Alex Ray
Shammie
Beyond the Imitation Game: Quantifying and extrapolating the capabilities of language models
Jun 10, 2022Abstract:Language models demonstrate both quantitative improvement and new qualitative capabilities with increasing scale. Despite their potentially transformative impact, these new capabilities are as yet poorly characterized. In order to inform future research, prepare for disruptive new model capabilities, and ameliorate socially harmful effects, it is vital that we understand the present and near-future capabilities and limitations of language models. To address this challenge, we introduce the Beyond the Imitation Game benchmark (BIG-bench). BIG-bench currently consists of 204 tasks, contributed by 442 authors across 132 institutions. Task topics are diverse, drawing problems from linguistics, childhood development, math, common-sense reasoning, biology, physics, social bias, software development, and beyond. BIG-bench focuses on tasks that are believed to be beyond the capabilities of current language models. We evaluate the behavior of OpenAI's GPT models, Google-internal dense transformer architectures, and Switch-style sparse transformers on BIG-bench, across model sizes spanning millions to hundreds of billions of parameters. In addition, a team of human expert raters performed all tasks in order to provide a strong baseline. Findings include: model performance and calibration both improve with scale, but are poor in absolute terms (and when compared with rater performance); performance is remarkably similar across model classes, though with benefits from sparsity; tasks that improve gradually and predictably commonly involve a large knowledge or memorization component, whereas tasks that exhibit "breakthrough" behavior at a critical scale often involve multiple steps or components, or brittle metrics; social bias typically increases with scale in settings with ambiguous context, but this can be improved with prompting.
Training language models to follow instructions with human feedback
Mar 04, 2022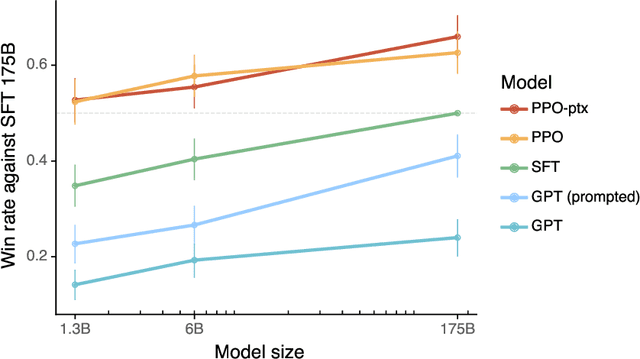

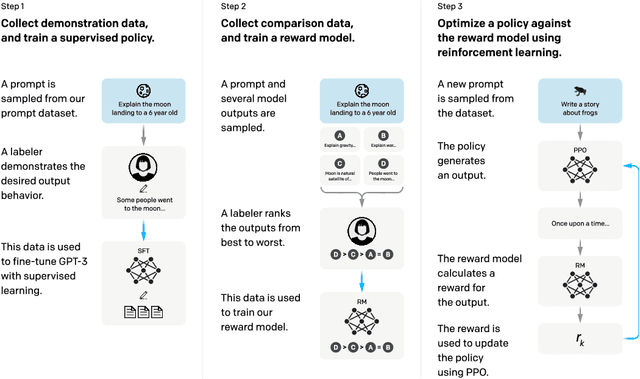

Abstract:Making language models bigger does not inherently make them better at following a user's intent. For example, large language models can generate outputs that are untruthful, toxic, or simply not helpful to the user. In other words, these models are not aligned with their users. In this paper, we show an avenue for aligning language models with user intent on a wide range of tasks by fine-tuning with human feedback. Starting with a set of labeler-written prompts and prompts submitted through the OpenAI API, we collect a dataset of labeler demonstrations of the desired model behavior, which we use to fine-tune GPT-3 using supervised learning. We then collect a dataset of rankings of model outputs, which we use to further fine-tune this supervised model using reinforcement learning from human feedback. We call the resulting models InstructGPT. In human evaluations on our prompt distribution, outputs from the 1.3B parameter InstructGPT model are preferred to outputs from the 175B GPT-3, despite having 100x fewer parameters. Moreover, InstructGPT models show improvements in truthfulness and reductions in toxic output generation while having minimal performance regressions on public NLP datasets. Even though InstructGPT still makes simple mistakes, our results show that fine-tuning with human feedback is a promising direction for aligning language models with human intent.
Unsupervised Neural Machine Translation with Generative Language Models Only
Oct 11, 2021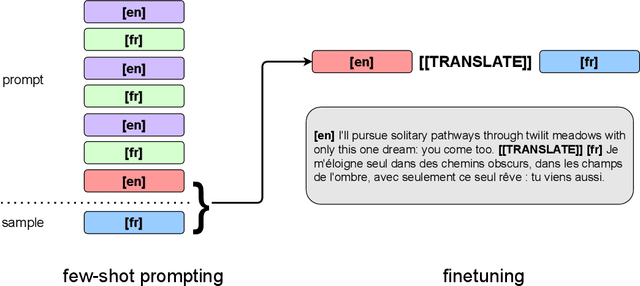
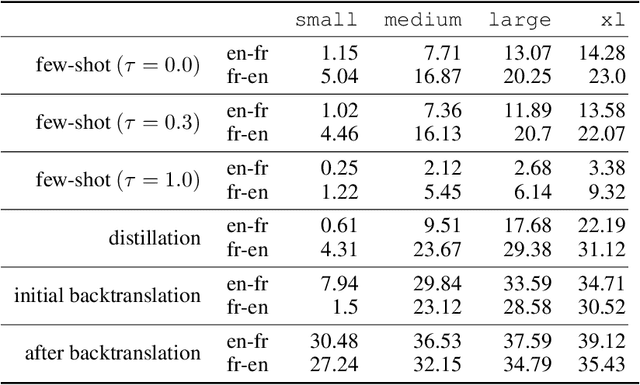
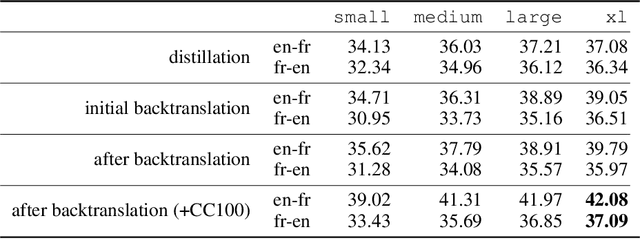
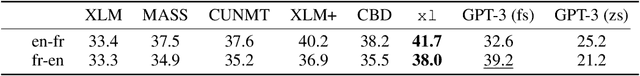
Abstract:We show how to derive state-of-the-art unsupervised neural machine translation systems from generatively pre-trained language models. Our method consists of three steps: few-shot amplification, distillation, and backtranslation. We first use the zero-shot translation ability of large pre-trained language models to generate translations for a small set of unlabeled sentences. We then amplify these zero-shot translations by using them as few-shot demonstrations for sampling a larger synthetic dataset. This dataset is distilled by discarding the few-shot demonstrations and then fine-tuning. During backtranslation, we repeatedly generate translations for a set of inputs and then fine-tune a single language model on both directions of the translation task at once, ensuring cycle-consistency by swapping the roles of gold monotext and generated translations when fine-tuning. By using our method to leverage GPT-3's zero-shot translation capability, we achieve a new state-of-the-art in unsupervised translation on the WMT14 English-French benchmark, attaining a BLEU score of 42.1.
Evaluating Large Language Models Trained on Code
Jul 14, 2021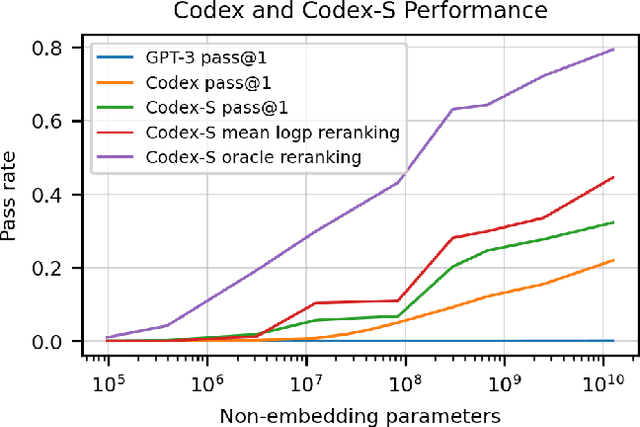
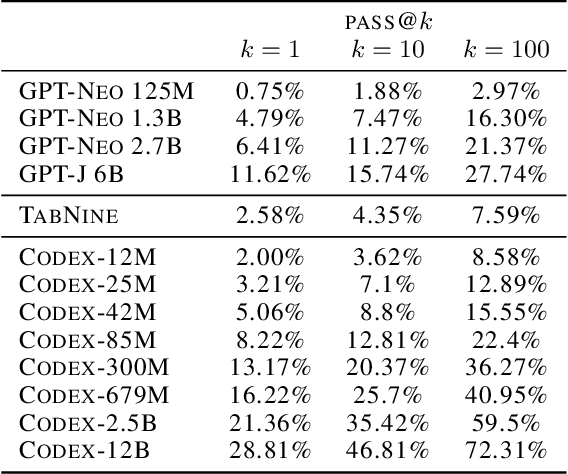
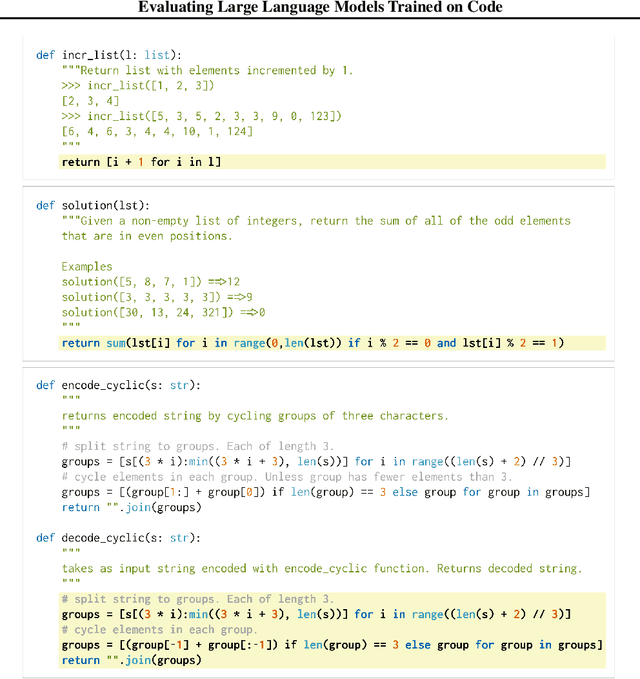
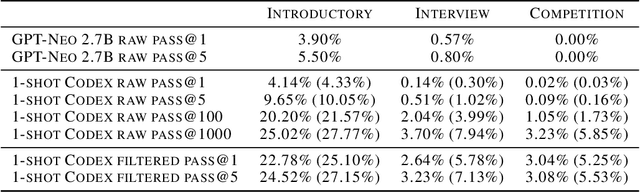
Abstract:We introduce Codex, a GPT language model fine-tuned on publicly available code from GitHub, and study its Python code-writing capabilities. A distinct production version of Codex powers GitHub Copilot. On HumanEval, a new evaluation set we release to measure functional correctness for synthesizing programs from docstrings, our model solves 28.8% of the problems, while GPT-3 solves 0% and GPT-J solves 11.4%. Furthermore, we find that repeated sampling from the model is a surprisingly effective strategy for producing working solutions to difficult prompts. Using this method, we solve 70.2% of our problems with 100 samples per problem. Careful investigation of our model reveals its limitations, including difficulty with docstrings describing long chains of operations and with binding operations to variables. Finally, we discuss the potential broader impacts of deploying powerful code generation technologies, covering safety, security, and economics.
Learning Dexterous In-Hand Manipulation
Jan 18, 2019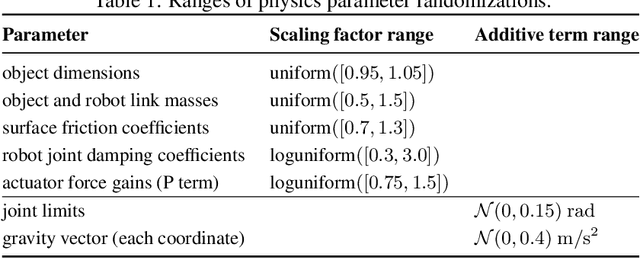
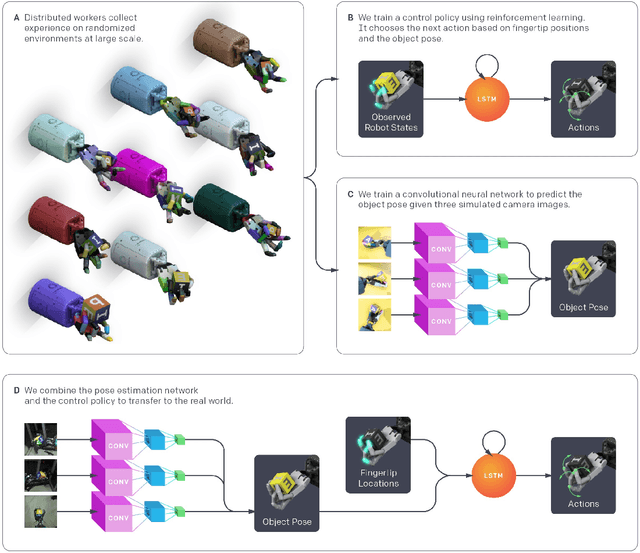
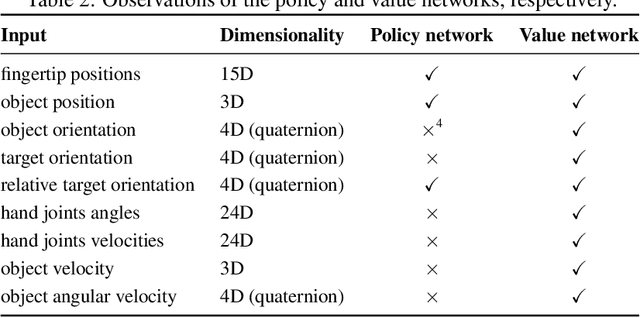
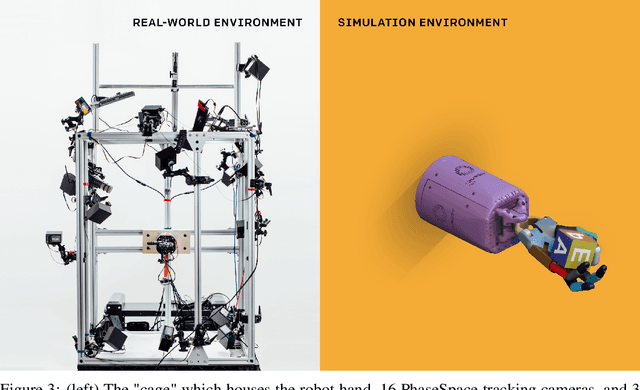
Abstract:We use reinforcement learning (RL) to learn dexterous in-hand manipulation policies which can perform vision-based object reorientation on a physical Shadow Dexterous Hand. The training is performed in a simulated environment in which we randomize many of the physical properties of the system like friction coefficients and an object's appearance. Our policies transfer to the physical robot despite being trained entirely in simulation. Our method does not rely on any human demonstrations, but many behaviors found in human manipulation emerge naturally, including finger gaiting, multi-finger coordination, and the controlled use of gravity. Our results were obtained using the same distributed RL system that was used to train OpenAI Five. We also include a video of our results: https://youtu.be/jwSbzNHGflM
Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning: Challenging Robotics Environments and Request for Research
Mar 10, 2018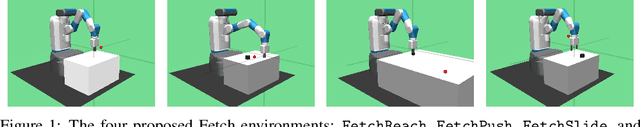
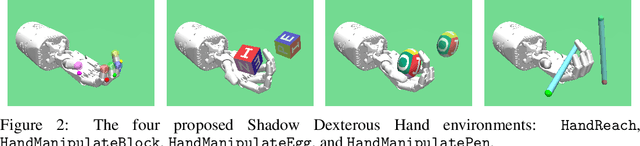
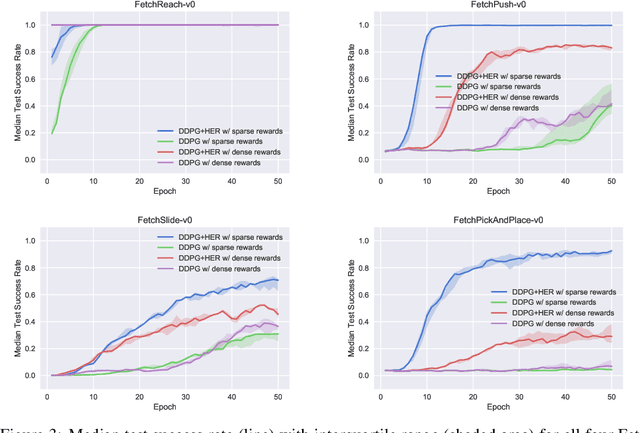
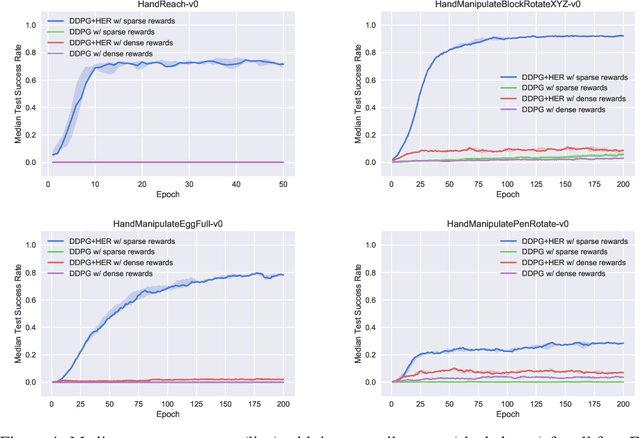
Abstract:The purpose of this technical report is two-fold. First of all, it introduces a suite of challenging continuous control tasks (integrated with OpenAI Gym) based on currently existing robotics hardware. The tasks include pushing, sliding and pick & place with a Fetch robotic arm as well as in-hand object manipulation with a Shadow Dexterous Hand. All tasks have sparse binary rewards and follow a Multi-Goal Reinforcement Learning (RL) framework in which an agent is told what to do using an additional input. The second part of the paper presents a set of concrete research ideas for improving RL algorithms, most of which are related to Multi-Goal RL and Hindsight Experience Replay.
Hindsight Experience Replay
Feb 23, 2018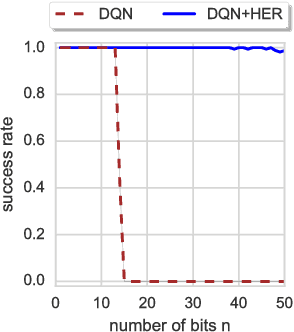
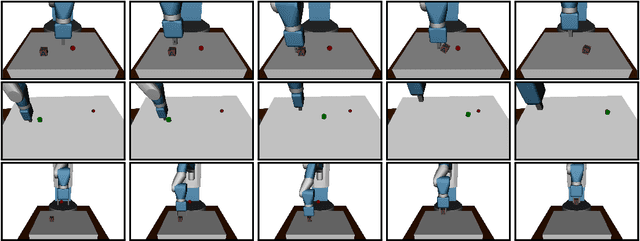
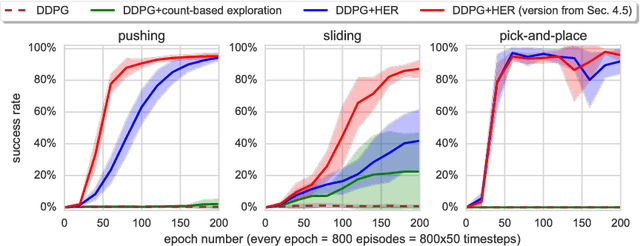
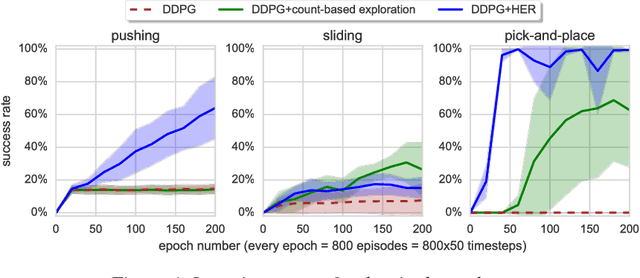
Abstract:Dealing with sparse rewards is one of the biggest challenges in Reinforcement Learning (RL). We present a novel technique called Hindsight Experience Replay which allows sample-efficient learning from rewards which are sparse and binary and therefore avoid the need for complicated reward engineering. It can be combined with an arbitrary off-policy RL algorithm and may be seen as a form of implicit curriculum. We demonstrate our approach on the task of manipulating objects with a robotic arm. In particular, we run experiments on three different tasks: pushing, sliding, and pick-and-place, in each case using only binary rewards indicating whether or not the task is completed. Our ablation studies show that Hindsight Experience Replay is a crucial ingredient which makes training possible in these challenging environments. We show that our policies trained on a physics simulation can be deployed on a physical robot and successfully complete the task.
Domain Randomization for Transferring Deep Neural Networks from Simulation to the Real World
Mar 20, 2017
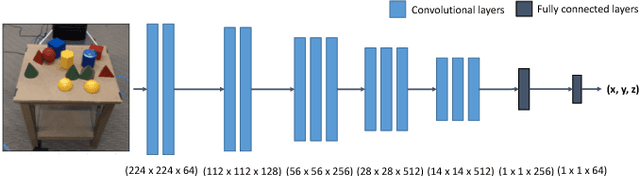
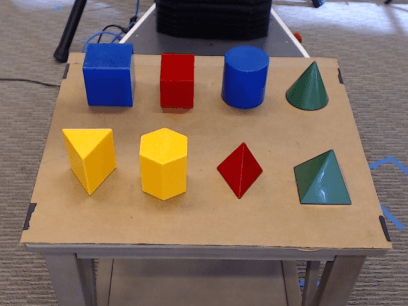
Abstract:Bridging the 'reality gap' that separates simulated robotics from experiments on hardware could accelerate robotic research through improved data availability. This paper explores domain randomization, a simple technique for training models on simulated images that transfer to real images by randomizing rendering in the simulator. With enough variability in the simulator, the real world may appear to the model as just another variation. We focus on the task of object localization, which is a stepping stone to general robotic manipulation skills. We find that it is possible to train a real-world object detector that is accurate to $1.5$cm and robust to distractors and partial occlusions using only data from a simulator with non-realistic random textures. To demonstrate the capabilities of our detectors, we show they can be used to perform grasping in a cluttered environment. To our knowledge, this is the first successful transfer of a deep neural network trained only on simulated RGB images (without pre-training on real images) to the real world for the purpose of robotic control.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge