Zi Ye
Radiomics-Integrated Deep Learning with Hierarchical Loss for Osteosarcoma Histology Classification
Jan 14, 2026Abstract:Osteosarcoma (OS) is an aggressive primary bone malignancy. Accurate histopathological assessment of viable versus non-viable tumor regions after neoadjuvant chemotherapy is critical for prognosis and treatment planning, yet manual evaluation remains labor-intensive, subjective, and prone to inter-observer variability. Recent advances in digital pathology have enabled automated necrosis quantification. Evaluating on test data, independently sampled on patient-level, revealed that the deep learning model performance dropped significantly from the tile-level generalization ability reported in previous studies. First, this work proposes the use of radiomic features as additional input in model training. We show that, despite that they are derived from the images, such a multimodal input effectively improved the classification performance, in addition to its added benefits in interpretability. Second, this work proposes to optimize two binary classification tasks with hierarchical classes (i.e. tumor-vs-non-tumor and viable-vs-non-viable), as opposed to the alternative ``flat'' three-class classification task (i.e. non-tumor, non-viable tumor, viable tumor), thereby enabling a hierarchical loss. We show that such a hierarchical loss, with trainable weightings between the two tasks, the per-class performance can be improved significantly. Using the TCIA OS Tumor Assessment dataset, we experimentally demonstrate the benefits from each of the proposed new approaches and their combination, setting a what we consider new state-of-the-art performance on this open dataset for this application. Code and trained models: https://github.com/YaxiiC/RadiomicsOS.git.
A Comprehensive Review of Agricultural Parcel and Boundary Delineation from Remote Sensing Images: Recent Progress and Future Perspectives
Aug 20, 2025



Abstract:Powered by advances in multiple remote sensing sensors, the production of high spatial resolution images provides great potential to achieve cost-efficient and high-accuracy agricultural inventory and analysis in an automated way. Lots of studies that aim at providing an inventory of the level of each agricultural parcel have generated many methods for Agricultural Parcel and Boundary Delineation (APBD). This review covers APBD methods for detecting and delineating agricultural parcels and systematically reviews the past and present of APBD-related research applied to remote sensing images. With the goal to provide a clear knowledge map of existing APBD efforts, we conduct a comprehensive review of recent APBD papers to build a meta-data analysis, including the algorithm, the study site, the crop type, the sensor type, the evaluation method, etc. We categorize the methods into three classes: (1) traditional image processing methods (including pixel-based, edge-based and region-based); (2) traditional machine learning methods (such as random forest, decision tree); and (3) deep learning-based methods. With deep learning-oriented approaches contributing to a majority, we further discuss deep learning-based methods like semantic segmentation-based, object detection-based and Transformer-based methods. In addition, we discuss five APBD-related issues to further comprehend the APBD domain using remote sensing data, such as multi-sensor data in APBD task, comparisons between single-task learning and multi-task learning in the APBD domain, comparisons among different algorithms and different APBD tasks, etc. Finally, this review proposes some APBD-related applications and a few exciting prospects and potential hot topics in future APBD research. We hope this review help researchers who involved in APBD domain to keep track of its development and tendency.
OPT-Tree: Speculative Decoding with Adaptive Draft Tree Structure
Jun 25, 2024



Abstract:Autoregressive language models demonstrate excellent performance in various scenarios. However, the inference efficiency is limited by its one-step-one-word generation mode, which has become a pressing problem recently as the models become increasingly larger. Speculative decoding employs a "draft and then verify" mechanism to allow multiple tokens to be generated in one step, realizing lossless acceleration. Existing methods mainly adopt fixed heuristic draft structures, which fail to adapt to different situations to maximize the acceptance length during verification. To alleviate this dilemma, we proposed OPT-Tree, an algorithm to construct adaptive and scalable draft trees. It searches the optimal tree structure that maximizes the mathematical expectation of the acceptance length in each decoding step. Experimental results reveal that OPT-Tree outperforms the existing draft structures and achieves a speed-up ratio of up to 3.2 compared with autoregressive decoding. If the draft model is powerful enough and the node budget is sufficient, it can generate more than ten tokens in a single step. Our code is available at https://github.com/Jikai0Wang/OPT-Tree.
A Survey on Visual Mamba
Apr 26, 2024Abstract:State space models (SSMs) with selection mechanisms and hardware-aware architectures, namely Mamba, have recently demonstrated significant promise in long-sequence modeling. Since the self-attention mechanism in transformers has quadratic complexity with image size and increasing computational demands, the researchers are now exploring how to adapt Mamba for computer vision tasks. This paper is the first comprehensive survey aiming to provide an in-depth analysis of Mamba models in the field of computer vision. It begins by exploring the foundational concepts contributing to Mamba's success, including the state space model framework, selection mechanisms, and hardware-aware design. Next, we review these vision mamba models by categorizing them into foundational ones and enhancing them with techniques such as convolution, recurrence, and attention to improve their sophistication. We further delve into the widespread applications of Mamba in vision tasks, which include their use as a backbone in various levels of vision processing. This encompasses general visual tasks, Medical visual tasks (e.g., 2D / 3D segmentation, classification, and image registration, etc.), and Remote Sensing visual tasks. We specially introduce general visual tasks from two levels: High/Mid-level vision (e.g., Object detection, Segmentation, Video classification, etc.) and Low-level vision (e.g., Image super-resolution, Image restoration, Visual generation, etc.). We hope this endeavor will spark additional interest within the community to address current challenges and further apply Mamba models in computer vision.
Joint Communication and Sensing for 6G -- A Cross-Layer Perspective
Feb 14, 2024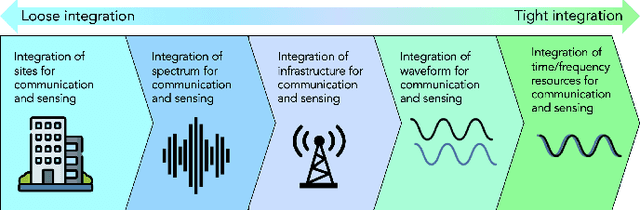
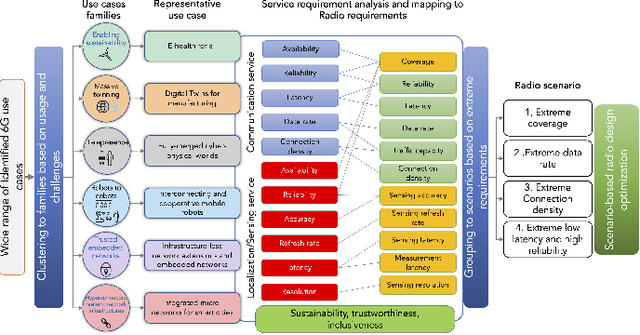
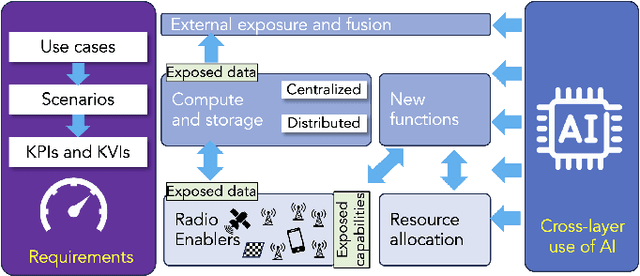
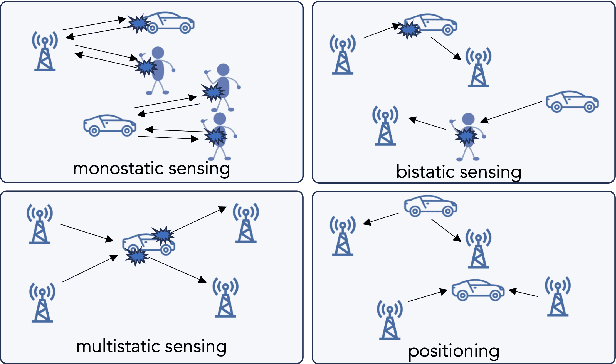
Abstract:As 6G emerges, cellular systems are envisioned to integrate sensing with communication capabilities, leading to multi-faceted communication and sensing (JCAS). This paper presents a comprehensive cross-layer overview of the Hexa-X-II project's endeavors in JCAS, aligning 6G use cases with service requirements and pinpointing distinct scenarios that bridge communication and sensing. This work relates to these scenarios through the lens of the cross-layer physical and networking domains, covering models, deployments, resource allocation, storage challenges, computational constraints, interfaces, and innovative functions.
P-Mamba: Marrying Perona Malik Diffusion with Mamba for Efficient Pediatric Echocardiographic Left Ventricular Segmentation
Feb 13, 2024Abstract:In pediatric cardiology, the accurate and immediate assessment of cardiac function through echocardiography is important since it can determine whether urgent intervention is required in many emergencies. However, echocardiography is characterized by ambiguity and heavy background noise interference, bringing more difficulty to accurate segmentation. Present methods lack efficiency and are also prone to mistakenly segmenting some background noise areas as the left ventricular area due to noise disturbance. To relieve the two issues, we introduce P-Mamba for efficient pediatric echocardiographic left ventricular segmentation. Specifically, we turn to the recently proposed vision mamba layers in our vision mamba encoder branch to improve the computing and memory efficiency of our model while modeling global dependencies. In the other DWT-based PMD encoder branch, we devise DWT-based Perona-Malik Diffusion (PMD) Blocks that utilize PMD for noise suppression, while simultaneously preserving the local shape cues of the left ventricle. Leveraging the strengths of both the two encoder branches, P-Mamba achieves superior accuracy and efficiency to established models, such as vision transformers with quadratic and linear computational complexity. This innovative approach promises significant advancements in pediatric cardiac imaging and beyond.
Exploring linguistic feature and model combination for speech recognition based automatic AD detection
Jun 28, 2022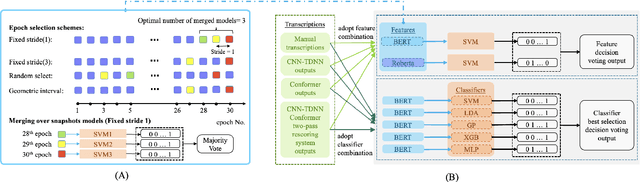
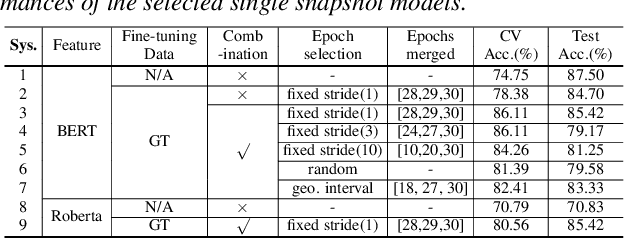
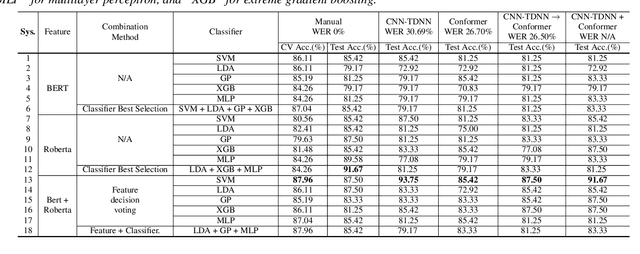
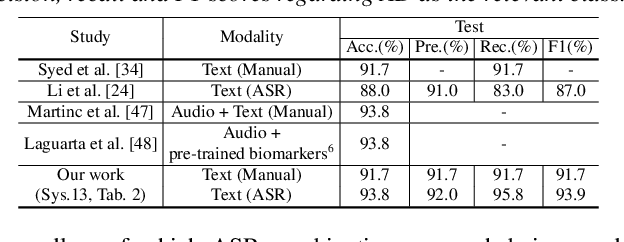
Abstract:Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is crucial in facilitating preventive care and delay progression. Speech based automatic AD screening systems provide a non-intrusive and more scalable alternative to other clinical screening techniques. Scarcity of such specialist data leads to uncertainty in both model selection and feature learning when developing such systems. To this end, this paper investigates the use of feature and model combination approaches to improve the robustness of domain fine-tuning of BERT and Roberta pre-trained text encoders on limited data, before the resulting embedding features being fed into an ensemble of backend classifiers to produce the final AD detection decision via majority voting. Experiments conducted on the ADReSS20 Challenge dataset suggest consistent performance improvements were obtained using model and feature combination in system development. State-of-the-art AD detection accuracies of 91.67 percent and 93.75 percent were obtained using manual and ASR speech transcripts respectively on the ADReSS20 test set consisting of 48 elderly speakers.
Conformer Based Elderly Speech Recognition System for Alzheimer's Disease Detection
Jun 23, 2022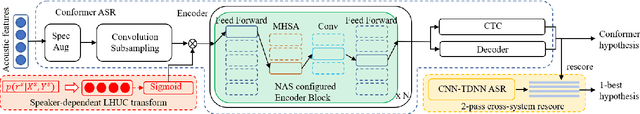

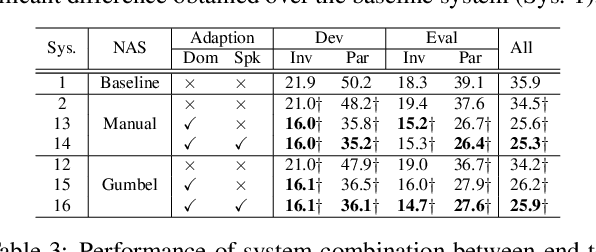
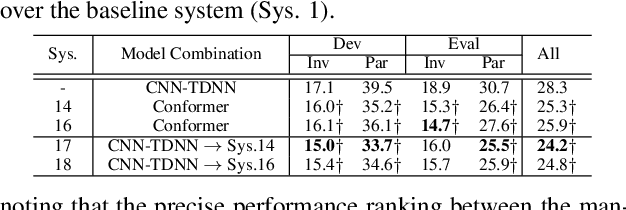
Abstract:Early diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) is crucial in facilitating preventive care to delay further progression. This paper presents the development of a state-of-the-art Conformer based speech recognition system built on the DementiaBank Pitt corpus for automatic AD detection. The baseline Conformer system trained with speed perturbation and SpecAugment based data augmentation is significantly improved by incorporating a set of purposefully designed modeling features, including neural architecture search based auto-configuration of domain-specific Conformer hyper-parameters in addition to parameter fine-tuning; fine-grained elderly speaker adaptation using learning hidden unit contributions (LHUC); and two-pass cross-system rescoring based combination with hybrid TDNN systems. An overall word error rate (WER) reduction of 13.6% absolute (34.8% relative) was obtained on the evaluation data of 48 elderly speakers. Using the final systems' recognition outputs to extract textual features, the best-published speech recognition based AD detection accuracy of 91.7% was obtained.
On-the-fly Feature Based Speaker Adaptation for Dysarthric and Elderly Speech Recognition
Apr 05, 2022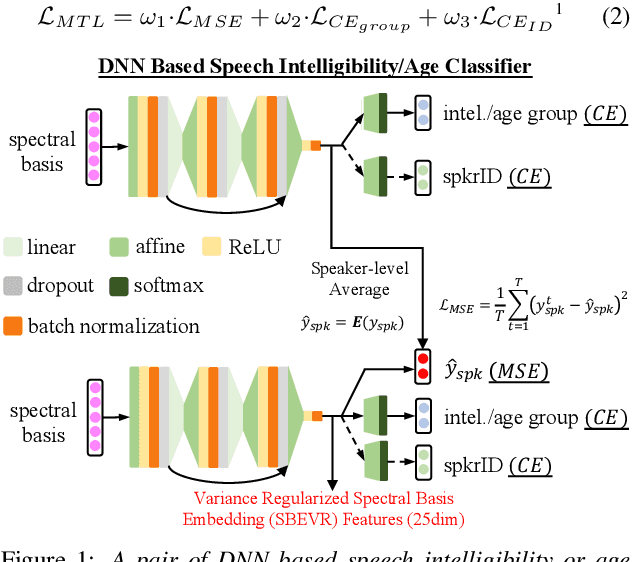
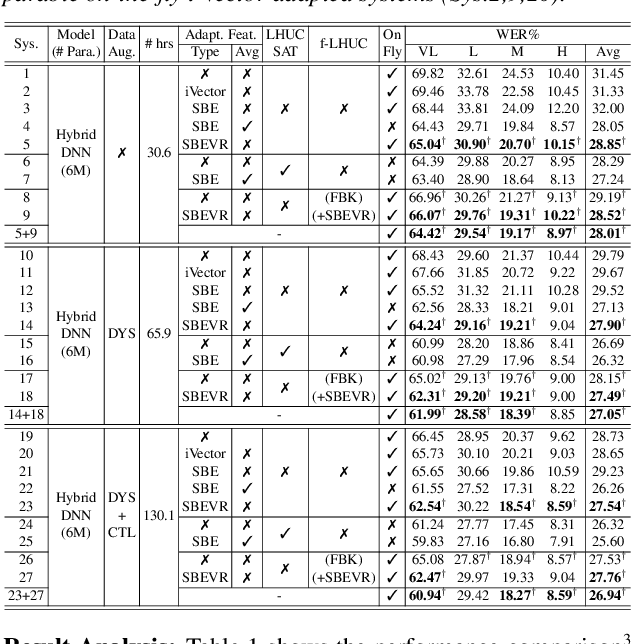
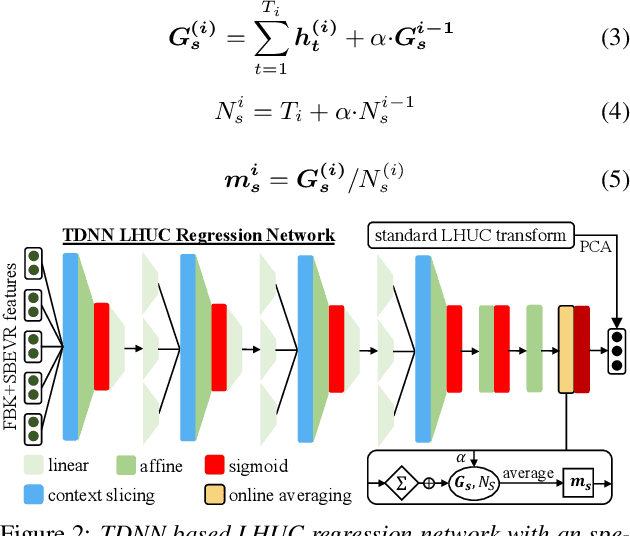
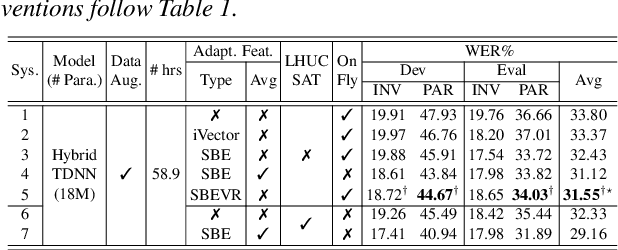
Abstract:Automatic recognition of dysarthric and elderly speech highly challenging tasks to date. Speaker-level heterogeneity attributed to accent or gender commonly found in normal speech, when aggregated with age and speech impairment severity, create large diversity among speakers. Speaker adaptation techniques play a crucial role in personalization of ASR systems for such users. Their mobility issues limit the amount of speaker-level data available for model based adaptation. To this end, this paper investigates two novel forms of feature based on-the-fly rapid speaker adaptation approaches. The first is based on speaker-level variance regularized spectral basis embedding (SBEVR) features, while the other uses on-the-fly learning hidden unit contributions (LHUC) transforms conditioned on speaker-level spectral features. Experiments conducted on the UASpeech dysarthric and DimentiaBank Pitt elderly speech datasets suggest the proposed SBEVR features based adaptation statistically significantly outperform both the baseline on-the-fly i-Vector adapted hybrid TDNN/DNN systems by up to 2.48% absolute (7.92% relative) reduction in word error rate (WER), and offline batch mode model based LHUC adaptation using all speaker-level data by 0.78% absolute (2.41% relative) in WER reduction.
Speaker Adaptation Using Spectro-Temporal Deep Features for Dysarthric and Elderly Speech Recognition
Mar 17, 2022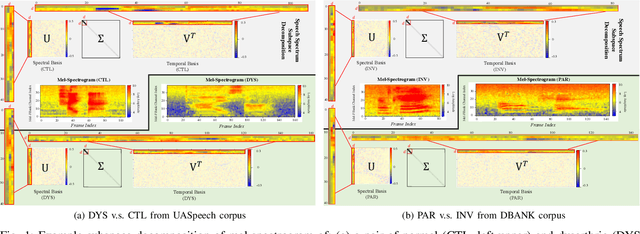
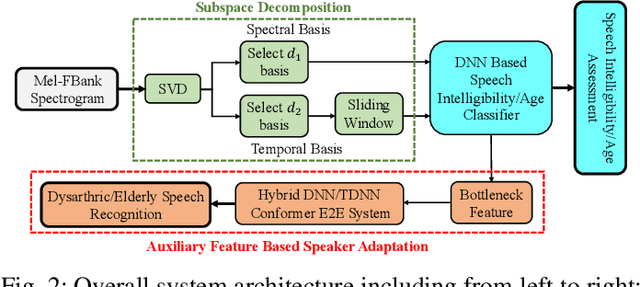
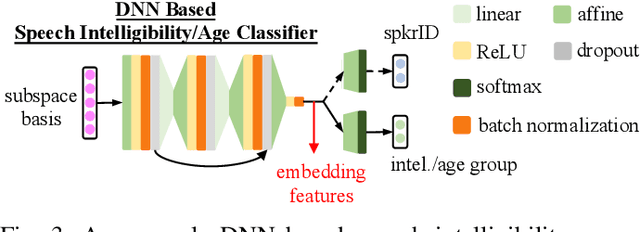
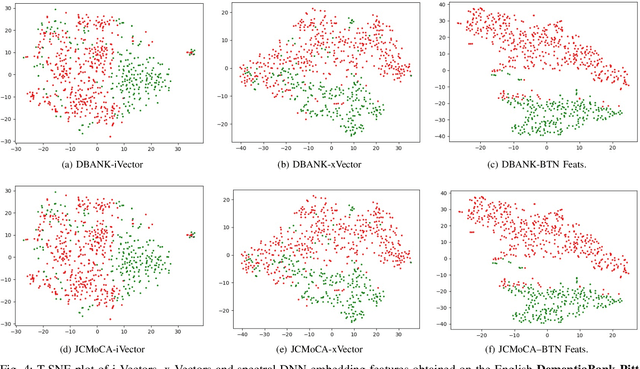
Abstract:Despite the rapid progress of automatic speech recognition (ASR) technologies targeting normal speech in recent decades, accurate recognition of dysarthric and elderly speech remains highly challenging tasks to date. Sources of heterogeneity commonly found in normal speech including accent or gender, when further compounded with the variability over age and speech pathology severity level, create large diversity among speakers. To this end, speaker adaptation techniques play a key role in personalization of ASR systems for such users. Motivated by the spectro-temporal level differences between dysarthric, elderly and normal speech that systematically manifest in articulatory imprecision, decreased volume and clarity, slower speaking rates and increased dysfluencies, novel spectrotemporal subspace basis deep embedding features derived using SVD speech spectrum decomposition are proposed in this paper to facilitate auxiliary feature based speaker adaptation of state-of-the-art hybrid DNN/TDNN and end-to-end Conformer speech recognition systems. Experiments were conducted on four tasks: the English UASpeech and TORGO dysarthric speech corpora; the English DementiaBank Pitt and Cantonese JCCOCC MoCA elderly speech datasets. The proposed spectro-temporal deep feature adapted systems outperformed baseline i-Vector and xVector adaptation by up to 2.63% absolute (8.63% relative) reduction in word error rate (WER). Consistent performance improvements were retained after model based speaker adaptation using learning hidden unit contributions (LHUC) was further applied. The best speaker adapted system using the proposed spectral basis embedding features produced the lowest published WER of 25.05% on the UASpeech test set of 16 dysarthric speakers.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge