Amr Sharaf
The Llama 4 Herd: Architecture, Training, Evaluation, and Deployment Notes
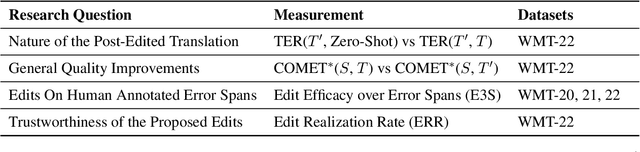
Jan 15, 2026Abstract:This document consolidates publicly reported technical details about Metas Llama 4 model family. It summarizes (i) released variants (Scout and Maverick) and the broader herd context including the previewed Behemoth teacher model, (ii) architectural characteristics beyond a high-level MoE description covering routed/shared-expert structure, early-fusion multimodality, and long-context design elements reported for Scout (iRoPE and length generalization strategies), (iii) training disclosures spanning pre-training, mid-training for long-context extension, and post-training methodology (lightweight SFT, online RL, and lightweight DPO) as described in release materials, (iv) developer-reported benchmark results for both base and instruction-tuned checkpoints, and (v) practical deployment constraints observed across major serving environments, including provider-specific context limits and quantization packaging. The manuscript also summarizes licensing obligations relevant to redistribution and derivative naming, and reviews publicly described safeguards and evaluation practices. The goal is to provide a compact technical reference for researchers and practitioners who need precise, source-backed facts about Llama 4.
Contrastive Preference Optimization: Pushing the Boundaries of LLM Performance in Machine Translation
Feb 02, 2024



Abstract:Moderate-sized large language models (LLMs) -- those with 7B or 13B parameters -- exhibit promising machine translation (MT) performance. However, even the top-performing 13B LLM-based translation models, like ALMA, does not match the performance of state-of-the-art conventional encoder-decoder translation models or larger-scale LLMs such as GPT-4. In this study, we bridge this performance gap. We first assess the shortcomings of supervised fine-tuning for LLMs in the MT task, emphasizing the quality issues present in the reference data, despite being human-generated. Then, in contrast to SFT which mimics reference translations, we introduce Contrastive Preference Optimization (CPO), a novel approach that trains models to avoid generating adequate but not perfect translations. Applying CPO to ALMA models with only 22K parallel sentences and 12M parameters yields significant improvements. The resulting model, called ALMA-R, can match or exceed the performance of the WMT competition winners and GPT-4 on WMT'21, WMT'22 and WMT'23 test datasets.
A Paradigm Shift in Machine Translation: Boosting Translation Performance of Large Language Models
Sep 20, 2023Abstract:Generative Large Language Models (LLMs) have achieved remarkable advancements in various NLP tasks. However, these advances have not been reflected in the translation task, especially those with moderate model sizes (i.e., 7B or 13B parameters), which still lag behind conventional supervised encoder-decoder translation models. Previous studies have attempted to improve the translation capabilities of these moderate LLMs, but their gains have been limited. In this study, we propose a novel fine-tuning approach for LLMs that is specifically designed for the translation task, eliminating the need for the abundant parallel data that traditional translation models usually depend on. Our approach consists of two fine-tuning stages: initial fine-tuning on monolingual data followed by subsequent fine-tuning on a small set of high-quality parallel data. We introduce the LLM developed through this strategy as Advanced Language Model-based trAnslator (ALMA). Based on LLaMA-2 as our underlying model, our results show that the model can achieve an average improvement of more than 12 BLEU and 12 COMET over its zero-shot performance across 10 translation directions from the WMT'21 (2 directions) and WMT'22 (8 directions) test datasets. The performance is significantly better than all prior work and even superior to the NLLB-54B model and GPT-3.5-text-davinci-003, with only 7B or 13B parameters. This method establishes the foundation for a novel training paradigm in machine translation.
Leveraging GPT-4 for Automatic Translation Post-Editing
May 24, 2023
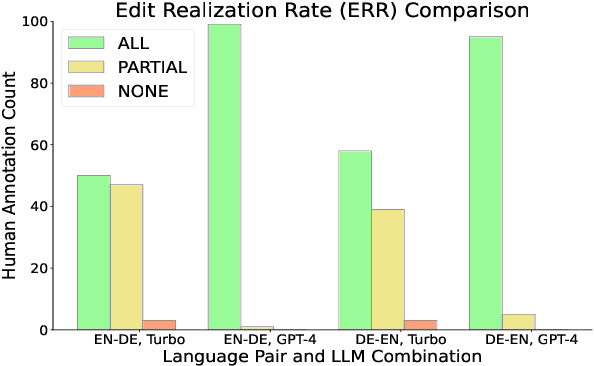

Abstract:While Neural Machine Translation (NMT) represents the leading approach to Machine Translation (MT), the outputs of NMT models still require translation post-editing to rectify errors and enhance quality, particularly under critical settings. In this work, we formalize the task of translation post-editing with Large Language Models (LLMs) and explore the use of GPT-4 to automatically post-edit NMT outputs across several language pairs. Our results demonstrate that GPT-4 is adept at translation post-editing and produces meaningful edits even when the target language is not English. Notably, we achieve state-of-the-art performance on WMT-22 English-Chinese, English-German, Chinese-English and German-English language pairs using GPT-4 based post-editing, as evaluated by state-of-the-art MT quality metrics.
How Good Are GPT Models at Machine Translation? A Comprehensive Evaluation
Feb 18, 2023



Abstract:Generative Pre-trained Transformer (GPT) models have shown remarkable capabilities for natural language generation, but their performance for machine translation has not been thoroughly investigated. In this paper, we present a comprehensive evaluation of GPT models for machine translation, covering various aspects such as quality of different GPT models in comparison with state-of-the-art research and commercial systems, effect of prompting strategies, robustness towards domain shifts and document-level translation. We experiment with eighteen different translation directions involving high and low resource languages, as well as non English-centric translations, and evaluate the performance of three GPT models: ChatGPT, GPT3.5 (text-davinci-003), and text-davinci-002. Our results show that GPT models achieve very competitive translation quality for high resource languages, while having limited capabilities for low resource languages. We also show that hybrid approaches, which combine GPT models with other translation systems, can further enhance the translation quality. We perform comprehensive analysis and human evaluation to further understand the characteristics of GPT translations. We hope that our paper provides valuable insights for researchers and practitioners in the field and helps to better understand the potential and limitations of GPT models for translation.
On Hard Episodes in Meta-Learning
Oct 21, 2021



Abstract:Existing meta-learners primarily focus on improving the average task accuracy across multiple episodes. Different episodes, however, may vary in hardness and quality leading to a wide gap in the meta-learner's performance across episodes. Understanding this issue is particularly critical in industrial few-shot settings, where there is limited control over test episodes as they are typically uploaded by end-users. In this paper, we empirically analyse the behaviour of meta-learners on episodes of varying hardness across three standard benchmark datasets: CIFAR-FS, mini-ImageNet, and tiered-ImageNet. Surprisingly, we observe a wide gap in accuracy of around 50% between the hardest and easiest episodes across all the standard benchmarks and meta-learners. We additionally investigate various properties of hard episodes and highlight their connection to catastrophic forgetting during meta-training. To address the issue of sub-par performance on hard episodes, we investigate and benchmark different meta-training strategies based on adversarial training and curriculum learning. We find that adversarial training strategies are much more powerful than curriculum learning in improving the prediction performance on hard episodes.
Semi-Supervised Few-Shot Intent Classification and Slot Filling
Sep 17, 2021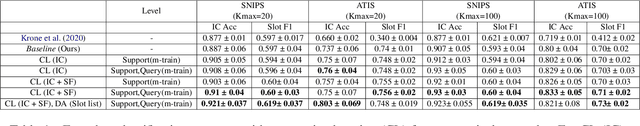
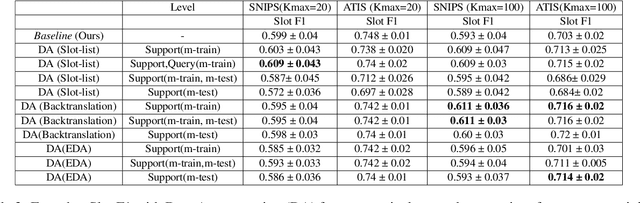
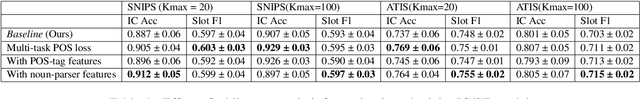
Abstract:Intent classification (IC) and slot filling (SF) are two fundamental tasks in modern Natural Language Understanding (NLU) systems. Collecting and annotating large amounts of data to train deep learning models for such systems is not scalable. This problem can be addressed by learning from few examples using fast supervised meta-learning techniques such as prototypical networks. In this work, we systematically investigate how contrastive learning and unsupervised data augmentation methods can benefit these existing supervised meta-learning pipelines for jointly modelled IC/SF tasks. Through extensive experiments across standard IC/SF benchmarks (SNIPS and ATIS), we show that our proposed semi-supervised approaches outperform standard supervised meta-learning methods: contrastive losses in conjunction with prototypical networks consistently outperform the existing state-of-the-art for both IC and SF tasks, while data augmentation strategies primarily improve few-shot IC by a significant margin.
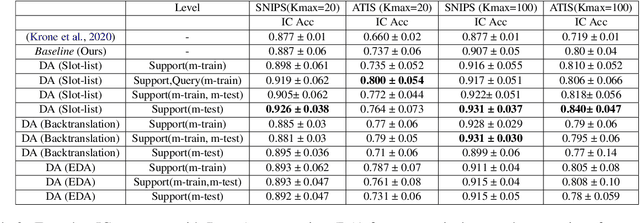
Data Augmentation for Meta-Learning
Oct 14, 2020



Abstract:Conventional image classifiers are trained by randomly sampling mini-batches of images. To achieve state-of-the-art performance, sophisticated data augmentation schemes are used to expand the amount of training data available for sampling. In contrast, meta-learning algorithms sample not only images, but classes as well. We investigate how data augmentation can be used not only to expand the number of images available per class, but also to generate entirely new classes. We systematically dissect the meta-learning pipeline and investigate the distinct ways in which data augmentation can be integrated at both the image and class levels. Our proposed meta-specific data augmentation significantly improves the performance of meta-learners on few-shot classification benchmarks.
Random Network Distillation as a Diversity Metric for Both Image and Text Generation
Oct 13, 2020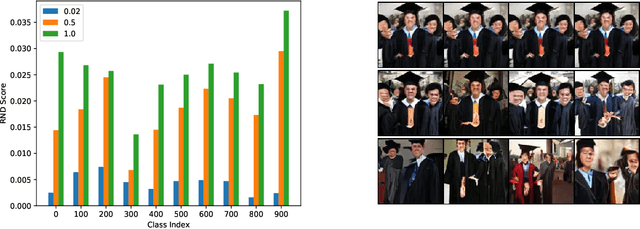
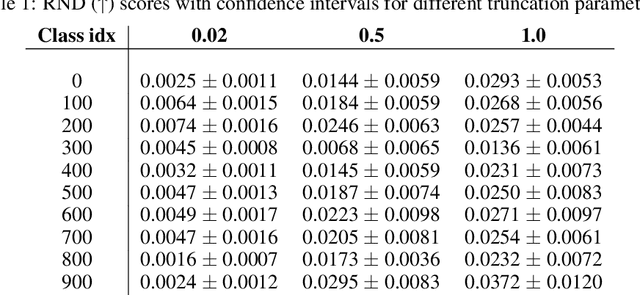
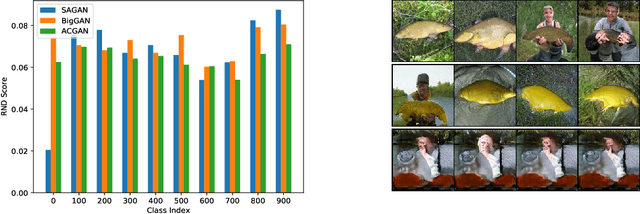
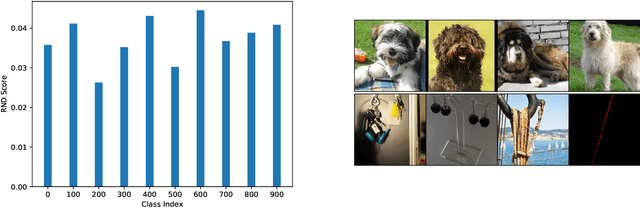
Abstract:Generative models are increasingly able to produce remarkably high quality images and text. The community has developed numerous evaluation metrics for comparing generative models. However, these metrics do not effectively quantify data diversity. We develop a new diversity metric that can readily be applied to data, both synthetic and natural, of any type. Our method employs random network distillation, a technique introduced in reinforcement learning. We validate and deploy this metric on both images and text. We further explore diversity in few-shot image generation, a setting which was previously difficult to evaluate.
Active Imitation Learning with Noisy Guidance
May 26, 2020



Abstract:Imitation learning algorithms provide state-of-the-art results on many structured prediction tasks by learning near-optimal search policies. Such algorithms assume training-time access to an expert that can provide the optimal action at any queried state; unfortunately, the number of such queries is often prohibitive, frequently rendering these approaches impractical. To combat this query complexity, we consider an active learning setting in which the learning algorithm has additional access to a much cheaper noisy heuristic that provides noisy guidance. Our algorithm, LEAQI, learns a difference classifier that predicts when the expert is likely to disagree with the heuristic, and queries the expert only when necessary. We apply LEAQI to three sequence labeling tasks, demonstrating significantly fewer queries to the expert and comparable (or better) accuracies over a passive approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge