Zhenhua Feng
Revisiting Generative Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Based on Human Cognitive Laws
Oct 30, 2025Abstract:Existing infrared and visible image fusion methods often face the dilemma of balancing modal information. Generative fusion methods reconstruct fused images by learning from data distributions, but their generative capabilities remain limited. Moreover, the lack of interpretability in modal information selection further affects the reliability and consistency of fusion results in complex scenarios. This manuscript revisits the essence of generative image fusion under the inspiration of human cognitive laws and proposes a novel infrared and visible image fusion method, termed HCLFuse. First, HCLFuse investigates the quantification theory of information mapping in unsupervised fusion networks, which leads to the design of a multi-scale mask-regulated variational bottleneck encoder. This encoder applies posterior probability modeling and information decomposition to extract accurate and concise low-level modal information, thereby supporting the generation of high-fidelity structural details. Furthermore, the probabilistic generative capability of the diffusion model is integrated with physical laws, forming a time-varying physical guidance mechanism that adaptively regulates the generation process at different stages, thereby enhancing the ability of the model to perceive the intrinsic structure of data and reducing dependence on data quality. Experimental results show that the proposed method achieves state-of-the-art fusion performance in qualitative and quantitative evaluations across multiple datasets and significantly improves semantic segmentation metrics. This fully demonstrates the advantages of this generative image fusion method, drawing inspiration from human cognition, in enhancing structural consistency and detail quality.
MAGIC-Talk: Motion-aware Audio-Driven Talking Face Generation with Customizable Identity Control
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Audio-driven talking face generation has gained significant attention for applications in digital media and virtual avatars. While recent methods improve audio-lip synchronization, they often struggle with temporal consistency, identity preservation, and customization, especially in long video generation. To address these issues, we propose MAGIC-Talk, a one-shot diffusion-based framework for customizable and temporally stable talking face generation. MAGIC-Talk consists of ReferenceNet, which preserves identity and enables fine-grained facial editing via text prompts, and AnimateNet, which enhances motion coherence using structured motion priors. Unlike previous methods requiring multiple reference images or fine-tuning, MAGIC-Talk maintains identity from a single image while ensuring smooth transitions across frames. Additionally, a progressive latent fusion strategy is introduced to improve long-form video quality by reducing motion inconsistencies and flickering. Extensive experiments demonstrate that MAGIC-Talk outperforms state-of-the-art methods in visual quality, identity preservation, and synchronization accuracy, offering a robust solution for talking face generation.
PropVG: End-to-End Proposal-Driven Visual Grounding with Multi-Granularity Discrimination
Sep 05, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in visual grounding have largely shifted away from traditional proposal-based two-stage frameworks due to their inefficiency and high computational complexity, favoring end-to-end direct reference paradigms. However, these methods rely exclusively on the referred target for supervision, overlooking the potential benefits of prominent prospective targets. Moreover, existing approaches often fail to incorporate multi-granularity discrimination, which is crucial for robust object identification in complex scenarios. To address these limitations, we propose PropVG, an end-to-end proposal-based framework that, to the best of our knowledge, is the first to seamlessly integrate foreground object proposal generation with referential object comprehension without requiring additional detectors. Furthermore, we introduce a Contrastive-based Refer Scoring (CRS) module, which employs contrastive learning at both sentence and word levels to enhance the capability in understanding and distinguishing referred objects. Additionally, we design a Multi-granularity Target Discrimination (MTD) module that fuses object- and semantic-level information to improve the recognition of absent targets. Extensive experiments on gRefCOCO (GREC/GRES), Ref-ZOM, R-RefCOCO, and RefCOCO (REC/RES) benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of PropVG. The codes and models are available at https://github.com/Dmmm1997/PropVG.
DASViT: Differentiable Architecture Search for Vision Transformer
Jul 17, 2025Abstract:Designing effective neural networks is a cornerstone of deep learning, and Neural Architecture Search (NAS) has emerged as a powerful tool for automating this process. Among the existing NAS approaches, Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS) has gained prominence for its efficiency and ease of use, inspiring numerous advancements. Since the rise of Vision Transformers (ViT), researchers have applied NAS to explore ViT architectures, often focusing on macro-level search spaces and relying on discrete methods like evolutionary algorithms. While these methods ensure reliability, they face challenges in discovering innovative architectural designs, demand extensive computational resources, and are time-intensive. To address these limitations, we introduce Differentiable Architecture Search for Vision Transformer (DASViT), which bridges the gap in differentiable search for ViTs and uncovers novel designs. Experiments show that DASViT delivers architectures that break traditional Transformer encoder designs, outperform ViT-B/16 on multiple datasets, and achieve superior efficiency with fewer parameters and FLOPs.
Offline Reinforcement Learning using Human-Aligned Reward Labeling for Autonomous Emergency Braking in Occluded Pedestrian Crossing
Apr 11, 2025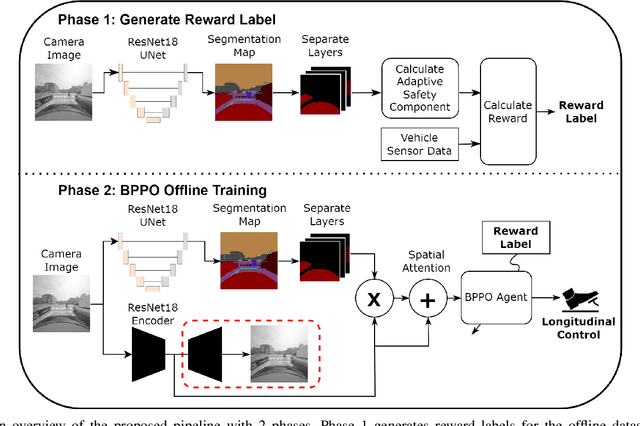
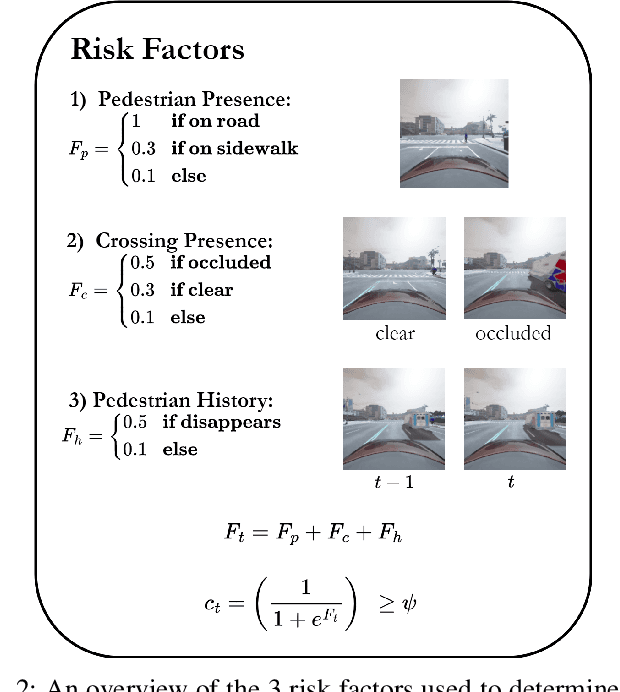
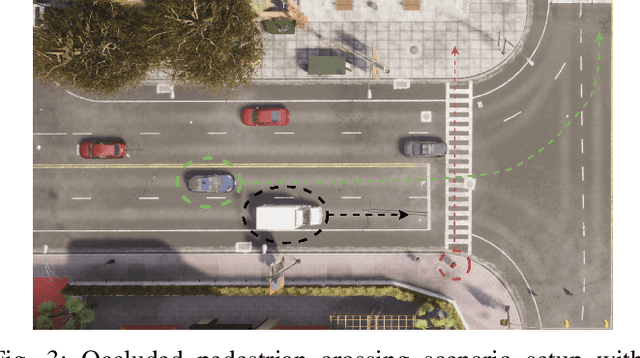
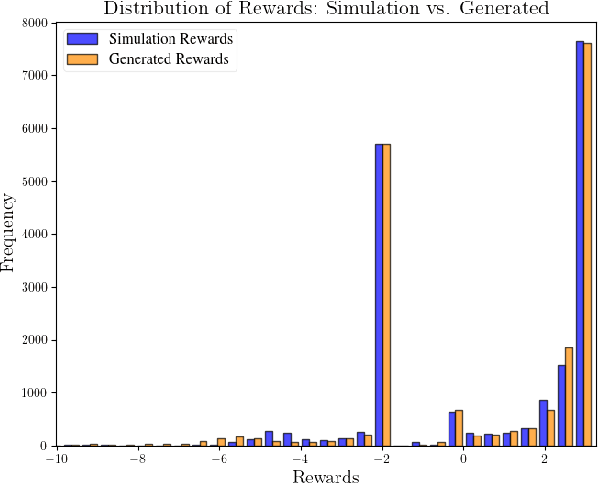
Abstract:Effective leveraging of real-world driving datasets is crucial for enhancing the training of autonomous driving systems. While Offline Reinforcement Learning enables the training of autonomous vehicles using such data, most available datasets lack meaningful reward labels. Reward labeling is essential as it provides feedback for the learning algorithm to distinguish between desirable and undesirable behaviors, thereby improving policy performance. This paper presents a novel pipeline for generating human-aligned reward labels. The proposed approach addresses the challenge of absent reward signals in real-world datasets by generating labels that reflect human judgment and safety considerations. The pipeline incorporates an adaptive safety component, activated by analyzing semantic segmentation maps, allowing the autonomous vehicle to prioritize safety over efficiency in potential collision scenarios. The proposed pipeline is applied to an occluded pedestrian crossing scenario with varying levels of pedestrian traffic, using synthetic and simulation data. The results indicate that the generated reward labels closely match the simulation reward labels. When used to train the driving policy using Behavior Proximal Policy Optimisation, the results are competitive with other baselines. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our method in producing reliable and human-aligned reward signals, facilitating the training of autonomous driving systems through Reinforcement Learning outside of simulation environments and in alignment with human values.
One Model for ALL: Low-Level Task Interaction Is a Key to Task-Agnostic Image Fusion
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Advanced image fusion methods mostly prioritise high-level missions, where task interaction struggles with semantic gaps, requiring complex bridging mechanisms. In contrast, we propose to leverage low-level vision tasks from digital photography fusion, allowing for effective feature interaction through pixel-level supervision. This new paradigm provides strong guidance for unsupervised multimodal fusion without relying on abstract semantics, enhancing task-shared feature learning for broader applicability. Owning to the hybrid image features and enhanced universal representations, the proposed GIFNet supports diverse fusion tasks, achieving high performance across both seen and unseen scenarios with a single model. Uniquely, experimental results reveal that our framework also supports single-modality enhancement, offering superior flexibility for practical applications. Our code will be available at https://github.com/AWCXV/GIFNet.
DGFM: Full Body Dance Generation Driven by Music Foundation Models
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:In music-driven dance motion generation, most existing methods use hand-crafted features and neglect that music foundation models have profoundly impacted cross-modal content generation. To bridge this gap, we propose a diffusion-based method that generates dance movements conditioned on text and music. Our approach extracts music features by combining high-level features obtained by music foundation model with hand-crafted features, thereby enhancing the quality of generated dance sequences. This method effectively leverages the advantages of high-level semantic information and low-level temporal details to improve the model's capability in music feature understanding. To show the merits of the proposed method, we compare it with four music foundation models and two sets of hand-crafted music features. The results demonstrate that our method obtains the most realistic dance sequences and achieves the best match with the input music.
Learning Structure-Supporting Dependencies via Keypoint Interactive Transformer for General Mammal Pose Estimation
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:General mammal pose estimation is an important and challenging task in computer vision, which is essential for understanding mammal behaviour in real-world applications. However, existing studies are at their preliminary research stage, which focus on addressing the problem for only a few specific mammal species. In principle, from specific to general mammal pose estimation, the biggest issue is how to address the huge appearance and pose variances for different species. We argue that given appearance context, instance-level prior and the structural relation among keypoints can serve as complementary evidence. To this end, we propose a Keypoint Interactive Transformer (KIT) to learn instance-level structure-supporting dependencies for general mammal pose estimation. Specifically, our KITPose consists of two coupled components. The first component is to extract keypoint features and generate body part prompts. The features are supervised by a dedicated generalised heatmap regression loss (GHRL). Instead of introducing external visual/text prompts, we devise keypoints clustering to generate body part biases, aligning them with image context to generate corresponding instance-level prompts. Second, we propose a novel interactive transformer that takes feature slices as input tokens without performing spatial splitting. In addition, to enhance the capability of the KIT model, we design an adaptive weight strategy to address the imbalance issue among different keypoints.
GCDance: Genre-Controlled 3D Full Body Dance Generation Driven By Music
Feb 25, 2025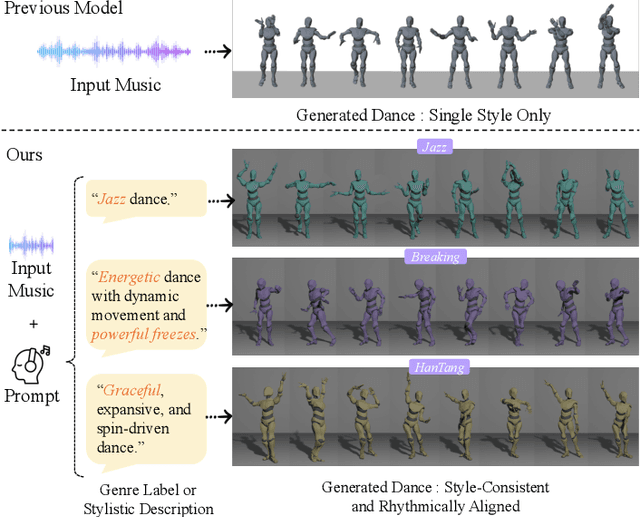
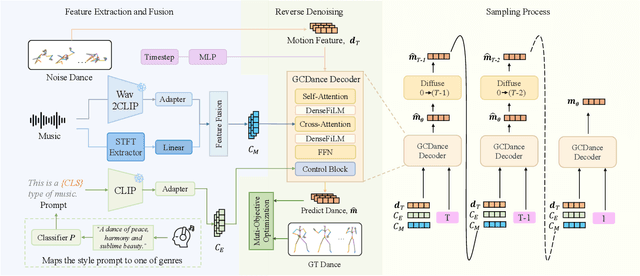
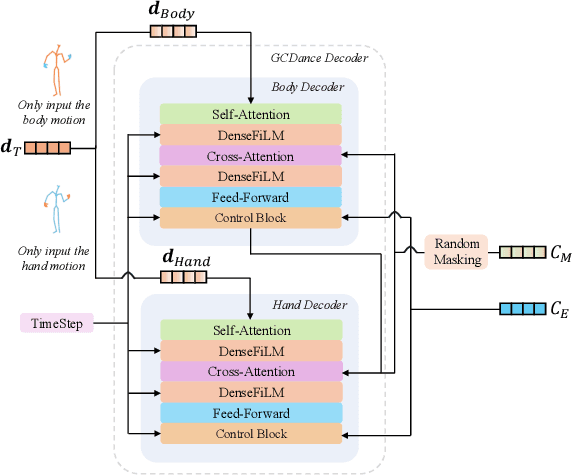
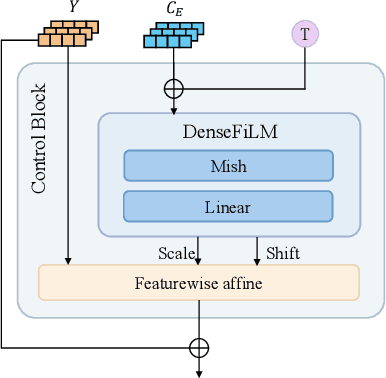
Abstract:Generating high-quality full-body dance sequences from music is a challenging task as it requires strict adherence to genre-specific choreography. Moreover, the generated sequences must be both physically realistic and precisely synchronized with the beats and rhythm of the music. To overcome these challenges, we propose GCDance, a classifier-free diffusion framework for generating genre-specific dance motions conditioned on both music and textual prompts. Specifically, our approach extracts music features by combining high-level pre-trained music foundation model features with hand-crafted features for multi-granularity feature fusion. To achieve genre controllability, we leverage CLIP to efficiently embed genre-based textual prompt representations at each time step within our dance generation pipeline. Our GCDance framework can generate diverse dance styles from the same piece of music while ensuring coherence with the rhythm and melody of the music. Extensive experimental results obtained on the FineDance dataset demonstrate that GCDance significantly outperforms the existing state-of-the-art approaches, which also achieve competitive results on the AIST++ dataset. Our ablation and inference time analysis demonstrate that GCDance provides an effective solution for high-quality music-driven dance generation.
PortraitTalk: Towards Customizable One-Shot Audio-to-Talking Face Generation
Dec 10, 2024



Abstract:Audio-driven talking face generation is a challenging task in digital communication. Despite significant progress in the area, most existing methods concentrate on audio-lip synchronization, often overlooking aspects such as visual quality, customization, and generalization that are crucial to producing realistic talking faces. To address these limitations, we introduce a novel, customizable one-shot audio-driven talking face generation framework, named PortraitTalk. Our proposed method utilizes a latent diffusion framework consisting of two main components: IdentityNet and AnimateNet. IdentityNet is designed to preserve identity features consistently across the generated video frames, while AnimateNet aims to enhance temporal coherence and motion consistency. This framework also integrates an audio input with the reference images, thereby reducing the reliance on reference-style videos prevalent in existing approaches. A key innovation of PortraitTalk is the incorporation of text prompts through decoupled cross-attention mechanisms, which significantly expands creative control over the generated videos. Through extensive experiments, including a newly developed evaluation metric, our model demonstrates superior performance over the state-of-the-art methods, setting a new standard for the generation of customizable realistic talking faces suitable for real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge