Mustafa Yildirim
Training Hybrid Neural Networks with Multimode Optical Nonlinearities Using Digital Twins
Jan 14, 2025



Abstract:The ability to train ever-larger neural networks brings artificial intelligence to the forefront of scientific and technical discoveries. However, their exponentially increasing size creates a proportionally greater demand for energy and computational hardware. Incorporating complex physical events in networks as fixed, efficient computation modules can address this demand by decreasing the complexity of trainable layers. Here, we utilize ultrashort pulse propagation in multimode fibers, which perform large-scale nonlinear transformations, for this purpose. Training the hybrid architecture is achieved through a neural model that differentiably approximates the optical system. The training algorithm updates the neural simulator and backpropagates the error signal over this proxy to optimize layers preceding the optical one. Our experimental results achieve state-of-the-art image classification accuracies and simulation fidelity. Moreover, the framework demonstrates exceptional resilience to experimental drifts. By integrating low-energy physical systems into neural networks, this approach enables scalable, energy-efficient AI models with significantly reduced computational demands.
Behavioral Cloning Models Reality Check for Autonomous Driving
Sep 11, 2024Abstract:How effective are recent advancements in autonomous vehicle perception systems when applied to real-world autonomous vehicle control? While numerous vision-based autonomous vehicle systems have been trained and evaluated in simulated environments, there is a notable lack of real-world validation for these systems. This paper addresses this gap by presenting the real-world validation of state-of-the-art perception systems that utilize Behavior Cloning (BC) for lateral control, processing raw image data to predict steering commands. The dataset was collected using a scaled research vehicle and tested on various track setups. Experimental results demonstrate that these methods predict steering angles with low error margins in real-time, indicating promising potential for real-world applications.
Optical Diffusion Models for Image Generation
Jul 15, 2024



Abstract:Diffusion models generate new samples by progressively decreasing the noise from the initially provided random distribution. This inference procedure generally utilizes a trained neural network numerous times to obtain the final output, creating significant latency and energy consumption on digital electronic hardware such as GPUs. In this study, we demonstrate that the propagation of a light beam through a semi-transparent medium can be programmed to implement a denoising diffusion model on image samples. This framework projects noisy image patterns through passive diffractive optical layers, which collectively only transmit the predicted noise term in the image. The optical transparent layers, which are trained with an online training approach, backpropagating the error to the analytical model of the system, are passive and kept the same across different steps of denoising. Hence this method enables high-speed image generation with minimal power consumption, benefiting from the bandwidth and energy efficiency of optical information processing.
HighwayLLM: Decision-Making and Navigation in Highway Driving with RL-Informed Language Model
May 22, 2024Abstract:Autonomous driving is a complex task which requires advanced decision making and control algorithms. Understanding the rationale behind the autonomous vehicles' decision is crucial to ensure their safe and effective operation on highway driving. This study presents a novel approach, HighwayLLM, which harnesses the reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) to predict the future waypoints for ego-vehicle's navigation. Our approach also utilizes a pre-trained Reinforcement Learning (RL) model to serve as a high-level planner, making decisions on appropriate meta-level actions. The HighwayLLM combines the output from the RL model and the current state information to make safe, collision-free, and explainable predictions for the next states, thereby constructing a trajectory for the ego-vehicle. Subsequently, a PID-based controller guides the vehicle to the waypoints predicted by the LLM agent. This integration of LLM with RL and PID enhances the decision-making process and provides interpretability for highway autonomous driving.
Human-Like Autonomous Driving on Dense Traffic
Oct 03, 2023Abstract:This paper proposes a imitation learning model for autonomous driving on highway traffic by mimicking human drivers' driving behaviours. The study utilizes the HighD traffic dataset, which is complex, high-dimensional, and diverse in vehicle variations. Imitation learning is an alternative solution to autonomous highway driving that reduces the sample complexity of learning a challenging task compared to reinforcement learning. However, imitation learning has limitations such as vulnerability to compounding errors in unseen states, poor generalization, and inability to predict outlier driver profiles. To address these issues, the paper proposes mixture density network behaviour cloning model to manage complex and non-linear relationships between inputs and outputs and make more informed decisions about the vehicle's actions. Additional improvement is using collision penalty based on the GAIL model. The paper includes a simulated driving test to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method based on real traffic scenarios and provides conclusions on its potential impact on autonomous driving.
Nonlinear Processing with Linear Optics
Jul 18, 2023Abstract:Deep neural networks have achieved remarkable breakthroughs by leveraging multiple layers of data processing to extract hidden representations, albeit at the cost of large electronic computing power. To enhance energy efficiency and speed, the optical implementation of neural networks aims to harness the advantages of optical bandwidth and the energy efficiency of optical interconnections. In the absence of low-power optical nonlinearities, the challenge in the implementation of multilayer optical networks lies in realizing multiple optical layers without resorting to electronic components. In this study, we present a novel framework that uses multiple scattering that is capable of synthesizing programmable linear and nonlinear transformations concurrently at low optical power by leveraging the nonlinear relationship between the scattering potential, represented by data, and the scattered field. Theoretical and experimental investigations show that repeating the data by multiple scattering enables non-linear optical computing at low power continuous wave light.
Towards Safe Autonomous Driving Policies using a Neuro-Symbolic Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach
Jul 13, 2023Abstract:The dynamic nature of driving environments and the presence of diverse road users pose significant challenges for decision-making in autonomous driving. Deep reinforcement learning (DRL) has emerged as a popular approach to tackle this problem. However, the application of existing DRL solutions is mainly confined to simulated environments due to safety concerns, impeding their deployment in real-world. To overcome this limitation, this paper introduces a novel neuro-symbolic model-free DRL approach, called DRL with Symbolic Logics (DRLSL) that combines the strengths of DRL (learning from experience) and symbolic first-order logics (knowledge-driven reasoning) to enable safe learning in real-time interactions of autonomous driving within real environments. This innovative approach provides a means to learn autonomous driving policies by actively engaging with the physical environment while ensuring safety. We have implemented the DRLSL framework in autonomous driving using the highD dataset and demonstrated that our method successfully avoids unsafe actions during both the training and testing phases. Furthermore, our results indicate that DRLSL achieves faster convergence during training and exhibits better generalizability to new driving scenarios compared to traditional DRL methods.
Forward-Forward Training of an Optical Neural Network
May 30, 2023



Abstract:Neural networks (NN) have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in various tasks, but their computation-intensive nature demands faster and more energy-efficient hardware implementations. Optics-based platforms, using technologies such as silicon photonics and spatial light modulators, offer promising avenues for achieving this goal. However, training multiple trainable layers in tandem with these physical systems poses challenges, as they are difficult to fully characterize and describe with differentiable functions, hindering the use of error backpropagation algorithm. The recently introduced Forward-Forward Algorithm (FFA) eliminates the need for perfect characterization of the learning system and shows promise for efficient training with large numbers of programmable parameters. The FFA does not require backpropagating an error signal to update the weights, rather the weights are updated by only sending information in one direction. The local loss function for each set of trainable weights enables low-power analog hardware implementations without resorting to metaheuristic algorithms or reinforcement learning. In this paper, we present an experiment utilizing multimode nonlinear wave propagation in an optical fiber demonstrating the feasibility of the FFA approach using an optical system. The results show that incorporating optical transforms in multilayer NN architectures trained with the FFA, can lead to performance improvements, even with a relatively small number of trainable weights. The proposed method offers a new path to the challenge of training optical NNs and provides insights into leveraging physical transformations for enhancing NN performance.
Prediction Based Decision Making for Autonomous Highway Driving
Sep 05, 2022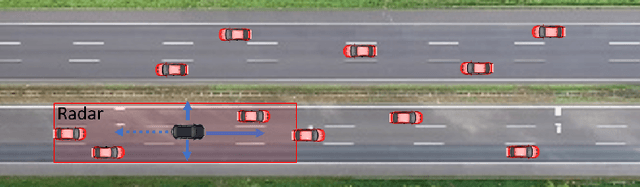
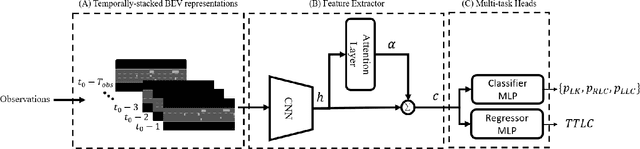
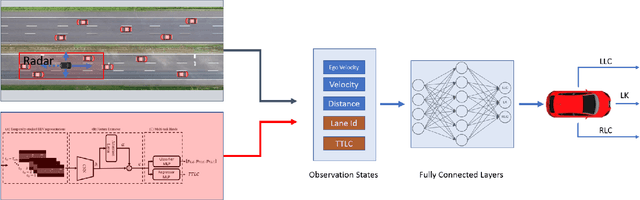

Abstract:Autonomous driving decision-making is a challenging task due to the inherent complexity and uncertainty in traffic. For example, adjacent vehicles may change their lane or overtake at any time to pass a slow vehicle or to help traffic flow. Anticipating the intention of surrounding vehicles, estimating their future states and integrating them into the decision-making process of an automated vehicle can enhance the reliability of autonomous driving in complex driving scenarios. This paper proposes a Prediction-based Deep Reinforcement Learning (PDRL) decision-making model that considers the manoeuvre intentions of surrounding vehicles in the decision-making process for highway driving. The model is trained using real traffic data and tested in various traffic conditions through a simulation platform. The results show that the proposed PDRL model improves the decision-making performance compared to a Deep Reinforcement Learning (DRL) model by decreasing collision numbers, resulting in safer driving.
Nonlinear Optical Data Transformer for Machine Learning
Aug 19, 2022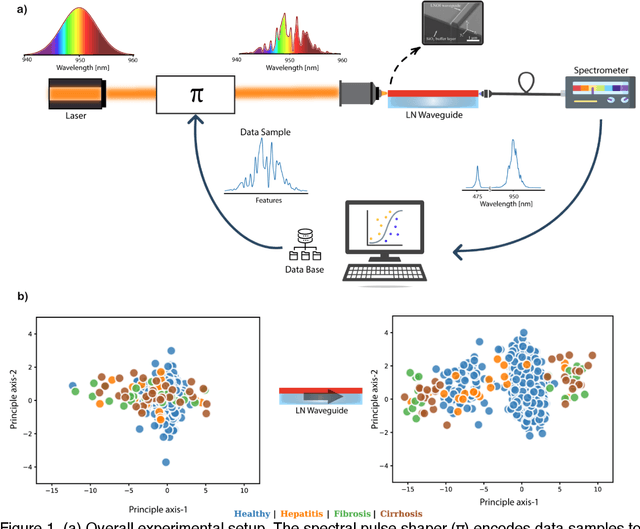
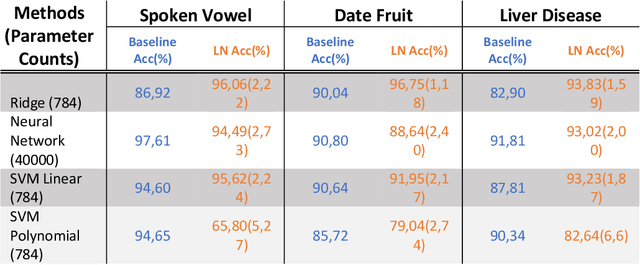

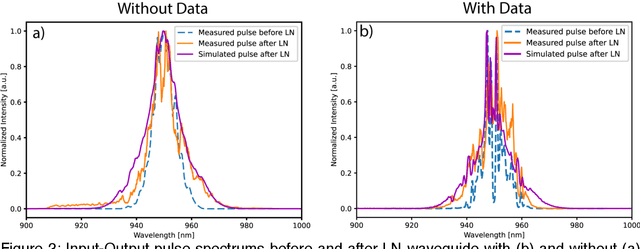
Abstract:Modern machine learning models use an ever-increasing number of parameters to train (175 billion parameters for GPT-3) with large datasets to obtain better performance. Bigger is better has been the norm. Optical computing has been reawakened as a potential solution to large-scale computing through optical accelerators that carry out linear operations while reducing electrical power. However, to achieve efficient computing with light, creating and controlling nonlinearity optically rather than electronically remains a challenge. This study explores a reservoir computing (RC) approach whereby a 14 mm long few-mode waveguide in LiNbO3 on insulator is used as a complex nonlinear optical processor. A dataset is encoded digitally on the spectrum of a femtosecond pulse which is then launched in the waveguide. The output spectrum depends nonlinearly on the input. We experimentally show that a simple digital linear classifier with 784 parameters using the output spectrum from the waveguide as input increased the classification accuracy of several databases compared to non-transformed data, approximately 10$\%$. In comparison, a deep digital neural network (NN) with 40000 parameters was necessary to achieve the same accuracy. Reducing the number of parameters by a factor of $\sim$50 illustrates that a compact optical RC approach can perform on par with a deep digital NN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge