Yongkang Wang
Improving Paratope and Epitope Prediction by Multi-Modal Contrastive Learning and Interaction Informativeness Estimation
May 31, 2024



Abstract:Accurately predicting antibody-antigen binding residues, i.e., paratopes and epitopes, is crucial in antibody design. However, existing methods solely focus on uni-modal data (either sequence or structure), disregarding the complementary information present in multi-modal data, and most methods predict paratopes and epitopes separately, overlooking their specific spatial interactions. In this paper, we propose a novel Multi-modal contrastive learning and Interaction informativeness estimation-based method for Paratope and Epitope prediction, named MIPE, by using both sequence and structure data of antibodies and antigens. MIPE implements a multi-modal contrastive learning strategy, which maximizes representations of binding and non-binding residues within each modality and meanwhile aligns uni-modal representations towards effective modal representations. To exploit the spatial interaction information, MIPE also incorporates an interaction informativeness estimation that computes the estimated interaction matrices between antibodies and antigens, thereby approximating them to the actual ones. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of our method compared to baselines. Additionally, the ablation studies and visualizations demonstrate the superiority of MIPE owing to the better representations acquired through multi-modal contrastive learning and the interaction patterns comprehended by the interaction informativeness estimation.
A Multi-Modal Contrastive Diffusion Model for Therapeutic Peptide Generation
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Therapeutic peptides represent a unique class of pharmaceutical agents crucial for the treatment of human diseases. Recently, deep generative models have exhibited remarkable potential for generating therapeutic peptides, but they only utilize sequence or structure information alone, which hinders the performance in generation. In this study, we propose a Multi-Modal Contrastive Diffusion model (MMCD), fusing both sequence and structure modalities in a diffusion framework to co-generate novel peptide sequences and structures. Specifically, MMCD constructs the sequence-modal and structure-modal diffusion models, respectively, and devises a multi-modal contrastive learning strategy with intercontrastive and intra-contrastive in each diffusion timestep, aiming to capture the consistency between two modalities and boost model performance. The inter-contrastive aligns sequences and structures of peptides by maximizing the agreement of their embeddings, while the intra-contrastive differentiates therapeutic and non-therapeutic peptides by maximizing the disagreement of their sequence/structure embeddings simultaneously. The extensive experiments demonstrate that MMCD performs better than other state-of-theart deep generative methods in generating therapeutic peptides across various metrics, including antimicrobial/anticancer score, diversity, and peptide-docking.
Deep Automated Mechanism Design for Integrating Ad Auction and Allocation in Feed
Jan 03, 2024



Abstract:E-commerce platforms usually present an ordered list, mixed with several organic items and an advertisement, in response to each user's page view request. This list, the outcome of ad auction and allocation processes, directly impacts the platform's ad revenue and gross merchandise volume (GMV). Specifically, the ad auction determines which ad is displayed and the corresponding payment, while the ad allocation decides the display positions of the advertisement and organic items. The prevalent methods of segregating the ad auction and allocation into two distinct stages face two problems: 1) Ad auction does not consider externalities, such as the influence of actual display position and context on ad Click-Through Rate (CTR); 2) The ad allocation, which utilizes the auction-winning ad's payment to determine the display position dynamically, fails to maintain incentive compatibility (IC) for the advertisement. For instance, in the auction stage employing the traditional Generalized Second Price (GSP) , even if the winning ad increases its bid, its payment remains unchanged. This implies that the advertisement cannot secure a better position and thus loses the opportunity to achieve higher utility in the subsequent ad allocation stage. Previous research often focused on one of the two stages, neglecting the two-stage problem, which may result in suboptimal outcomes...
TBIN: Modeling Long Textual Behavior Data for CTR Prediction
Aug 09, 2023



Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction plays a pivotal role in the success of recommendations. Inspired by the recent thriving of language models (LMs), a surge of works improve prediction by organizing user behavior data in a \textbf{textual} format and using LMs to understand user interest at a semantic level. While promising, these works have to truncate the textual data to reduce the quadratic computational overhead of self-attention in LMs. However, it has been studied that long user behavior data can significantly benefit CTR prediction. In addition, these works typically condense user diverse interests into a single feature vector, which hinders the expressive capability of the model. In this paper, we propose a \textbf{T}extual \textbf{B}ehavior-based \textbf{I}nterest Chunking \textbf{N}etwork (TBIN), which tackles the above limitations by combining an efficient locality-sensitive hashing algorithm and a shifted chunk-based self-attention. The resulting user diverse interests are dynamically activated, producing user interest representation towards the target item. Finally, the results of both offline and online experiments on real-world food recommendation platform demonstrate the effectiveness of TBIN.
Cross-Element Combinatorial Selection for Multi-Element Creative in Display Advertising
Jul 04, 2023



Abstract:The effectiveness of ad creatives is greatly influenced by their visual appearance. Advertising platforms can generate ad creatives with different appearances by combining creative elements provided by advertisers. However, with the increasing number of ad creative elements, it becomes challenging to select a suitable combination from the countless possibilities. The industry's mainstream approach is to select individual creative elements independently, which often overlooks the importance of interaction between creative elements during the modeling process. In response, this paper proposes a Cross-Element Combinatorial Selection framework for multiple creative elements, termed CECS. In the encoder process, a cross-element interaction is adopted to dynamically adjust the expression of a single creative element based on the current candidate creatives. In the decoder process, the creative combination problem is transformed into a cascade selection problem of multiple creative elements. A pointer mechanism with a cascade design is used to model the associations among candidates. Comprehensive experiments on real-world datasets show that CECS achieved the SOTA score on offline metrics. Moreover, the CECS algorithm has been deployed in our industrial application, resulting in a significant 6.02% CTR and 10.37% GMV lift, which is beneficial to the business.
MDDL: A Framework for Reinforcement Learning-based Position Allocation in Multi-Channel Feed
Apr 17, 2023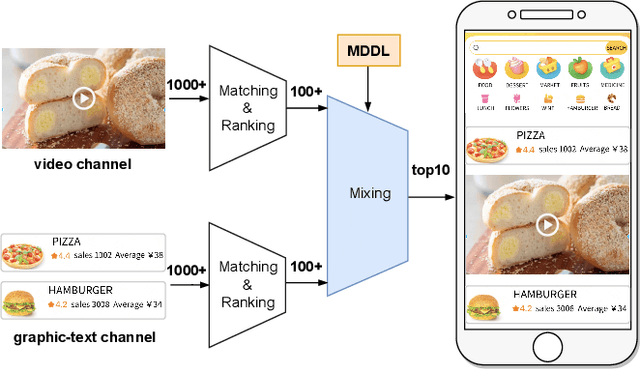
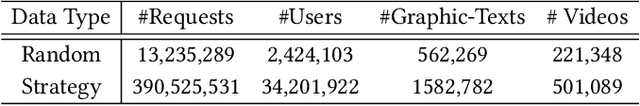
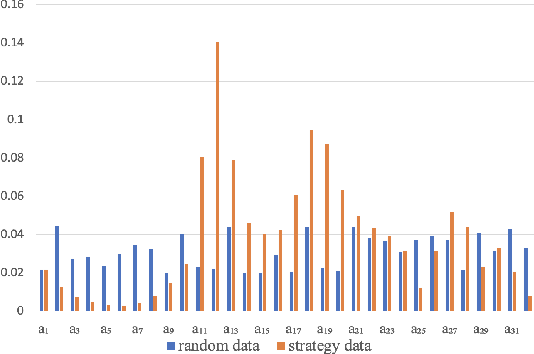
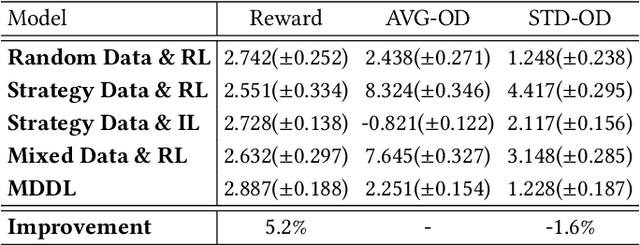
Abstract:Nowadays, the mainstream approach in position allocation system is to utilize a reinforcement learning model to allocate appropriate locations for items in various channels and then mix them into the feed. There are two types of data employed to train reinforcement learning (RL) model for position allocation, named strategy data and random data. Strategy data is collected from the current online model, it suffers from an imbalanced distribution of state-action pairs, resulting in severe overestimation problems during training. On the other hand, random data offers a more uniform distribution of state-action pairs, but is challenging to obtain in industrial scenarios as it could negatively impact platform revenue and user experience due to random exploration. As the two types of data have different distributions, designing an effective strategy to leverage both types of data to enhance the efficacy of the RL model training has become a highly challenging problem. In this study, we propose a framework named Multi-Distribution Data Learning (MDDL) to address the challenge of effectively utilizing both strategy and random data for training RL models on mixed multi-distribution data. Specifically, MDDL incorporates a novel imitation learning signal to mitigate overestimation problems in strategy data and maximizes the RL signal for random data to facilitate effective learning. In our experiments, we evaluated the proposed MDDL framework in a real-world position allocation system and demonstrated its superior performance compared to the previous baseline. MDDL has been fully deployed on the Meituan food delivery platform and currently serves over 300 million users.
PIER: Permutation-Level Interest-Based End-to-End Re-ranking Framework in E-commerce
Feb 06, 2023



Abstract:Re-ranking draws increased attention on both academics and industries, which rearranges the ranking list by modeling the mutual influence among items to better meet users' demands. Many existing re-ranking methods directly take the initial ranking list as input, and generate the optimal permutation through a well-designed context-wise model, which brings the evaluation-before-reranking problem. Meanwhile, evaluating all candidate permutations brings unacceptable computational costs in practice. Thus, to better balance efficiency and effectiveness, online systems usually use a two-stage architecture which uses some heuristic methods such as beam-search to generate a suitable amount of candidate permutations firstly, which are then fed into the evaluation model to get the optimal permutation. However, existing methods in both stages can be improved through the following aspects. As for generation stage, heuristic methods only use point-wise prediction scores and lack an effective judgment. As for evaluation stage, most existing context-wise evaluation models only consider the item context and lack more fine-grained feature context modeling. This paper presents a novel end-to-end re-ranking framework named PIER to tackle the above challenges which still follows the two-stage architecture and contains two mainly modules named FPSM and OCPM. We apply SimHash in FPSM to select top-K candidates from the full permutation based on user's permutation-level interest in an efficient way. Then we design a novel omnidirectional attention mechanism in OCPM to capture the context information in the permutation. Finally, we jointly train these two modules end-to-end by introducing a comparative learning loss. Offline experiment results demonstrate that PIER outperforms baseline models on both public and industrial datasets, and we have successfully deployed PIER on Meituan food delivery platform.
A Deep Behavior Path Matching Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Feb 01, 2023



Abstract:User behaviors on an e-commerce app not only contain different kinds of feedback on items but also sometimes imply the cognitive clue of the user's decision-making. For understanding the psychological procedure behind user decisions, we present the behavior path and propose to match the user's current behavior path with historical behavior paths to predict user behaviors on the app. Further, we design a deep neural network for behavior path matching and solve three difficulties in modeling behavior paths: sparsity, noise interference, and accurate matching of behavior paths. In particular, we leverage contrastive learning to augment user behavior paths, provide behavior path self-activation to alleviate the effect of noise, and adopt a two-level matching mechanism to identify the most appropriate candidate. Our model shows excellent performance on two real-world datasets, outperforming the state-of-the-art CTR model. Moreover, our model has been deployed on the Meituan food delivery platform and has accumulated 1.6% improvement in CTR and 1.8% improvement in advertising revenue.
Decision-Making Context Interaction Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Jan 29, 2023



Abstract:Click-through rate (CTR) prediction is crucial in recommendation and online advertising systems. Existing methods usually model user behaviors, while ignoring the informative context which influences the user to make a click decision, e.g., click pages and pre-ranking candidates that inform inferences about user interests, leading to suboptimal performance. In this paper, we propose a Decision-Making Context Interaction Network (DCIN), which deploys a carefully designed Context Interaction Unit (CIU) to learn decision-making contexts and thus benefits CTR prediction. In addition, the relationship between different decision-making context sources is explored by the proposed Adaptive Interest Aggregation Unit (AIAU) to improve CTR prediction further. In the experiments on public and industrial datasets, DCIN significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods. Notably, the model has obtained the improvement of CTR+2.9%/CPM+2.1%/GMV+1.5% for online A/B testing and served the main traffic of Meituan Waimai advertising system.
NMA: Neural Multi-slot Auctions with Externalities for Online Advertising
May 20, 2022
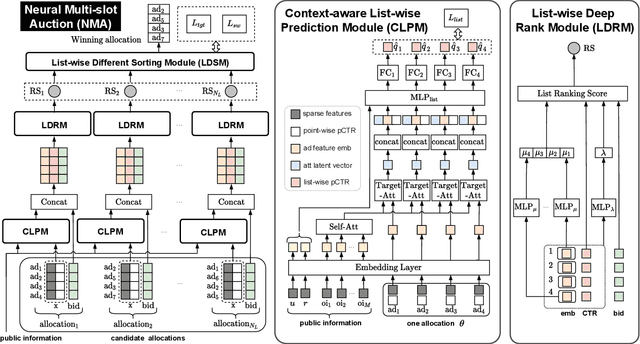

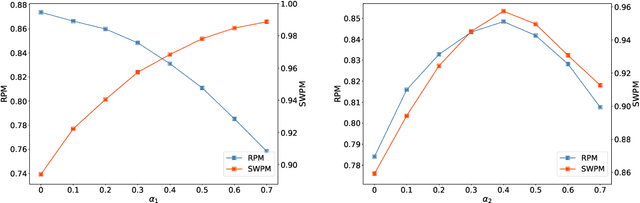
Abstract:Online advertising driven by auctions brings billions of dollars in revenue for social networking services and e-commerce platforms. GSP auction, which is simple and easy to understand for advertisers, has almost become the benchmark for ad auction mechanisms in the industry. However, the allocation stability of GSP depends on the separable CTR assumption, which means that GSP considers neither position-dependent externalities nor ad-dependent externalities in multi-slot scenario, leading to suboptimal performance. Some GSP-based deep auctions (e.g., DeepGSP, DNA) have attempted to upgrade GSP with deep neural networks, while only modeling local externalities and thus still suboptimal. On the other hand, although VCG-based multi-slot auctions (e.g., VCG, WVCG) take externalities into consideration, they lack an efficient balance of both revenue and social welfare. In this paper, we propose a novel auction named Neural Multi-slot Auction (NMA) to tackle the above-mentioned challenges. Specifically, we model the global externalities effectively with a context-aware list-wise prediction module to achieve better performance. We design a list-wise deep rank module to guarantee incentive compatibility in end-to-end learning. Furthermore, we propose an auxiliary loss for social welfare to effectively reduce the decline of social welfare while maximizing revenue. Experiment results on both offline large-scale datasets and online A/B tests demonstrate that NMA obtains higher revenue with balanced social welfare than other existing auction mechanisms (i.e., GSP, DNA, WVCG) in industrial practice, and we have successfully deployed NMA on Meituan food delivery platform.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge