Vinal Asodia
Reinforcement Learning Enhancement Using Vector Semantic Representation and Symbolic Reasoning for Human-Centered Autonomous Emergency Braking
Feb 04, 2026Abstract:The problem with existing camera-based Deep Reinforcement Learning approaches is twofold: they rarely integrate high-level scene context into the feature representation, and they rely on rigid, fixed reward functions. To address these challenges, this paper proposes a novel pipeline that produces a neuro-symbolic feature representation that encompasses semantic, spatial, and shape information, as well as spatially boosted features of dynamic entities in the scene, with an emphasis on safety-critical road users. It also proposes a Soft First-Order Logic (SFOL) reward function that balances human values via a symbolic reasoning module. Here, semantic and spatial predicates are extracted from segmentation maps and applied to linguistic rules to obtain reward weights. Quantitative experiments in the CARLA simulation environment show that the proposed neuro-symbolic representation and SFOL reward function improved policy robustness and safety-related performance metrics compared to baseline representations and reward formulations across varying traffic densities and occlusion levels. The findings demonstrate that integrating holistic representations and soft reasoning into Reinforcement Learning can support more context-aware and value-aligned decision-making for autonomous driving.
Offline Reinforcement Learning using Human-Aligned Reward Labeling for Autonomous Emergency Braking in Occluded Pedestrian Crossing
Apr 11, 2025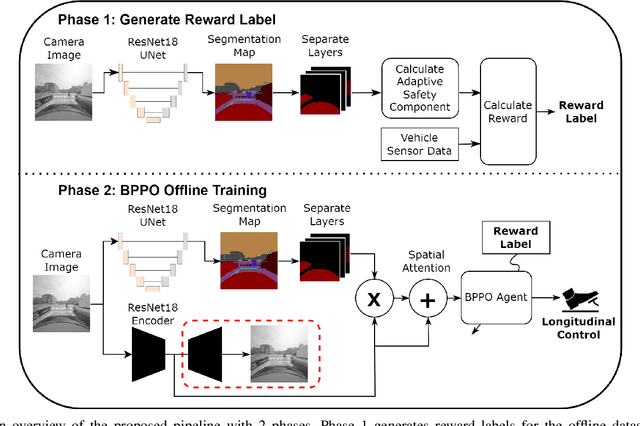
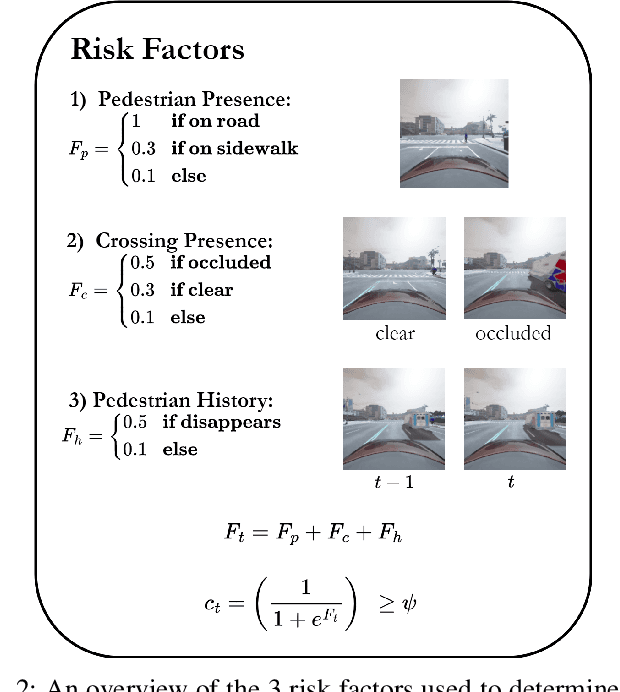
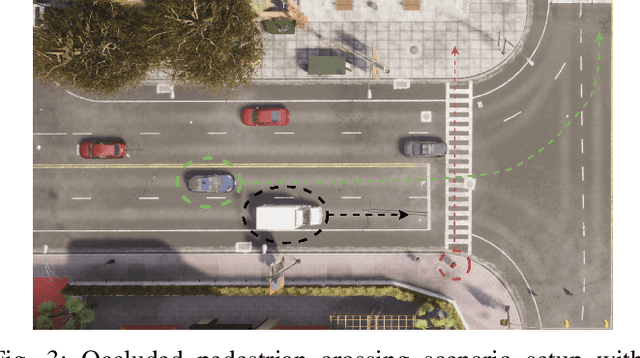
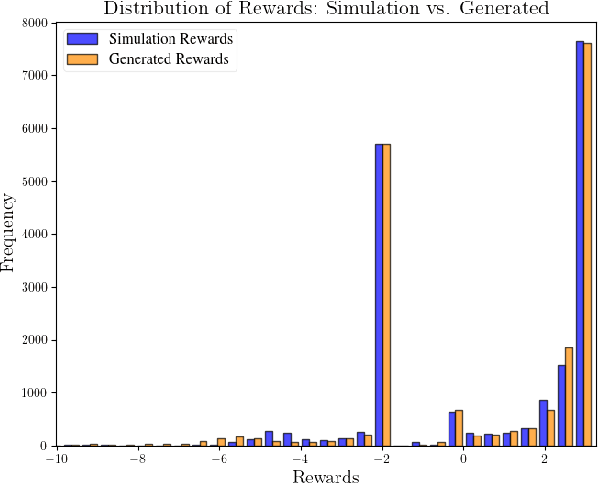
Abstract:Effective leveraging of real-world driving datasets is crucial for enhancing the training of autonomous driving systems. While Offline Reinforcement Learning enables the training of autonomous vehicles using such data, most available datasets lack meaningful reward labels. Reward labeling is essential as it provides feedback for the learning algorithm to distinguish between desirable and undesirable behaviors, thereby improving policy performance. This paper presents a novel pipeline for generating human-aligned reward labels. The proposed approach addresses the challenge of absent reward signals in real-world datasets by generating labels that reflect human judgment and safety considerations. The pipeline incorporates an adaptive safety component, activated by analyzing semantic segmentation maps, allowing the autonomous vehicle to prioritize safety over efficiency in potential collision scenarios. The proposed pipeline is applied to an occluded pedestrian crossing scenario with varying levels of pedestrian traffic, using synthetic and simulation data. The results indicate that the generated reward labels closely match the simulation reward labels. When used to train the driving policy using Behavior Proximal Policy Optimisation, the results are competitive with other baselines. This demonstrates the effectiveness of our method in producing reliable and human-aligned reward signals, facilitating the training of autonomous driving systems through Reinforcement Learning outside of simulation environments and in alignment with human values.
Behavioral Cloning Models Reality Check for Autonomous Driving
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:How effective are recent advancements in autonomous vehicle perception systems when applied to real-world autonomous vehicle control? While numerous vision-based autonomous vehicle systems have been trained and evaluated in simulated environments, there is a notable lack of real-world validation for these systems. This paper addresses this gap by presenting the real-world validation of state-of-the-art perception systems that utilize Behavior Cloning (BC) for lateral control, processing raw image data to predict steering commands. The dataset was collected using a scaled research vehicle and tested on various track setups. Experimental results demonstrate that these methods predict steering angles with low error margins in real-time, indicating promising potential for real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge