Zhiyang Teng
MMaDA-Parallel: Multimodal Large Diffusion Language Models for Thinking-Aware Editing and Generation
Nov 18, 2025Abstract:While thinking-aware generation aims to improve performance on complex tasks, we identify a critical failure mode where existing sequential, autoregressive approaches can paradoxically degrade performance due to error propagation. To systematically analyze this issue, we propose ParaBench, a new benchmark designed to evaluate both text and image output modalities. Our analysis using ParaBench reveals that this performance degradation is strongly correlated with poor alignment between the generated reasoning and the final image. To resolve this, we propose a parallel multimodal diffusion framework, MMaDA-Parallel, that enables continuous, bidirectional interaction between text and images throughout the entire denoising trajectory. MMaDA-Parallel is trained with supervised finetuning and then further optimized by Parallel Reinforcement Learning (ParaRL), a novel strategy that applies semantic rewards along the trajectory to enforce cross-modal consistency. Experiments validate that our model significantly improves cross-modal alignment and semantic consistency, achieving a 6.9\% improvement in Output Alignment on ParaBench compared to the state-of-the-art model, Bagel, establishing a more robust paradigm for thinking-aware image synthesis. Our code is open-sourced at https://github.com/tyfeld/MMaDA-Parallel
Open-o3 Video: Grounded Video Reasoning with Explicit Spatio-Temporal Evidence
Oct 23, 2025Abstract:Most video reasoning models only generate textual reasoning traces without indicating when and where key evidence appears. Recent models such as OpenAI-o3 have sparked wide interest in evidence-centered reasoning for images, yet extending this ability to videos is more challenging, as it requires joint temporal tracking and spatial localization across dynamic scenes. We introduce Open-o3 Video, a non-agent framework that integrates explicit spatio-temporal evidence into video reasoning, and carefully collect training data and design training strategies to address the aforementioned challenges. The model highlights key timestamps, objects, and bounding boxes alongside its answers, allowing reasoning to be grounded in concrete visual observations. To enable this functionality, we first curate and build two high-quality datasets, STGR-CoT-30k for SFT and STGR-RL-36k for RL, with carefully constructed temporal and spatial annotations, since most existing datasets offer either temporal spans for videos or spatial boxes on images, lacking unified spatio-temporal supervision and reasoning traces. Then, we adopt a cold-start reinforcement learning strategy with multiple specially designed rewards that jointly encourage answer accuracy, temporal alignment, and spatial precision. On V-STAR benchmark, Open-o3 Video achieves state-of-the-art performance, raising mAM by 14.4% and mLGM by 24.2% on the Qwen2.5-VL baseline. Consistent improvements are also observed on a broad range of video understanding benchmarks, including VideoMME, WorldSense, VideoMMMU, and TVGBench. Beyond accuracy, the reasoning traces produced by Open-o3 Video also provide valuable signals for test-time scaling, enabling confidence-aware verification and improving answer reliability.
GeoSketch: A Neural-Symbolic Approach to Geometric Multimodal Reasoning with Auxiliary Line Construction and Affine Transformation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Geometric Problem Solving (GPS) poses a unique challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), requiring not only the joint interpretation of text and diagrams but also iterative visuospatial reasoning. While existing approaches process diagrams as static images, they lack the capacity for dynamic manipulation - a core aspect of human geometric reasoning involving auxiliary line construction and affine transformations. We present GeoSketch, a neural-symbolic framework that recasts geometric reasoning as an interactive perception-reasoning-action loop. GeoSketch integrates: (1) a Perception module that abstracts diagrams into structured logic forms, (2) a Symbolic Reasoning module that applies geometric theorems to decide the next deductive step, and (3) a Sketch Action module that executes operations such as drawing auxiliary lines or applying transformations, thereby updating the diagram in a closed loop. To train this agent, we develop a two-stage pipeline: supervised fine-tuning on 2,000 symbolic-curated trajectories followed by reinforcement learning with dense, symbolic rewards to enhance robustness and strategic exploration. To evaluate this paradigm, we introduce the GeoSketch Benchmark, a high-quality set of 390 geometry problems requiring auxiliary construction or affine transformations. Experiments on strong MLLM baselines demonstrate that GeoSketch significantly improves stepwise reasoning accuracy and problem-solving success over static perception methods. By unifying hierarchical decision-making, executable visual actions, and symbolic verification, GeoSketch advances multimodal reasoning from static interpretation to dynamic, verifiable interaction, establishing a new foundation for solving complex visuospatial problems.
Logic Agent: Enhancing Validity with Logic Rule Invocation
Apr 28, 2024Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has emerged as a pivotal technique for augmenting the inferential capabilities of language models during reasoning tasks. Despite its advancements, CoT often grapples with challenges in validating reasoning validity and ensuring informativeness. Addressing these limitations, this paper introduces the Logic Agent (LA), an agent-based framework aimed at enhancing the validity of reasoning processes in Large Language Models (LLMs) through strategic logic rule invocation. Unlike conventional approaches, LA transforms LLMs into logic agents that dynamically apply propositional logic rules, initiating the reasoning process by converting natural language inputs into structured logic forms. The logic agent leverages a comprehensive set of predefined functions to systematically navigate the reasoning process. This methodology not only promotes the structured and coherent generation of reasoning constructs but also significantly improves their interpretability and logical coherence. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate LA's capacity to scale effectively across various model sizes, markedly improving the precision of complex reasoning across diverse tasks.
Multi-scale 2D Temporal Map Diffusion Models for Natural Language Video Localization
Jan 16, 2024Abstract:Natural Language Video Localization (NLVL), grounding phrases from natural language descriptions to corresponding video segments, is a complex yet critical task in video understanding. Despite ongoing advancements, many existing solutions lack the capability to globally capture temporal dynamics of the video data. In this study, we present a novel approach to NLVL that aims to address this issue. Our method involves the direct generation of a global 2D temporal map via a conditional denoising diffusion process, based on the input video and language query. The main challenges are the inherent sparsity and discontinuity of a 2D temporal map in devising the diffusion decoder. To address these challenges, we introduce a multi-scale technique and develop an innovative diffusion decoder. Our approach effectively encapsulates the interaction between the query and video data across various time scales. Experiments on the Charades and DiDeMo datasets underscore the potency of our design.
Refining Latent Homophilic Structures over Heterophilic Graphs for Robust Graph Convolution Networks
Dec 27, 2023



Abstract:Graph convolution networks (GCNs) are extensively utilized in various graph tasks to mine knowledge from spatial data. Our study marks the pioneering attempt to quantitatively investigate the GCN robustness over omnipresent heterophilic graphs for node classification. We uncover that the predominant vulnerability is caused by the structural out-of-distribution (OOD) issue. This finding motivates us to present a novel method that aims to harden GCNs by automatically learning Latent Homophilic Structures over heterophilic graphs. We term such a methodology as LHS. To elaborate, our initial step involves learning a latent structure by employing a novel self-expressive technique based on multi-node interactions. Subsequently, the structure is refined using a pairwisely constrained dual-view contrastive learning approach. We iteratively perform the above procedure, enabling a GCN model to aggregate information in a homophilic way on heterophilic graphs. Armed with such an adaptable structure, we can properly mitigate the structural OOD threats over heterophilic graphs. Experiments on various benchmarks show the effectiveness of the proposed LHS approach for robust GCNs.
How Well Do Text Embedding Models Understand Syntax?
Nov 14, 2023Abstract:Text embedding models have significantly contributed to advancements in natural language processing by adeptly capturing semantic properties of textual data. However, the ability of these models to generalize across a wide range of syntactic contexts remains under-explored. In this paper, we first develop an evaluation set, named \textbf{SR}, to scrutinize the capability for syntax understanding of text embedding models from two crucial syntactic aspects: Structural heuristics, and Relational understanding among concepts, as revealed by the performance gaps in previous studies. Our findings reveal that existing text embedding models have not sufficiently addressed these syntactic understanding challenges, and such ineffectiveness becomes even more apparent when evaluated against existing benchmark datasets. Furthermore, we conduct rigorous analysis to unearth factors that lead to such limitations and examine why previous evaluations fail to detect such ineffectiveness. Lastly, we propose strategies to augment the generalization ability of text embedding models in diverse syntactic scenarios. This study serves to highlight the hurdles associated with syntactic generalization and provides pragmatic guidance for boosting model performance across varied syntactic contexts.
GLoRE: Evaluating Logical Reasoning of Large Language Models
Oct 13, 2023



Abstract:Recently, large language models (LLMs), including notable models such as GPT-4 and burgeoning community models, have showcased significant general language understanding abilities. However, there has been a scarcity of attempts to assess the logical reasoning capacities of these LLMs, an essential facet of natural language understanding. To encourage further investigation in this area, we introduce GLoRE, a meticulously assembled General Logical Reasoning Evaluation benchmark comprised of 12 datasets that span three different types of tasks. Our experimental results show that compared to the performance of human and supervised fine-tuning, the logical reasoning capabilities of open LLM models necessitate additional improvement; ChatGPT and GPT-4 show a strong capability of logical reasoning, with GPT-4 surpassing ChatGPT by a large margin. We propose a self-consistency probing method to enhance the accuracy of ChatGPT and a fine-tuned method to boost the performance of an open LLM. We release the datasets and evaluation programs to facilitate future research.
Fast-DetectGPT: Efficient Zero-Shot Detection of Machine-Generated Text via Conditional Probability Curvature
Oct 08, 2023
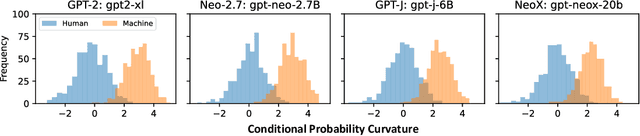
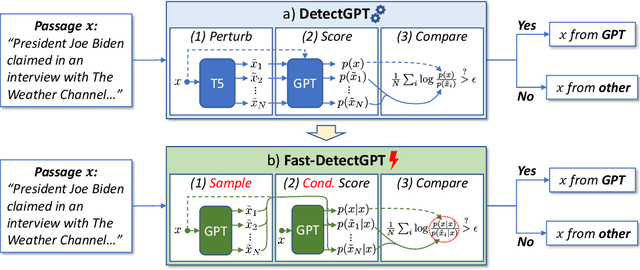
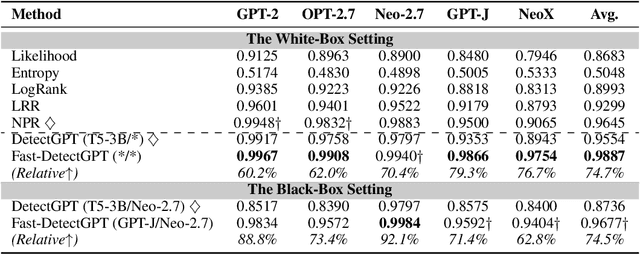
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have shown the ability to produce fluent and cogent content, presenting both productivity opportunities and societal risks. To build trustworthy AI systems, it is imperative to distinguish between machine-generated and human-authored content. The leading zero-shot detector, DetectGPT, showcases commendable performance but is marred by its intensive computational costs. In this paper, we introduce the concept of conditional probability curvature to elucidate discrepancies in word choices between LLMs and humans within a given context. Utilizing this curvature as a foundational metric, we present Fast-DetectGPT, an optimized zero-shot detector, which substitutes DetectGPT's perturbation step with a more efficient sampling step. Our evaluations on various datasets, source models, and test conditions indicate that Fast-DetectGPT not only outperforms DetectGPT in both the white-box and black-box settings but also accelerates the detection process by a factor of 340, as detailed in Table 1.
Multimodal Relation Extraction with Cross-Modal Retrieval and Synthesis
May 25, 2023Abstract:Multimodal relation extraction (MRE) is the task of identifying the semantic relationships between two entities based on the context of the sentence image pair. Existing retrieval-augmented approaches mainly focused on modeling the retrieved textual knowledge, but this may not be able to accurately identify complex relations. To improve the prediction, this research proposes to retrieve textual and visual evidence based on the object, sentence, and whole image. We further develop a novel approach to synthesize the object-level, image-level, and sentence-level information for better reasoning between the same and different modalities. Extensive experiments and analyses show that the proposed method is able to effectively select and compare evidence across modalities and significantly outperforms state-of-the-art models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge