Antibody Antigen Binding Prediction
Papers and Code
AbFlow : End-to-end Paratope-Centric Antibody Design by Interaction Enhanced Flow Matching
Feb 06, 2026Antigen-antibody binding is a critical process in the immune response. Although recent progress has advanced antibody design, current methods lack a generative framework for end-to-end modeling of full-atom antibody structures and struggle to fully exploit antigen-specific geometric information for optimizing local binding interfaces and global structures. To overcome these limitations, we introduce AbFlow, a flow-matching framework that leverages optimal transport to design full-atom antibodies end-to-end. AbFlow incorporates an extended velocity field network featuring an equivariant Surface Multi-channel Encoder, which uses surface-level antigen interaction data to refine the antibody structure, particularly the CDR-H3 region. Extensive experiments in paratoep-centric antibody design, multi-CDRs and full-atom antibody design, binding affinity optimization, and complex structure prediction show that AbFlow produces superior antigen-antibody complexes, especially at the contact interface, and markedly improves the binding affinity of generated antibodies.
DuaDeep-SeqAffinity: Dual-Stream Deep Learning Framework for Sequence-Only Antigen-Antibody Affinity Prediction
Dec 26, 2025


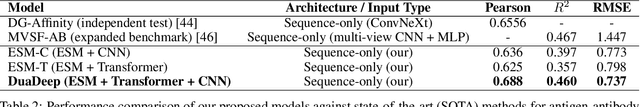
Predicting the binding affinity between antigens and antibodies is fundamental to drug discovery and vaccine development. Traditional computational approaches often rely on experimentally determined 3D structures, which are scarce and computationally expensive to obtain. This paper introduces DuaDeep-SeqAffinity, a novel sequence-only deep learning framework that predicts affinity scores solely from their amino acid sequences using a dual-stream hybrid architecture. Our approach leverages pre-trained ESM-2 protein language model embeddings, combining 1D Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) for local motif detection with Transformer encoders for global contextual representation. A subsequent fusion module integrates these multi-faceted features, which are then passed to a fully connected network for final score regression. Experimental results demonstrate that DuaDeep-SeqAffinity significantly outperforms individual architectural components and existing state-of-the-art (SOTA) methods. DuaDeep achieved a superior Pearson correlation of 0.688, an R^2 of 0.460, and a Root Mean Square Error (RMSE) of 0.737, surpassing single-branch variants ESM-CNN and ESM-Transformer. Notably, the model achieved an Area Under the Curve (AUC) of 0.890, outperforming sequence-only benchmarks and even surpassing structure-sequence hybrid models. These findings prove that high-fidelity sequence embeddings can capture essential binding patterns typically reserved for structural modeling. By eliminating the reliance on 3D structures, DuaDeep-SeqAffinity provides a highly scalable and efficient solution for high-throughput screening of vast sequence libraries, significantly accelerating the therapeutic discovery pipeline.
Tokenizing Loops of Antibodies
Sep 10, 2025The complementarity-determining regions of antibodies are loop structures that are key to their interactions with antigens, and of high importance to the design of novel biologics. Since the 1980s, categorizing the diversity of CDR structures into canonical clusters has enabled the identification of key structural motifs of antibodies. However, existing approaches have limited coverage and cannot be readily incorporated into protein foundation models. Here we introduce ImmunoGlobulin LOOp Tokenizer, Igloo, a multimodal antibody loop tokenizer that encodes backbone dihedral angles and sequence. Igloo is trained using a contrastive learning objective to map loops with similar backbone dihedral angles closer together in latent space. Igloo can efficiently retrieve the closest matching loop structures from a structural antibody database, outperforming existing methods on identifying similar H3 loops by 5.9\%. Igloo assigns tokens to all loops, addressing the limited coverage issue of canonical clusters, while retaining the ability to recover canonical loop conformations. To demonstrate the versatility of Igloo tokens, we show that they can be incorporated into protein language models with IglooLM and IglooALM. On predicting binding affinity of heavy chain variants, IglooLM outperforms the base protein language model on 8 out of 10 antibody-antigen targets. Additionally, it is on par with existing state-of-the-art sequence-based and multimodal protein language models, performing comparably to models with $7\times$ more parameters. IglooALM samples antibody loops which are diverse in sequence and more consistent in structure than state-of-the-art antibody inverse folding models. Igloo demonstrates the benefit of introducing multimodal tokens for antibody loops for encoding the diverse landscape of antibody loops, improving protein foundation models, and for antibody CDR design.
NbBench: Benchmarking Language Models for Comprehensive Nanobody Tasks
May 04, 2025Nanobodies, single-domain antibody fragments derived from camelid heavy-chain-only antibodies, exhibit unique advantages such as compact size, high stability, and strong binding affinity, making them valuable tools in therapeutics and diagnostics. While recent advances in pretrained protein and antibody language models (PPLMs and PALMs) have greatly enhanced biomolecular understanding, nanobody-specific modeling remains underexplored and lacks a unified benchmark. To address this gap, we introduce NbBench, the first comprehensive benchmark suite for nanobody representation learning. Spanning eight biologically meaningful tasks across nine curated datasets, NbBench encompasses structure annotation, binding prediction, and developability assessment. We systematically evaluate eleven representative models--including general-purpose protein LMs, antibody-specific LMs, and nanobody-specific LMs--in a frozen setting. Our analysis reveals that antibody language models excel in antigen-related tasks, while performance on regression tasks such as thermostability and affinity remains challenging across all models. Notably, no single model consistently outperforms others across all tasks. By standardizing datasets, task definitions, and evaluation protocols, NbBench offers a reproducible foundation for assessing and advancing nanobody modeling.
S$^2$ALM: Sequence-Structure Pre-trained Large Language Model for Comprehensive Antibody Representation Learning
Nov 20, 2024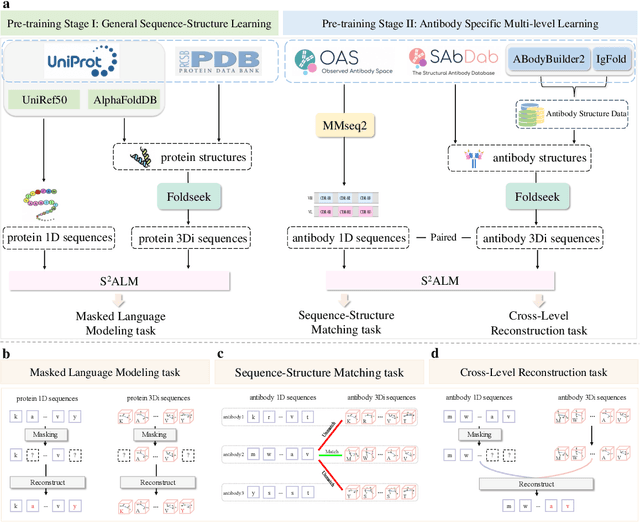
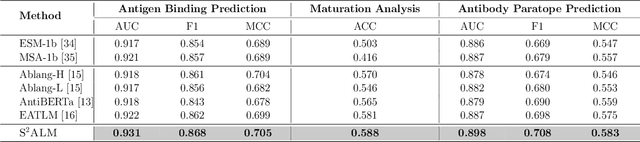
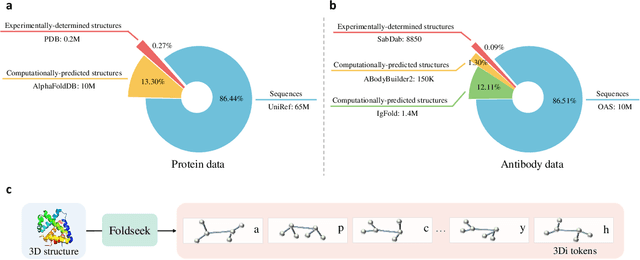
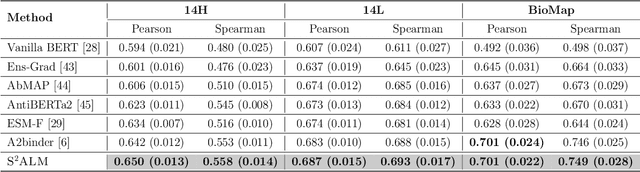
Antibodies safeguard our health through their precise and potent binding to specific antigens, demonstrating promising therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of numerous diseases, including COVID-19. Recent advancements in biomedical language models have shown the great potential to interpret complex biological structures and functions. However, existing antibody specific models have a notable limitation that they lack explicit consideration for antibody structural information, despite the fact that both 1D sequence and 3D structure carry unique and complementary insights into antibody behavior and functionality. This paper proposes Sequence-Structure multi-level pre-trained Antibody Language Model (S$^2$ALM), combining holistic sequential and structural information in one unified, generic antibody foundation model. We construct a hierarchical pre-training paradigm incorporated with two customized multi-level training objectives to facilitate the modeling of comprehensive antibody representations. S$^2$ALM's representation space uncovers inherent functional binding mechanisms, biological evolution properties and structural interaction patterns. Pre-trained over 75 million sequences and 11.7 million structures, S$^2$ALM can be adopted for diverse downstream tasks: accurately predicting antigen-antibody binding affinities, precisely distinguishing B cell maturation stages, identifying antibody crucial binding positions, and specifically designing novel coronavirus-binding antibodies. Remarkably, S$^2$ALM outperforms well-established and renowned baselines and sets new state-of-the-art performance across extensive antibody specific understanding and generation tasks. S$^2$ALM's ability to model comprehensive and generalized representations further positions its potential to advance real-world therapeutic antibody development, potentially addressing unmet academic, industrial, and clinical needs.
Precise Antigen-Antibody Structure Predictions Enhance Antibody Development with HelixFold-Multimer
Dec 13, 2024



The accurate prediction of antigen-antibody structures is essential for advancing immunology and therapeutic development, as it helps elucidate molecular interactions that underlie immune responses. Despite recent progress with deep learning models like AlphaFold and RoseTTAFold, accurately modeling antigen-antibody complexes remains a challenge due to their unique evolutionary characteristics. HelixFold-Multimer, a specialized model developed for this purpose, builds on the framework of AlphaFold-Multimer and demonstrates improved precision for antigen-antibody structures. HelixFold-Multimer not only surpasses other models in accuracy but also provides essential insights into antibody development, enabling more precise identification of binding sites, improved interaction prediction, and enhanced design of therapeutic antibodies. These advances underscore HelixFold-Multimer's potential in supporting antibody research and therapeutic innovation.
Generative Humanization for Therapeutic Antibodies
Dec 09, 2024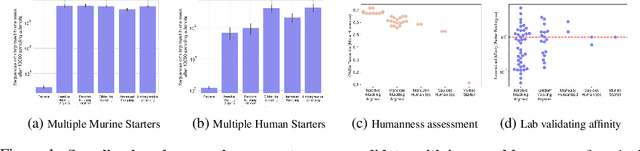
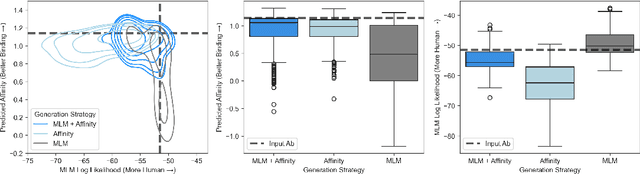
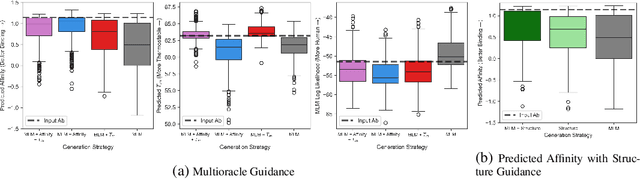
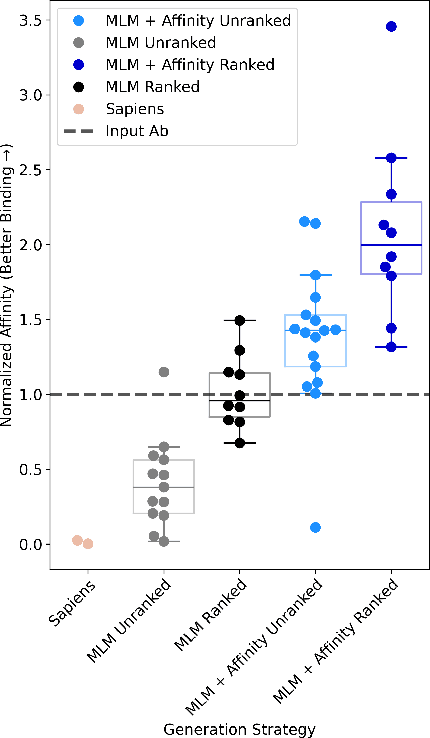
Antibody therapies have been employed to address some of today's most challenging diseases, but must meet many criteria during drug development before reaching a patient. Humanization is a sequence optimization strategy that addresses one critical risk called immunogenicity - a patient's immune response to the drug - by making an antibody more "human-like" in the absence of a predictive lab-based test for immunogenicity. However, existing humanization strategies generally yield very few humanized candidates, which may have degraded biophysical properties or decreased drug efficacy. Here, we re-frame humanization as a conditional generative modeling task, where humanizing mutations are sampled from a language model trained on human antibody data. We describe a sampling process that incorporates models of therapeutic attributes, such as antigen binding affinity, to obtain candidate sequences that have both reduced immunogenicity risk and maintained or improved therapeutic properties, allowing this algorithm to be readily embedded into an iterative antibody optimization campaign. We demonstrate in silico and in lab validation that in real therapeutic programs our generative humanization method produces diverse sets of antibodies that are both (1) highly-human and (2) have favorable therapeutic properties, such as improved binding to target antigens.
Efficient Antibody Structure Refinement Using Energy-Guided SE(3) Flow Matching
Oct 22, 2024



Antibodies are proteins produced by the immune system that recognize and bind to specific antigens, and their 3D structures are crucial for understanding their binding mechanism and designing therapeutic interventions. The specificity of antibody-antigen binding predominantly depends on the complementarity-determining regions (CDR) within antibodies. Despite recent advancements in antibody structure prediction, the quality of predicted CDRs remains suboptimal. In this paper, we develop a novel antibody structure refinement method termed FlowAB based on energy-guided flow matching. FlowAB adopts the powerful deep generative method SE(3) flow matching and simultaneously incorporates important physical prior knowledge into the flow model to guide the generation process. The extensive experiments demonstrate that FlowAB can significantly improve the antibody CDR structures. It achieves new state-of-the-art performance on the antibody structure prediction task when used in conjunction with an appropriate prior model while incurring only marginal computational overhead. This advantage makes FlowAB a practical tool in antibody engineering.
Improving Paratope and Epitope Prediction by Multi-Modal Contrastive Learning and Interaction Informativeness Estimation
May 31, 2024



Accurately predicting antibody-antigen binding residues, i.e., paratopes and epitopes, is crucial in antibody design. However, existing methods solely focus on uni-modal data (either sequence or structure), disregarding the complementary information present in multi-modal data, and most methods predict paratopes and epitopes separately, overlooking their specific spatial interactions. In this paper, we propose a novel Multi-modal contrastive learning and Interaction informativeness estimation-based method for Paratope and Epitope prediction, named MIPE, by using both sequence and structure data of antibodies and antigens. MIPE implements a multi-modal contrastive learning strategy, which maximizes representations of binding and non-binding residues within each modality and meanwhile aligns uni-modal representations towards effective modal representations. To exploit the spatial interaction information, MIPE also incorporates an interaction informativeness estimation that computes the estimated interaction matrices between antibodies and antigens, thereby approximating them to the actual ones. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to baselines. Additionally, the ablation studies and visualizations demonstrate the superiority of MIPE owing to the better representations acquired through multi-modal contrastive learning and the interaction patterns comprehended by the interaction informativeness estimation.
AsEP: Benchmarking Deep Learning Methods for Antibody-specific Epitope Prediction
Jul 25, 2024Epitope identification is vital for antibody design yet challenging due to the inherent variability in antibodies. While many deep learning methods have been developed for general protein binding site prediction tasks, whether they work for epitope prediction remains an understudied research question. The challenge is also heightened by the lack of a consistent evaluation pipeline with sufficient dataset size and epitope diversity. We introduce a filtered antibody-antigen complex structure dataset, AsEP (Antibody-specific Epitope Prediction). AsEP is the largest of its kind and provides clustered epitope groups, allowing the community to develop and test novel epitope prediction methods. AsEP comes with an easy-to-use interface in Python and pre-built graph representations of each antibody-antigen complex while also supporting customizable embedding methods. Based on this new dataset, we benchmarked various representative general protein-binding site prediction methods and find that their performances are not satisfactory as expected for epitope prediction. We thus propose a new method, WALLE, that leverages both protein language models and graph neural networks. WALLE demonstrate about 5X performance gain over existing methods. Our empirical findings evidence that epitope prediction benefits from combining sequential embeddings provided by language models and geometrical information from graph representations, providing a guideline for future method design. In addition, we reformulate the task as bipartite link prediction, allowing easy model performance attribution and interpretability. We open-source our data and code at https://github.com/biochunan/AsEP-dataset.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge