Xiao-Jun Wu
Jiangnan University, China
Wasserstein-Aligned Hyperbolic Multi-View Clustering
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Multi-view clustering (MVC) aims to uncover the latent structure of multi-view data by learning view-common and view-specific information. Although recent studies have explored hyperbolic representations for better tackling the representation gap between different views, they focus primarily on instance-level alignment and neglect global semantic consistency, rendering them vulnerable to view-specific information (\textit{e.g.}, noise and cross-view discrepancies). To this end, this paper proposes a novel Wasserstein-Aligned Hyperbolic (WAH) framework for multi-view clustering. Specifically, our method exploits a view-specific hyperbolic encoder for each view to embed features into the Lorentz manifold for hierarchical semantic modeling. Whereafter, a global semantic loss based on the hyperbolic sliced-Wasserstein distance is introduced to align manifold distributions across views. This is followed by soft cluster assignments to encourage cross-view semantic consistency. Extensive experiments on multiple benchmarking datasets show that our method can achieve SOTA clustering performance.
MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning: Datasets, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Outlook
Sep 17, 2025
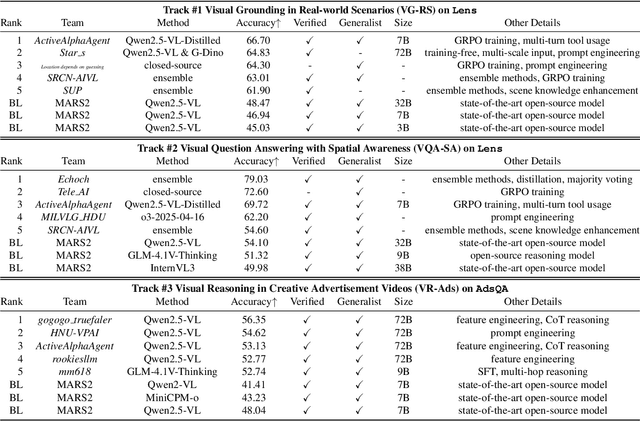

Abstract:This paper reviews the MARS2 2025 Challenge on Multimodal Reasoning. We aim to bring together different approaches in multimodal machine learning and LLMs via a large benchmark. We hope it better allows researchers to follow the state-of-the-art in this very dynamic area. Meanwhile, a growing number of testbeds have boosted the evolution of general-purpose large language models. Thus, this year's MARS2 focuses on real-world and specialized scenarios to broaden the multimodal reasoning applications of MLLMs. Our organizing team released two tailored datasets Lens and AdsQA as test sets, which support general reasoning in 12 daily scenarios and domain-specific reasoning in advertisement videos, respectively. We evaluated 40+ baselines that include both generalist MLLMs and task-specific models, and opened up three competition tracks, i.e., Visual Grounding in Real-world Scenarios (VG-RS), Visual Question Answering with Spatial Awareness (VQA-SA), and Visual Reasoning in Creative Advertisement Videos (VR-Ads). Finally, 76 teams from the renowned academic and industrial institutions have registered and 40+ valid submissions (out of 1200+) have been included in our ranking lists. Our datasets, code sets (40+ baselines and 15+ participants' methods), and rankings are publicly available on the MARS2 workshop website and our GitHub organization page https://github.com/mars2workshop/, where our updates and announcements of upcoming events will be continuously provided.
Riemannian Batch Normalization: A Gyro Approach
Sep 08, 2025Abstract:Normalization layers are crucial for deep learning, but their Euclidean formulations are inadequate for data on manifolds. On the other hand, many Riemannian manifolds in machine learning admit gyro-structures, enabling principled extensions of Euclidean neural networks to non-Euclidean domains. Inspired by this, we introduce GyroBN, a principled Riemannian batch normalization framework for gyrogroups. We establish two necessary conditions, namely \emph{pseudo-reduction} and \emph{gyroisometric gyrations}, that guarantee GyroBN with theoretical control over sample statistics, and show that these conditions hold for all known gyrogroups in machine learning. Our framework also incorporates several existing Riemannian normalization methods as special cases. We further instantiate GyroBN on seven representative geometries, including the Grassmannian, five constant curvature spaces, and the correlation manifold, and derive novel gyro and Riemannian structures to enable these instantiations. Experiments across these geometries demonstrate the effectiveness of GyroBN. The code is available at https://github.com/GitZH-Chen/GyroBN.git.
Uncertainty-aware Cross-training for Semi-supervised Medical Image Segmentation
Aug 12, 2025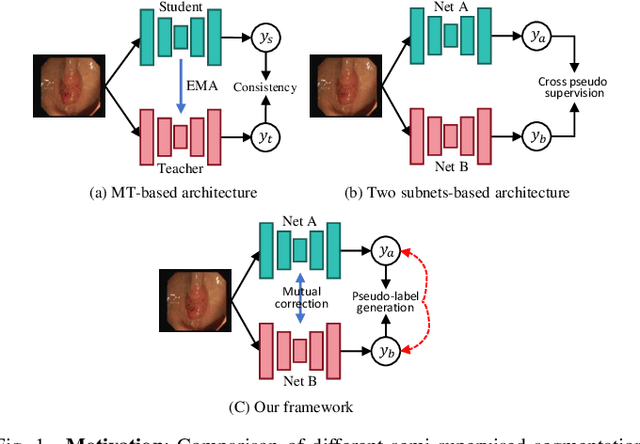
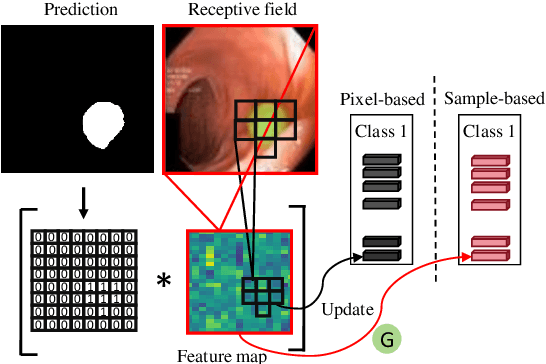
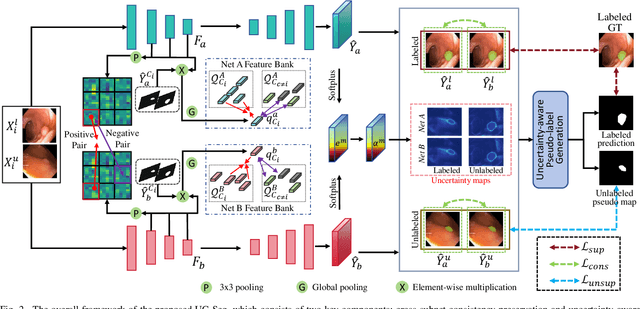
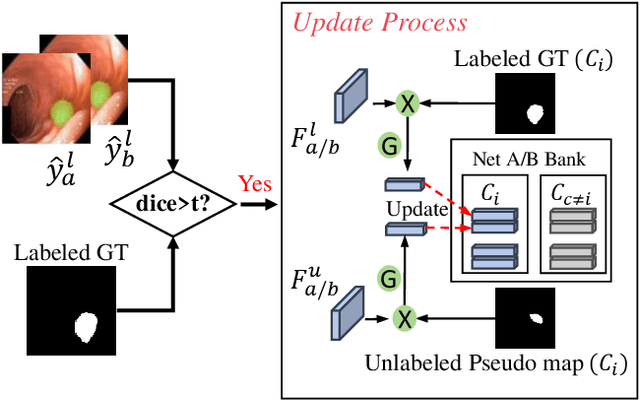
Abstract:Semi-supervised learning has gained considerable popularity in medical image segmentation tasks due to its capability to reduce reliance on expert-examined annotations. Several mean-teacher (MT) based semi-supervised methods utilize consistency regularization to effectively leverage valuable information from unlabeled data. However, these methods often heavily rely on the student model and overlook the potential impact of cognitive biases within the model. Furthermore, some methods employ co-training using pseudo-labels derived from different inputs, yet generating high-confidence pseudo-labels from perturbed inputs during training remains a significant challenge. In this paper, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Cross-training framework for semi-supervised medical image Segmentation (UC-Seg). Our UC-Seg framework incorporates two distinct subnets to effectively explore and leverage the correlation between them, thereby mitigating cognitive biases within the model. Specifically, we present a Cross-subnet Consistency Preservation (CCP) strategy to enhance feature representation capability and ensure feature consistency across the two subnets. This strategy enables each subnet to correct its own biases and learn shared semantics from both labeled and unlabeled data. Additionally, we propose an Uncertainty-aware Pseudo-label Generation (UPG) component that leverages segmentation results and corresponding uncertainty maps from both subnets to generate high-confidence pseudo-labels. We extensively evaluate the proposed UC-Seg on various medical image segmentation tasks involving different modality images, such as MRI, CT, ultrasound, colonoscopy, and so on. The results demonstrate that our method achieves superior segmentation accuracy and generalization performance compared to other state-of-the-art semi-supervised methods. Our code will be released at https://github.com/taozh2017/UCSeg.
GrFormer: A Novel Transformer on Grassmann Manifold for Infrared and Visible Image Fusion
Jun 17, 2025Abstract:In the field of image fusion, promising progress has been made by modeling data from different modalities as linear subspaces. However, in practice, the source images are often located in a non-Euclidean space, where the Euclidean methods usually cannot encapsulate the intrinsic topological structure. Typically, the inner product performed in the Euclidean space calculates the algebraic similarity rather than the semantic similarity, which results in undesired attention output and a decrease in fusion performance. While the balance of low-level details and high-level semantics should be considered in infrared and visible image fusion task. To address this issue, in this paper, we propose a novel attention mechanism based on Grassmann manifold for infrared and visible image fusion (GrFormer). Specifically, our method constructs a low-rank subspace mapping through projection constraints on the Grassmann manifold, compressing attention features into subspaces of varying rank levels. This forces the features to decouple into high-frequency details (local low-rank) and low-frequency semantics (global low-rank), thereby achieving multi-scale semantic fusion. Additionally, to effectively integrate the significant information, we develop a cross-modal fusion strategy (CMS) based on a covariance mask to maximise the complementary properties between different modalities and to suppress the features with high correlation, which are deemed redundant. The experimental results demonstrate that our network outperforms SOTA methods both qualitatively and quantitatively on multiple image fusion benchmarks. The codes are available at https://github.com/Shaoyun2023.
Learning to Normalize on the SPD Manifold under Bures-Wasserstein Geometry
Apr 01, 2025



Abstract:Covariance matrices have proven highly effective across many scientific fields. Since these matrices lie within the Symmetric Positive Definite (SPD) manifold - a Riemannian space with intrinsic non-Euclidean geometry, the primary challenge in representation learning is to respect this underlying geometric structure. Drawing inspiration from the success of Euclidean deep learning, researchers have developed neural networks on the SPD manifolds for more faithful covariance embedding learning. A notable advancement in this area is the implementation of Riemannian batch normalization (RBN), which has been shown to improve the performance of SPD network models. Nonetheless, the Riemannian metric beneath the existing RBN might fail to effectively deal with the ill-conditioned SPD matrices (ICSM), undermining the effectiveness of RBN. In contrast, the Bures-Wasserstein metric (BWM) demonstrates superior performance for ill-conditioning. In addition, the recently introduced Generalized BWM (GBWM) parameterizes the vanilla BWM via an SPD matrix, allowing for a more nuanced representation of vibrant geometries of the SPD manifold. Therefore, we propose a novel RBN algorithm based on the GBW geometry, incorporating a learnable metric parameter. Moreover, the deformation of GBWM by matrix power is also introduced to further enhance the representational capacity of GBWM-based RBN. Experimental results on different datasets validate the effectiveness of our proposed method.
OCCO: LVM-guided Infrared and Visible Image Fusion Framework based on Object-aware and Contextual COntrastive Learning
Mar 24, 2025Abstract:Image fusion is a crucial technique in the field of computer vision, and its goal is to generate high-quality fused images and improve the performance of downstream tasks. However, existing fusion methods struggle to balance these two factors. Achieving high quality in fused images may result in lower performance in downstream visual tasks, and vice versa. To address this drawback, a novel LVM (large vision model)-guided fusion framework with Object-aware and Contextual COntrastive learning is proposed, termed as OCCO. The pre-trained LVM is utilized to provide semantic guidance, allowing the network to focus solely on fusion tasks while emphasizing learning salient semantic features in form of contrastive learning. Additionally, a novel feature interaction fusion network is also designed to resolve information conflicts in fusion images caused by modality differences. By learning the distinction between positive samples and negative samples in the latent feature space (contextual space), the integrity of target information in fused image is improved, thereby benefiting downstream performance. Finally, compared with eight state-of-the-art methods on four datasets, the effectiveness of the proposed method is validated, and exceptional performance is also demonstrated on downstream visual task.
Learning a Unified Degradation-aware Representation Model for Multi-modal Image Fusion
Mar 10, 2025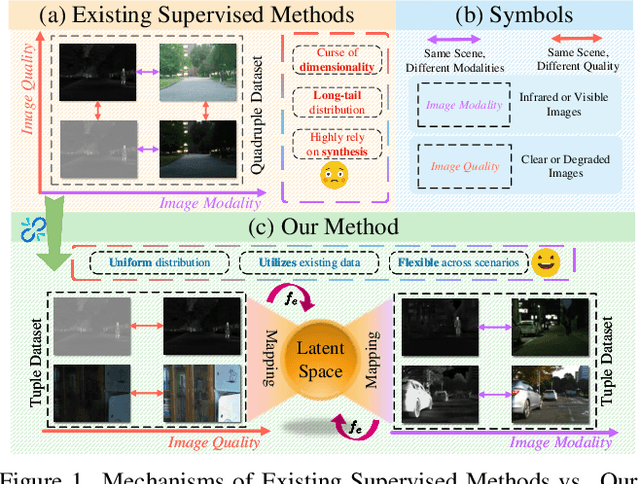
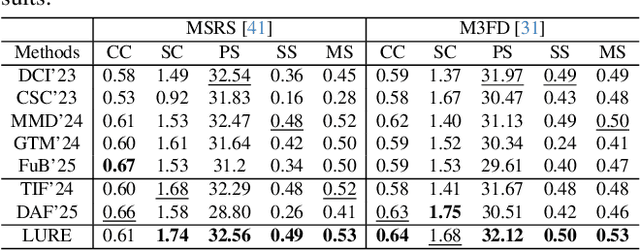
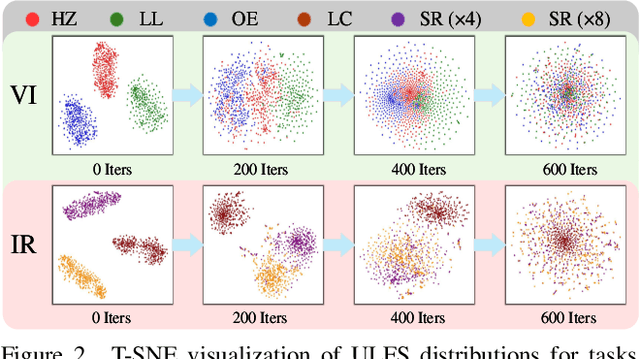
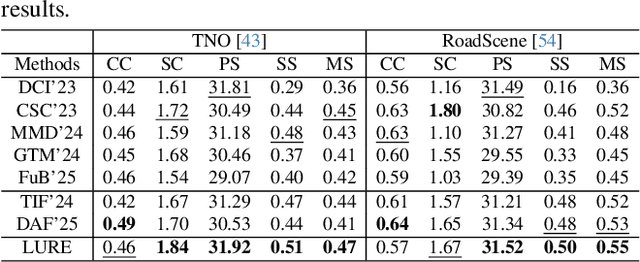
Abstract:All-in-One Degradation-Aware Fusion Models (ADFMs), a class of multi-modal image fusion models, address complex scenes by mitigating degradations from source images and generating high-quality fused images. Mainstream ADFMs often rely on highly synthetic multi-modal multi-quality images for supervision, limiting their effectiveness in cross-modal and rare degradation scenarios. The inherent relationship among these multi-modal, multi-quality images of the same scene provides explicit supervision for training, but also raises above problems. To address these limitations, we present LURE, a Learning-driven Unified Representation model for infrared and visible Image Fusion, which is degradation-aware. LURE decouples multi-modal multi-quality data at the data level and recouples this relationship in a unified latent feature space (ULFS) by proposing a novel unified loss. This decoupling circumvents data-level limitations of prior models and allows leveraging real-world restoration datasets for training high-quality degradation-aware models, sidestepping above issues. To enhance text-image interaction, we refine image-text interaction and residual structures via Text-Guided Attention (TGA) and an inner residual structure. These enhances text's spatial perception of images and preserve more visual details. Experiments show our method outperforms state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods across general fusion, degradation-aware fusion, and downstream tasks. The code will be publicly available.
UASTrack: A Unified Adaptive Selection Framework with Modality-Customization in Single Object Tracking
Feb 25, 2025



Abstract:Multi-modal tracking is essential in single-object tracking (SOT), as different sensor types contribute unique capabilities to overcome challenges caused by variations in object appearance. However, existing unified RGB-X trackers (X represents depth, event, or thermal modality) either rely on the task-specific training strategy for individual RGB-X image pairs or fail to address the critical importance of modality-adaptive perception in real-world applications. In this work, we propose UASTrack, a unified adaptive selection framework that facilitates both model and parameter unification, as well as adaptive modality discrimination across various multi-modal tracking tasks. To achieve modality-adaptive perception in joint RGB-X pairs, we design a Discriminative Auto-Selector (DAS) capable of identifying modality labels, thereby distinguishing the data distributions of auxiliary modalities. Furthermore, we propose a Task-Customized Optimization Adapter (TCOA) tailored to various modalities in the latent space. This strategy effectively filters noise redundancy and mitigates background interference based on the specific characteristics of each modality. Extensive comparisons conducted on five benchmarks including LasHeR, GTOT, RGBT234, VisEvent, and DepthTrack, covering RGB-T, RGB-E, and RGB-D tracking scenarios, demonstrate our innovative approach achieves comparative performance by introducing only additional training parameters of 1.87M and flops of 1.95G. The code will be available at https://github.com/wanghe/UASTrack.
Learning Structure-Supporting Dependencies via Keypoint Interactive Transformer for General Mammal Pose Estimation
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:General mammal pose estimation is an important and challenging task in computer vision, which is essential for understanding mammal behaviour in real-world applications. However, existing studies are at their preliminary research stage, which focus on addressing the problem for only a few specific mammal species. In principle, from specific to general mammal pose estimation, the biggest issue is how to address the huge appearance and pose variances for different species. We argue that given appearance context, instance-level prior and the structural relation among keypoints can serve as complementary evidence. To this end, we propose a Keypoint Interactive Transformer (KIT) to learn instance-level structure-supporting dependencies for general mammal pose estimation. Specifically, our KITPose consists of two coupled components. The first component is to extract keypoint features and generate body part prompts. The features are supervised by a dedicated generalised heatmap regression loss (GHRL). Instead of introducing external visual/text prompts, we devise keypoints clustering to generate body part biases, aligning them with image context to generate corresponding instance-level prompts. Second, we propose a novel interactive transformer that takes feature slices as input tokens without performing spatial splitting. In addition, to enhance the capability of the KIT model, we design an adaptive weight strategy to address the imbalance issue among different keypoints.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge