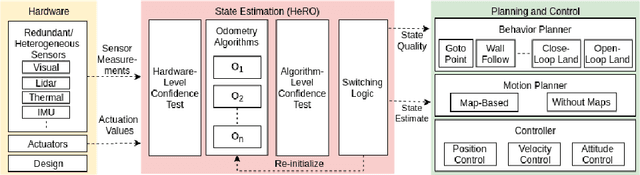
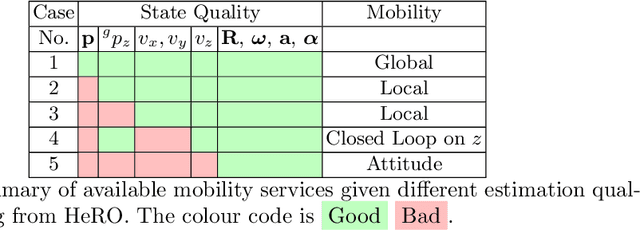
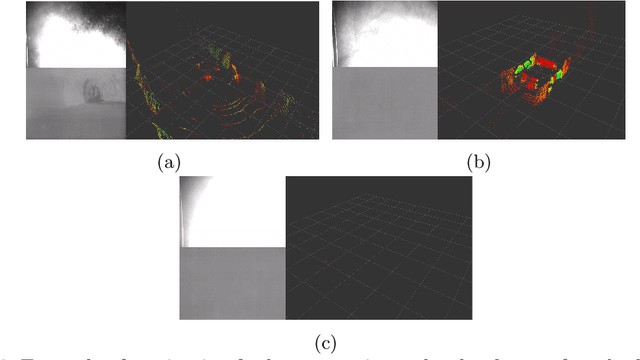

Abstract:Robots and particularly drones are especially useful in exploring extreme environments that pose hazards to humans. To ensure safe operations in these situations, usually perceptually degraded and without good GNSS, it is critical to have a reliable and robust state estimation solution. The main body of literature in robot state estimation focuses on developing complex algorithms favoring accuracy. Typically, these approaches rely on a strong underlying assumption: the main estimation engine will not fail during operation. In contrast, we propose an architecture that pursues robustness in state estimation by considering redundancy and heterogeneity in both sensing and estimation algorithms. The architecture is designed to expect and detect failures and adapt the behavior of the system to ensure safety. To this end, we present HeRO (Heterogeneous Redundant Odometry): a stack of estimation algorithms running in parallel supervised by a resiliency logic. This logic carries out three main functions: a) perform confidence tests both in data quality and algorithm health; b) re-initialize those algorithms that might be malfunctioning; c) generate a smooth state estimate by multiplexing the inputs based on their quality. The state and quality estimates are used by the guidance and control modules to adapt the mobility behaviors of the system. The validation and utility of the approach are shown with real experiments on a flying robot for the use case of autonomous exploration of subterranean environments, with particular results from the STIX event of the DARPA Subterranean Challenge.
The Shapeshifter: a Morphing, Multi-Agent,Multi-Modal Robotic Platform for the Exploration of Titan
Mar 16, 2020
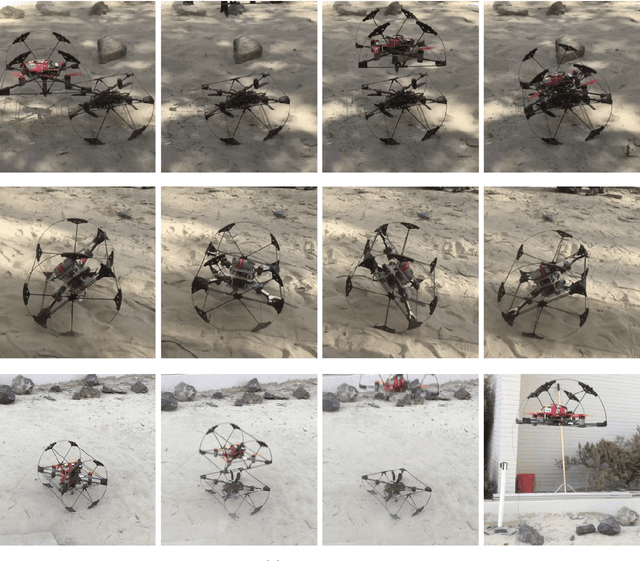
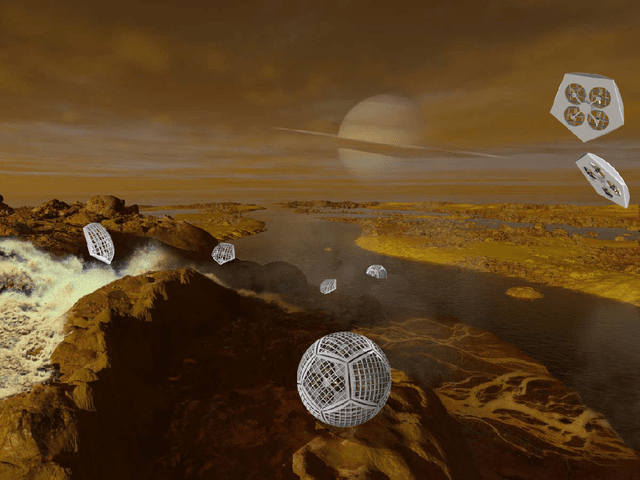
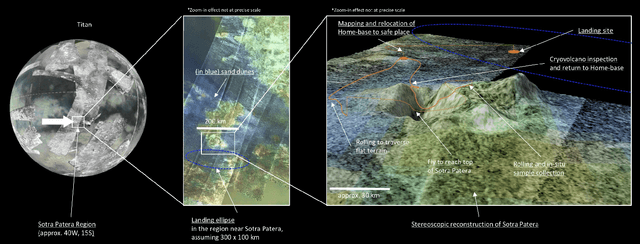

Abstract:In this report for the Nasa NIAC Phase I study, we present a mission architecture and a robotic platform, the Shapeshifter, that allow multi-domain and redundant mobility on Saturn's moon Titan, and potentially other bodies with atmospheres. The Shapeshifter is a collection of simple and affordable robotic units, called Cobots, comparable to personal palm-size quadcopters. By attaching and detaching with each other, multiple Cobots can shape-shift into novel structures, capable of (a) rolling on the surface, to increase the traverse range, (b) flying in a flight array formation, and (c) swimming on or under liquid. A ground station complements the robotic platform, hosting science instrumentation and providing power to recharge the batteries of the Cobots. Our Phase I study had the objective of providing an initial assessment of the feasibility of the proposed robotic platform architecture, and in particular (a) to characterize the expected science return of a mission to the Sotra-Patera region on Titan; (b) to verify the mechanical and algorithmic feasibility of building a multi-agent platform capable of flying, docking, rolling and un-docking; (c) to evaluate the increased range and efficiency of rolling on Titan w.r.t to flying; (d) to define a case-study of a mission for the exploration of the cryovolcano Sotra-Patera on Titan, whose expected variety of geological features challenges conventional mobility platforms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge