Magic
Papers and Code
Magic-MM-Embedding: Towards Visual-Token-Efficient Universal Multimodal Embedding with MLLMs
Feb 05, 2026Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have shown immense promise in universal multimodal retrieval, which aims to find relevant items of various modalities for a given query. But their practical application is often hindered by the substantial computational cost incurred from processing a large number of tokens from visual inputs. In this paper, we propose Magic-MM-Embedding, a series of novel models that achieve both high efficiency and state-of-the-art performance in universal multimodal embedding. Our approach is built on two synergistic pillars: (1) a highly efficient MLLM architecture incorporating visual token compression to drastically reduce inference latency and memory footprint, and (2) a multi-stage progressive training strategy designed to not only recover but significantly boost performance. This coarse-to-fine training paradigm begins with extensive continue pretraining to restore multimodal understanding and generation capabilities, progresses to large-scale contrastive pretraining and hard negative mining to enhance discriminative power, and culminates in a task-aware fine-tuning stage guided by an MLLM-as-a-Judge for precise data curation. Comprehensive experiments show that our model outperforms existing methods by a large margin while being more inference-efficient.
Beyond Static Cropping: Layer-Adaptive Visual Localization and Decoding Enhancement
Feb 04, 2026Large Vision-Language Models (LVLMs) have advanced rapidly by aligning visual patches with the text embedding space, but a fixed visual-token budget forces images to be resized to a uniform pretraining resolution, often erasing fine-grained details and causing hallucinations via over-reliance on language priors. Recent attention-guided enhancement (e.g., cropping or region-focused attention allocation) alleviates this, yet it commonly hinges on a static "magic layer" empirically chosen on simple recognition benchmarks and thus may not transfer to complex reasoning tasks. In contrast to this static assumption, we propose a dynamic perspective on visual grounding. Through a layer-wise sensitivity analysis, we demonstrate that visual grounding is a dynamic process: while simple object recognition tasks rely on middle layers, complex visual search and reasoning tasks require visual information to be reactivated at deeper layers. Based on this observation, we introduce Visual Activation by Query (VAQ), a metric that identifies the layer whose attention map is most relevant to query-specific visual grounding by measuring attention sensitivity to the input query. Building on VAQ, we further propose LASER (Layer-adaptive Attention-guided Selective visual and decoding Enhancement for Reasoning), a training-free inference procedure that adaptively selects task-appropriate layers for visual localization and question answering. Experiments across diverse VQA benchmarks show that LASER significantly improves VQA accuracy across tasks with varying levels of complexity.
Causal Discovery for Cross-Sectional Data Based on Super-Structure and Divide-and-Conquer
Feb 03, 2026This paper tackles a critical bottleneck in Super-Structure-based divide-and-conquer causal discovery: the high computational cost of constructing accurate Super-Structures--particularly when conditional independence (CI) tests are expensive and domain knowledge is unavailable. We propose a novel, lightweight framework that relaxes the strict requirements on Super-Structure construction while preserving the algorithmic benefits of divide-and-conquer. By integrating weakly constrained Super-Structures with efficient graph partitioning and merging strategies, our approach substantially lowers CI test overhead without sacrificing accuracy. We instantiate the framework in a concrete causal discovery algorithm and rigorously evaluate its components on synthetic data. Comprehensive experiments on Gaussian Bayesian networks, including magic-NIAB, ECOLI70, and magic-IRRI, demonstrate that our method matches or closely approximates the structural accuracy of PC and FCI while drastically reducing the number of CI tests. Further validation on the real-world China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS) dataset confirms its practical applicability. Our results establish that accurate, scalable causal discovery is achievable even under minimal assumptions about the initial Super-Structure, opening new avenues for applying divide-and-conquer methods to large-scale, knowledge-scarce domains such as biomedical and social science research.
MAGIC: A Co-Evolving Attacker-Defender Adversarial Game for Robust LLM Safety
Feb 02, 2026Ensuring robust safety alignment is crucial for Large Language Models (LLMs), yet existing defenses often lag behind evolving adversarial attacks due to their \textbf{reliance on static, pre-collected data distributions}. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{MAGIC}, a novel multi-turn multi-agent reinforcement learning framework that formulates LLM safety alignment as an adversarial asymmetric game. Specifically, an attacker agent learns to iteratively rewrite original queries into deceptive prompts, while a defender agent simultaneously optimizes its policy to recognize and refuse such inputs. This dynamic process triggers a \textbf{co-evolution}, where the attacker's ever-changing strategies continuously uncover long-tail vulnerabilities, driving the defender to generalize to unseen attack patterns. Remarkably, we observe that the attacker, endowed with initial reasoning ability, evolves \textbf{novel, previously unseen combinatorial strategies} through iterative RL training, underscoring our method's substantial potential. Theoretically, we provide insights into a more robust game equilibrium and derive safety guarantees. Extensive experiments validate our framework's effectiveness, demonstrating superior defense success rates without compromising the helpfulness of the model. Our code is available at https://github.com/BattleWen/MAGIC.
MAGIC: Achieving Superior Model Merging via Magnitude Calibration
Dec 22, 2025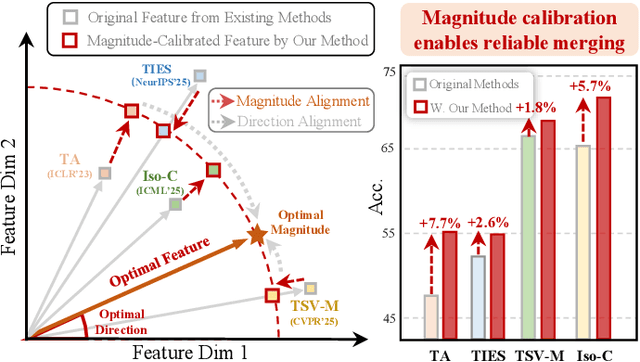
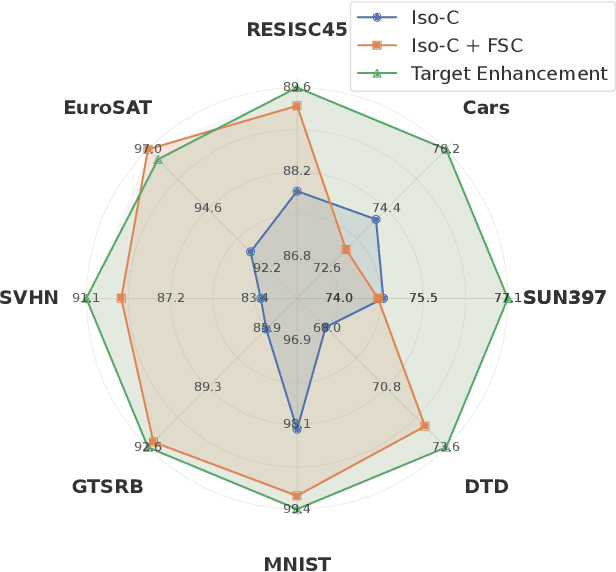
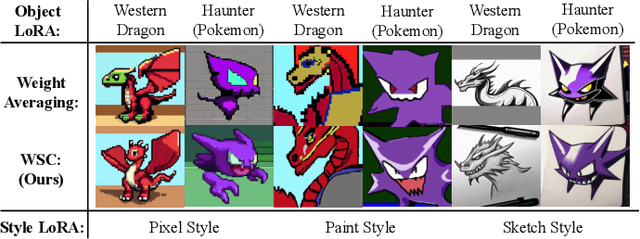
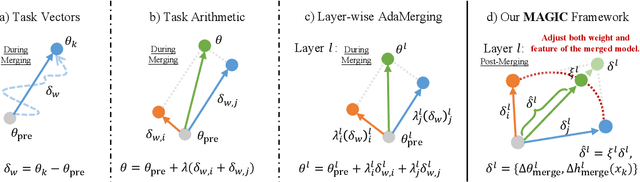
The proliferation of pre-trained models has given rise to a wide array of specialised, fine-tuned models. Model merging aims to merge the distinct capabilities of these specialised models into a unified model, requiring minimal or even no additional training. A core objective of model merging is to ensure the merged model retains the behavioural characteristics of the specialised models, typically achieved through feature alignment. We identify that features consist of two critical components: direction and magnitude. Prior research has predominantly focused on directional alignment, while the influence of magnitude remains largely neglected, despite its pronounced vulnerability to perturbations introduced by common merging operations (e.g., parameter fusion and sparsification). Such perturbations to magnitude inevitably lead to feature deviations in the merged model from the specialised models, resulting in subsequent performance degradation. To address this, we propose MAGnItude Calibration (MAGIC), a plug-and-play framework that rectifies layer-wise magnitudes in feature and weight spaces, with three variants. Specifically, our Feature Space Calibration (FSC) realigns the merged model's features using a small set of unlabelled data, while Weight Space Calibration (WSC) extends this calibration to the weight space without requiring additional data. Combining these yields Dual Space Calibration (DSC). Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that MAGIC consistently boosts performance across diverse Computer Vision tasks (+4.3% on eight datasets) and NLP tasks (+8.0% on Llama) without additional training. Our code is available at: https://github.com/lyymuwu/MAGIC
Physics of Language Models: Part 4.1, Architecture Design and the Magic of Canon Layers
Dec 19, 2025Understanding architectural differences in language models is challenging, especially at academic-scale pretraining (e.g., 1.3B parameters, 100B tokens), where results are often dominated by noise and randomness. To overcome this, we introduce controlled synthetic pretraining tasks that isolate and evaluate core model capabilities. Within this framework, we discover CANON LAYERS: lightweight architectural components -- named after the musical term "canon" -- that promote horizontal information flow across neighboring tokens. Canon layers compute weighted sums of nearby token representations and integrate seamlessly into Transformers, linear attention, state-space models, or any sequence architecture. We present 12 key results. This includes how Canon layers enhance reasoning depth (e.g., by $2\times$), reasoning breadth, knowledge manipulation, etc. They lift weak architectures like NoPE to match RoPE, and linear attention to rival SOTA linear models like Mamba2/GDN -- validated both through synthetic tasks and real-world academic-scale pretraining. This synthetic playground offers an economical, principled path to isolate core model capabilities often obscured at academic scales. Equipped with infinite high-quality data, it may even PREDICT how future architectures will behave as training pipelines improve -- e.g., through better data curation or RL-based post-training -- unlocking deeper reasoning and hierarchical inference.
MAGIC-Talk: Motion-aware Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation with Customizable Identity Control
Oct 26, 2025Audio-driven talking face generation has gained significant attention for applications in digital media and virtual avatars. While recent methods improve audio-lip synchronization, they often struggle with temporal consistency, identity preservation, and customization, especially in long video generation. To address these issues, we propose MAGIC-Talk, a one-shot diffusion-based framework for customizable and temporally stable talking face generation. MAGIC-Talk consists of ReferenceNet, which preserves identity and enables fine-grained facial editing via text prompts, and AnimateNet, which enhances motion coherence using structured motion priors. Unlike previous methods requiring multiple reference images or fine-tuning, MAGIC-Talk maintains identity from a single image while ensuring smooth transitions across frames. Additionally, a progressive latent fusion strategy is introduced to improve long-form video quality by reducing motion inconsistencies and flickering. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MAGIC-Talk outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, identity preservation, and synchronization accuracy, offering a robust solution for talking face generation.
What do AI-Generated Images Want?
Oct 23, 2025W.J.T. Mitchell's influential essay 'What do pictures want?' shifts the theoretical focus away from the interpretative act of understanding pictures and from the motivations of the humans who create them to the possibility that the picture itself is an entity with agency and wants. In this article, I reframe Mitchell's question in light of contemporary AI image generation tools to ask: what do AI-generated images want? Drawing from art historical discourse on the nature of abstraction, I argue that AI-generated images want specificity and concreteness because they are fundamentally abstract. Multimodal text-to-image models, which are the primary subject of this article, are based on the premise that text and image are interchangeable or exchangeable tokens and that there is a commensurability between them, at least as represented mathematically in data. The user pipeline that sees textual input become visual output, however, obscures this representational regress and makes it seem like one form transforms into the other -- as if by magic.
Reconquering Bell sampling on qudits: stabilizer learning and testing, quantum pseudorandomness bounds, and more
Oct 08, 2025

Bell sampling is a simple yet powerful tool based on measuring two copies of a quantum state in the Bell basis, and has found applications in a plethora of problems related to stabiliser states and measures of magic. However, it was not known how to generalise the procedure from qubits to $d$-level systems -- qudits -- for all dimensions $d > 2$ in a useful way. Indeed, a prior work of the authors (arXiv'24) showed that the natural extension of Bell sampling to arbitrary dimensions fails to provide meaningful information about the quantum states being measured. In this paper, we overcome the difficulties encountered in previous works and develop a useful generalisation of Bell sampling to qudits of all $d\geq 2$. At the heart of our primitive is a new unitary, based on Lagrange's four-square theorem, that maps four copies of any stabiliser state $|\mathcal{S}\rangle$ to four copies of its complex conjugate $|\mathcal{S}^\ast\rangle$ (up to some Pauli operator), which may be of independent interest. We then demonstrate the utility of our new Bell sampling technique by lifting several known results from qubits to qudits for any $d\geq 2$: 1. Learning stabiliser states in $O(n^3)$ time with $O(n)$ samples; 2. Solving the Hidden Stabiliser Group Problem in $\tilde{O}(n^3/\varepsilon)$ time with $\tilde{O}(n/\varepsilon)$ samples; 3. Testing whether $|\psi\rangle$ has stabiliser size at least $d^t$ or is $\varepsilon$-far from all such states in $\tilde{O}(n^3/\varepsilon)$ time with $\tilde{O}(n/\varepsilon)$ samples; 4. Clifford circuits with at most $n/2$ single-qudit non-Clifford gates cannot prepare pseudorandom states; 5. Testing whether $|\psi\rangle$ has stabiliser fidelity at least $1-\varepsilon_1$ or at most $1-\varepsilon_2$ with $O(d^2/\varepsilon_2)$ samples if $\varepsilon_1 = 0$ or $O(d^2/\varepsilon_2^2)$ samples if $\varepsilon_1 = O(d^{-2})$.
Where Do I 'Add the Egg'?: Exploring Agency and Ownership in AI Creative Co-Writing Systems
Sep 18, 2025AI co-writing systems challenge long held ideals about agency and ownership in the creative process, thereby hindering widespread adoption. In order to address this, we investigate conceptions of agency and ownership in AI creative co-writing. Drawing on insights from a review of commercial systems, we developed three co-writing systems with identical functionality but distinct interface metaphors: agentic, tool-like, and magical. Through interviews with professional and non-professional writers (n = 18), we explored how these metaphors influenced participants' sense of control and authorship. Our analysis resulted in a taxonomy of agency and ownership subtypes and underscore how tool-like metaphors shift writers' expected points of control while agentic metaphors foreground conceptual contributions. We argue that interface metaphors not only guide expectations of control but also frame conceptions of authorship. We conclude with recommendations for the design of AI co-writing systems, emphasizing how metaphor shapes user experience and creative practice.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge