Yisong Yu
Orthogonal Hyper-category Guided Multi-interest Elicitation for Micro-video Matching
Jul 20, 2024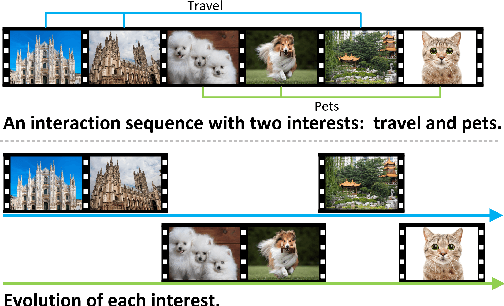
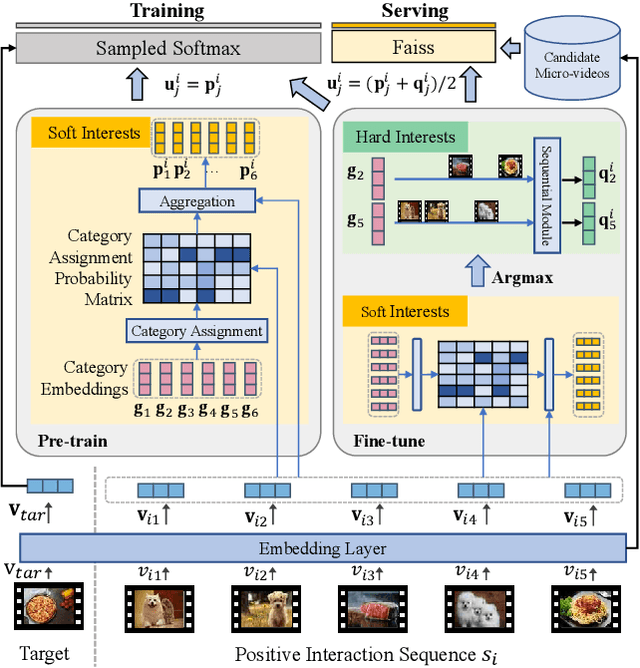
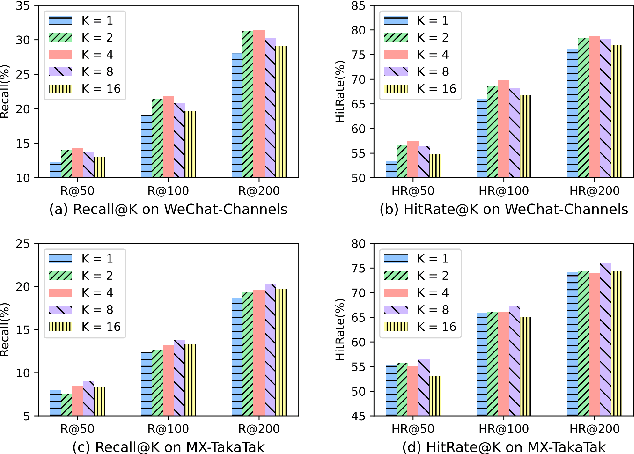
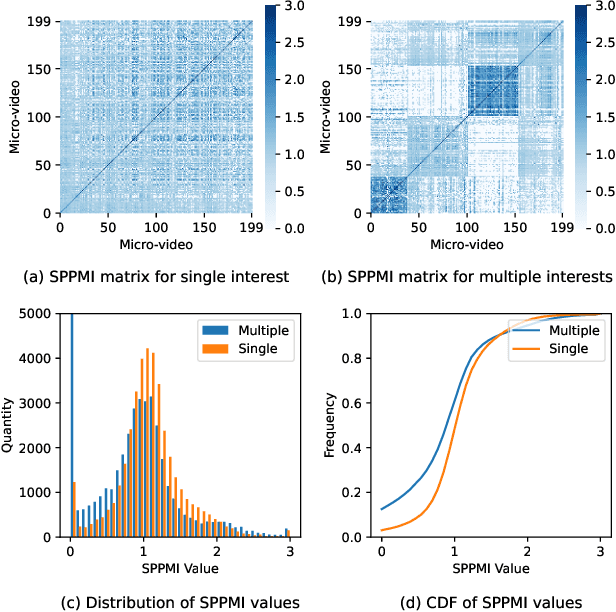
Abstract:Watching micro-videos is becoming a part of public daily life. Usually, user watching behaviors are thought to be rooted in their multiple different interests. In the paper, we propose a model named OPAL for micro-video matching, which elicits a user's multiple heterogeneous interests by disentangling multiple soft and hard interest embeddings from user interactions. Moreover, OPAL employs a two-stage training strategy, in which the pre-train is to generate soft interests from historical interactions under the guidance of orthogonal hyper-categories of micro-videos and the fine-tune is to reinforce the degree of disentanglement among the interests and learn the temporal evolution of each interest of each user. We conduct extensive experiments on two real-world datasets. The results show that OPAL not only returns diversified micro-videos but also outperforms six state-of-the-art models in terms of recall and hit rate.
A Deep Behavior Path Matching Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
Feb 01, 2023



Abstract:User behaviors on an e-commerce app not only contain different kinds of feedback on items but also sometimes imply the cognitive clue of the user's decision-making. For understanding the psychological procedure behind user decisions, we present the behavior path and propose to match the user's current behavior path with historical behavior paths to predict user behaviors on the app. Further, we design a deep neural network for behavior path matching and solve three difficulties in modeling behavior paths: sparsity, noise interference, and accurate matching of behavior paths. In particular, we leverage contrastive learning to augment user behavior paths, provide behavior path self-activation to alleviate the effect of noise, and adopt a two-level matching mechanism to identify the most appropriate candidate. Our model shows excellent performance on two real-world datasets, outperforming the state-of-the-art CTR model. Moreover, our model has been deployed on the Meituan food delivery platform and has accumulated 1.6% improvement in CTR and 1.8% improvement in advertising revenue.
Improving Micro-video Recommendation by Controlling Position Bias
Aug 09, 2022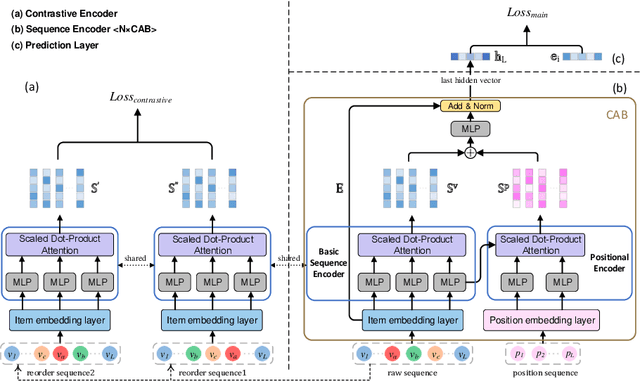
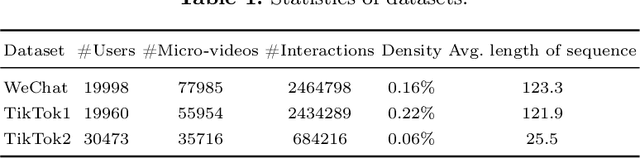
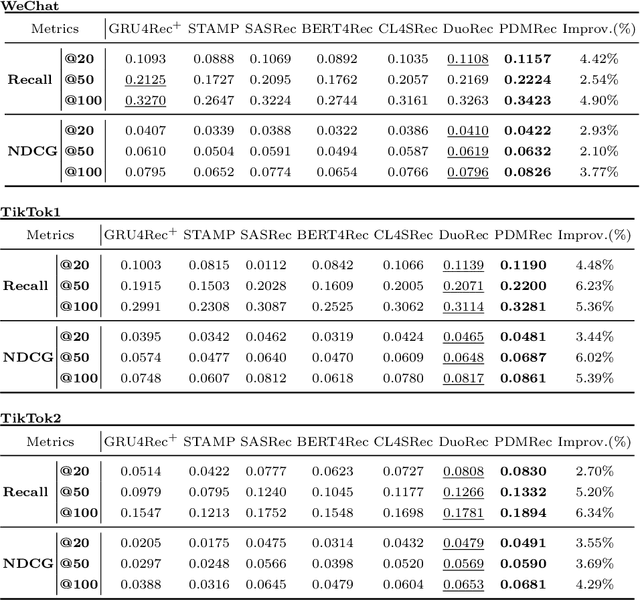
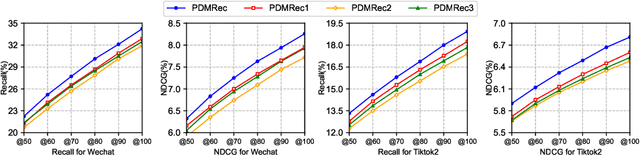
Abstract:As the micro-video apps become popular, the numbers of micro-videos and users increase rapidly, which highlights the importance of micro-video recommendation. Although the micro-video recommendation can be naturally treated as the sequential recommendation, the previous sequential recommendation models do not fully consider the characteristics of micro-video apps, and in their inductive biases, the role of positions is not in accord with the reality in the micro-video scenario. Therefore, in the paper, we present a model named PDMRec (Position Decoupled Micro-video Recommendation). PDMRec applies separate self-attention modules to model micro-video information and the positional information and then aggregate them together, avoid the noisy correlations between micro-video semantics and positional information being encoded into the sequence embeddings. Moreover, PDMRec proposes contrastive learning strategies which closely match with the characteristics of the micro-video scenario, thus reducing the interference from micro-video positions in sequences. We conduct the extensive experiments on two real-world datasets. The experimental results shows that PDMRec outperforms existing multiple state-of-the-art models and achieves significant performance improvements.
Improving Micro-video Recommendation via Contrastive Multiple Interests
May 19, 2022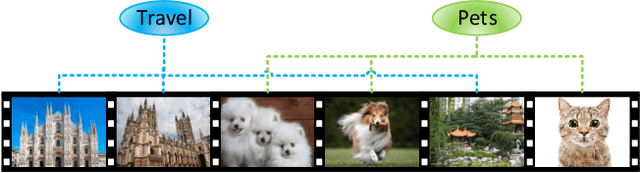

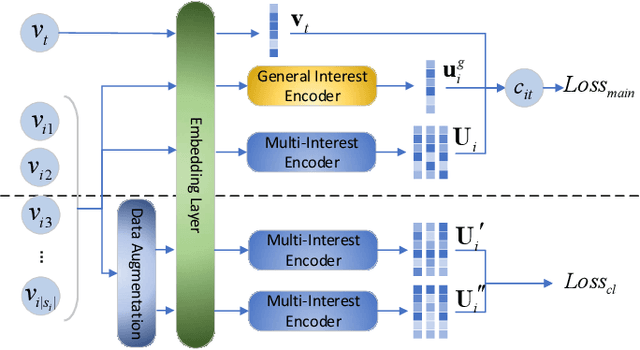
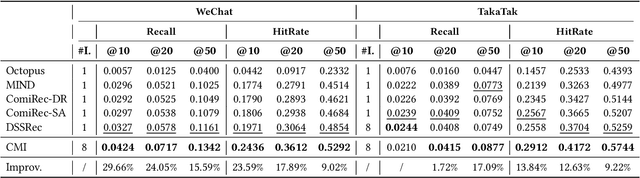
Abstract:With the rapid increase of micro-video creators and viewers, how to make personalized recommendations from a large number of candidates to viewers begins to attract more and more attention. However, existing micro-video recommendation models rely on expensive multi-modal information and learn an overall interest embedding that cannot reflect the user's multiple interests in micro-videos. Recently, contrastive learning provides a new opportunity for refining the existing recommendation techniques. Therefore, in this paper, we propose to extract contrastive multi-interests and devise a micro-video recommendation model CMI. Specifically, CMI learns multiple interest embeddings for each user from his/her historical interaction sequence, in which the implicit orthogonal micro-video categories are used to decouple multiple user interests. Moreover, it establishes the contrastive multi-interest loss to improve the robustness of interest embeddings and the performance of recommendations. The results of experiments on two micro-video datasets demonstrate that CMI achieves state-of-the-art performance over existing baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge