Guogang Liao
SEAS: Self-Evolving Adversarial Safety Optimization for Large Language Models
Aug 05, 2024Abstract:As large language models (LLMs) continue to advance in capability and influence, ensuring their security and preventing harmful outputs has become crucial. A promising approach to address these concerns involves training models to automatically generate adversarial prompts for red teaming. However, the evolving subtlety of vulnerabilities in LLMs challenges the effectiveness of current adversarial methods, which struggle to specifically target and explore the weaknesses of these models. To tackle these challenges, we introduce the $\mathbf{S}\text{elf-}\mathbf{E}\text{volving }\mathbf{A}\text{dversarial }\mathbf{S}\text{afety }\mathbf{(SEAS)}$ optimization framework, which enhances security by leveraging data generated by the model itself. SEAS operates through three iterative stages: Initialization, Attack, and Adversarial Optimization, refining both the Red Team and Target models to improve robustness and safety. This framework reduces reliance on manual testing and significantly enhances the security capabilities of LLMs. Our contributions include a novel adversarial framework, a comprehensive safety dataset, and after three iterations, the Target model achieves a security level comparable to GPT-4, while the Red Team model shows a marked increase in attack success rate (ASR) against advanced models.
MDDL: A Framework for Reinforcement Learning-based Position Allocation in Multi-Channel Feed
Apr 17, 2023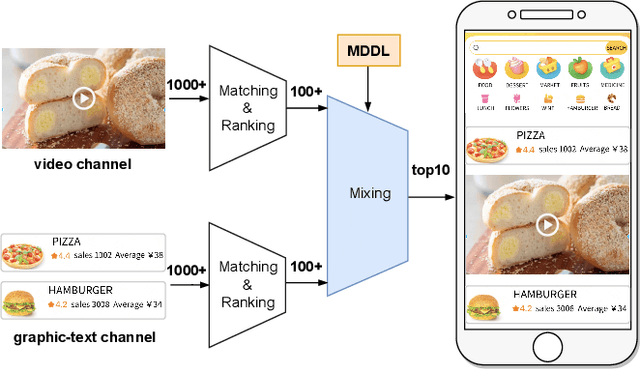
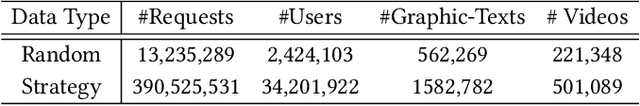
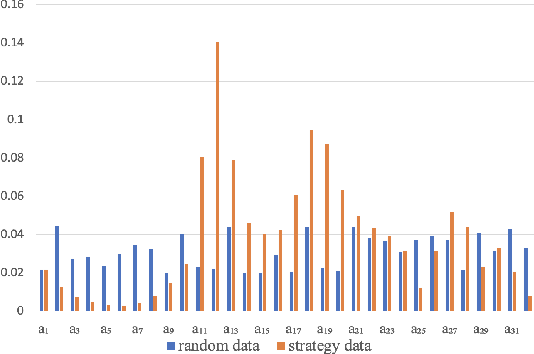
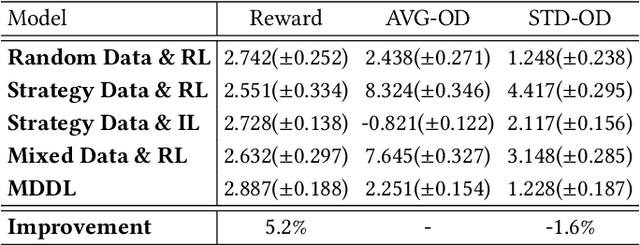
Abstract:Nowadays, the mainstream approach in position allocation system is to utilize a reinforcement learning model to allocate appropriate locations for items in various channels and then mix them into the feed. There are two types of data employed to train reinforcement learning (RL) model for position allocation, named strategy data and random data. Strategy data is collected from the current online model, it suffers from an imbalanced distribution of state-action pairs, resulting in severe overestimation problems during training. On the other hand, random data offers a more uniform distribution of state-action pairs, but is challenging to obtain in industrial scenarios as it could negatively impact platform revenue and user experience due to random exploration. As the two types of data have different distributions, designing an effective strategy to leverage both types of data to enhance the efficacy of the RL model training has become a highly challenging problem. In this study, we propose a framework named Multi-Distribution Data Learning (MDDL) to address the challenge of effectively utilizing both strategy and random data for training RL models on mixed multi-distribution data. Specifically, MDDL incorporates a novel imitation learning signal to mitigate overestimation problems in strategy data and maximizes the RL signal for random data to facilitate effective learning. In our experiments, we evaluated the proposed MDDL framework in a real-world position allocation system and demonstrated its superior performance compared to the previous baseline. MDDL has been fully deployed on the Meituan food delivery platform and currently serves over 300 million users.
PIER: Permutation-Level Interest-Based End-to-End Re-ranking Framework in E-commerce
Feb 06, 2023



Abstract:Re-ranking draws increased attention on both academics and industries, which rearranges the ranking list by modeling the mutual influence among items to better meet users' demands. Many existing re-ranking methods directly take the initial ranking list as input, and generate the optimal permutation through a well-designed context-wise model, which brings the evaluation-before-reranking problem. Meanwhile, evaluating all candidate permutations brings unacceptable computational costs in practice. Thus, to better balance efficiency and effectiveness, online systems usually use a two-stage architecture which uses some heuristic methods such as beam-search to generate a suitable amount of candidate permutations firstly, which are then fed into the evaluation model to get the optimal permutation. However, existing methods in both stages can be improved through the following aspects. As for generation stage, heuristic methods only use point-wise prediction scores and lack an effective judgment. As for evaluation stage, most existing context-wise evaluation models only consider the item context and lack more fine-grained feature context modeling. This paper presents a novel end-to-end re-ranking framework named PIER to tackle the above challenges which still follows the two-stage architecture and contains two mainly modules named FPSM and OCPM. We apply SimHash in FPSM to select top-K candidates from the full permutation based on user's permutation-level interest in an efficient way. Then we design a novel omnidirectional attention mechanism in OCPM to capture the context information in the permutation. Finally, we jointly train these two modules end-to-end by introducing a comparative learning loss. Offline experiment results demonstrate that PIER outperforms baseline models on both public and industrial datasets, and we have successfully deployed PIER on Meituan food delivery platform.
NMA: Neural Multi-slot Auctions with Externalities for Online Advertising
May 20, 2022
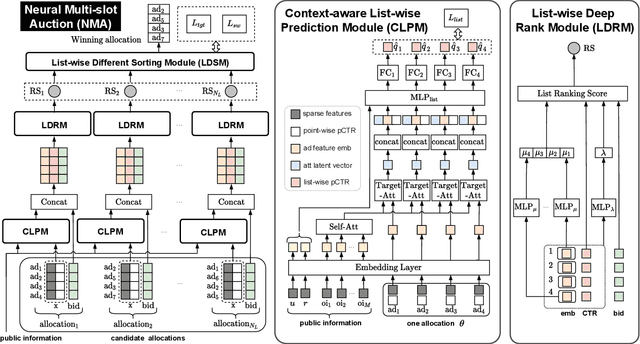

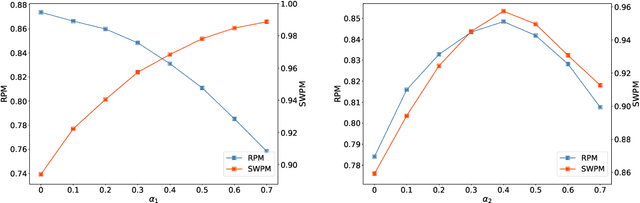
Abstract:Online advertising driven by auctions brings billions of dollars in revenue for social networking services and e-commerce platforms. GSP auction, which is simple and easy to understand for advertisers, has almost become the benchmark for ad auction mechanisms in the industry. However, the allocation stability of GSP depends on the separable CTR assumption, which means that GSP considers neither position-dependent externalities nor ad-dependent externalities in multi-slot scenario, leading to suboptimal performance. Some GSP-based deep auctions (e.g., DeepGSP, DNA) have attempted to upgrade GSP with deep neural networks, while only modeling local externalities and thus still suboptimal. On the other hand, although VCG-based multi-slot auctions (e.g., VCG, WVCG) take externalities into consideration, they lack an efficient balance of both revenue and social welfare. In this paper, we propose a novel auction named Neural Multi-slot Auction (NMA) to tackle the above-mentioned challenges. Specifically, we model the global externalities effectively with a context-aware list-wise prediction module to achieve better performance. We design a list-wise deep rank module to guarantee incentive compatibility in end-to-end learning. Furthermore, we propose an auxiliary loss for social welfare to effectively reduce the decline of social welfare while maximizing revenue. Experiment results on both offline large-scale datasets and online A/B tests demonstrate that NMA obtains higher revenue with balanced social welfare than other existing auction mechanisms (i.e., GSP, DNA, WVCG) in industrial practice, and we have successfully deployed NMA on Meituan food delivery platform.
Learning List-wise Representation in Reinforcement Learning for Ads Allocation with Multiple Auxiliary Tasks
Apr 02, 2022

Abstract:With the recent prevalence of reinforcement learning (RL), there have been tremendous interests in utilizing RL for ads allocation in recommendation platforms (e.g., e-commerce and news feed sites). For better performance, recent RL-based ads allocation agent makes decisions based on representations of list-wise item arrangement. This results in a high-dimensional state-action space, which makes it difficult to learn an efficient and generalizable list-wise representation. To address this problem, we propose a novel algorithm to learn a better representation by leveraging task-specific signals on Meituan food delivery platform. Specifically, we propose three different types of auxiliary tasks that are based on reconstruction, prediction, and contrastive learning respectively. We conduct extensive offline experiments on the effectiveness of these auxiliary tasks and test our method on real-world food delivery platform. The experimental results show that our method can learn better list-wise representations and achieve higher revenue for the platform.
Deep Page-Level Interest Network in Reinforcement Learning for Ads Allocation
Apr 01, 2022


Abstract:A mixed list of ads and organic items is usually displayed in feed and how to allocate the limited slots to maximize the overall revenue is a key problem. Meanwhile, modeling user preference with historical behavior is essential in recommendation and advertising (e.g., CTR prediction and ads allocation). Most previous works for user behavior modeling only model user's historical point-level positive feedback (i.e., click), which neglect the page-level information of feedback and other types of feedback. To this end, we propose Deep Page-level Interest Network (DPIN) to model the page-level user preference and exploit multiple types of feedback. Specifically, we introduce four different types of page-level feedback as input, and capture user preference for item arrangement under different receptive fields through the multi-channel interaction module. Through extensive offline and online experiments on Meituan food delivery platform, we demonstrate that DPIN can effectively model the page-level user preference and increase the revenue for the platform.
Cross DQN: Cross Deep Q Network for Ads Allocation in Feed
Sep 09, 2021



Abstract:E-commerce platforms usually display a mixed list of ads and organic items in feed. One key problem is to allocate the limited slots in the feed to maximize the overall revenue as well as improve user experience, which requires a good model for user preference. Instead of modeling the influence of individual items on user behaviors, the arrangement signal models the influence of the arrangement of items and may lead to a better allocation strategy. However, most of previous strategies fail to model such a signal and therefore result in suboptimal performance. To this end, we propose Cross Deep Q Network (Cross DQN) to extract the arrangement signal by crossing the embeddings of different items and processing the crossed sequence in the feed. Our model results in higher revenue and better user experience than state-of-the-art baselines in offline experiments. Moreover, our model demonstrates a significant improvement in the online A/B test and has been fully deployed on Meituan feed to serve more than 300 millions of customers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge