Hanmeng Liu
ReEfBench: Quantifying the Reasoning Efficiency of LLMs
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Test-time scaling has enabled Large Language Models (LLMs) to tackle complex reasoning, yet the limitations of current Chain-of-Thought (CoT) evaluation obscures whether performance gains stem from genuine reasoning or mere verbosity. To address this, (1) we propose a novel neuro-symbolic framework for the non-intrusive, comprehensive process-centric evaluation of reasoning. (2) Through this lens, we identify four distinct behavioral prototypes and diagnose the failure modes. (3) We examine the impact of inference mode, training strategy, and model scale. Our analysis reveals that extended token generation is not a prerequisite for deep reasoning. Furthermore, we reveal critical constraints: mixing long and short CoT data in training risks in premature saturation and collapse, while distillation into smaller models captures behavioral length but fails to replicate logical efficacy due to intrinsic capacity limits.
GeoSketch: A Neural-Symbolic Approach to Geometric Multimodal Reasoning with Auxiliary Line Construction and Affine Transformation
Sep 26, 2025Abstract:Geometric Problem Solving (GPS) poses a unique challenge for Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs), requiring not only the joint interpretation of text and diagrams but also iterative visuospatial reasoning. While existing approaches process diagrams as static images, they lack the capacity for dynamic manipulation - a core aspect of human geometric reasoning involving auxiliary line construction and affine transformations. We present GeoSketch, a neural-symbolic framework that recasts geometric reasoning as an interactive perception-reasoning-action loop. GeoSketch integrates: (1) a Perception module that abstracts diagrams into structured logic forms, (2) a Symbolic Reasoning module that applies geometric theorems to decide the next deductive step, and (3) a Sketch Action module that executes operations such as drawing auxiliary lines or applying transformations, thereby updating the diagram in a closed loop. To train this agent, we develop a two-stage pipeline: supervised fine-tuning on 2,000 symbolic-curated trajectories followed by reinforcement learning with dense, symbolic rewards to enhance robustness and strategic exploration. To evaluate this paradigm, we introduce the GeoSketch Benchmark, a high-quality set of 390 geometry problems requiring auxiliary construction or affine transformations. Experiments on strong MLLM baselines demonstrate that GeoSketch significantly improves stepwise reasoning accuracy and problem-solving success over static perception methods. By unifying hierarchical decision-making, executable visual actions, and symbolic verification, GeoSketch advances multimodal reasoning from static interpretation to dynamic, verifiable interaction, establishing a new foundation for solving complex visuospatial problems.
Evaluating the Logical Reasoning Abilities of Large Reasoning Models
May 17, 2025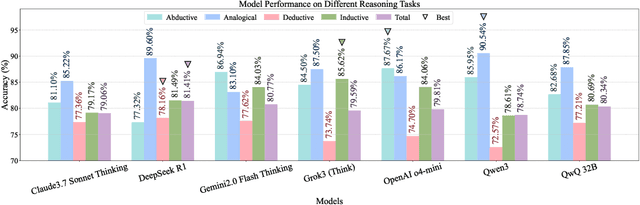
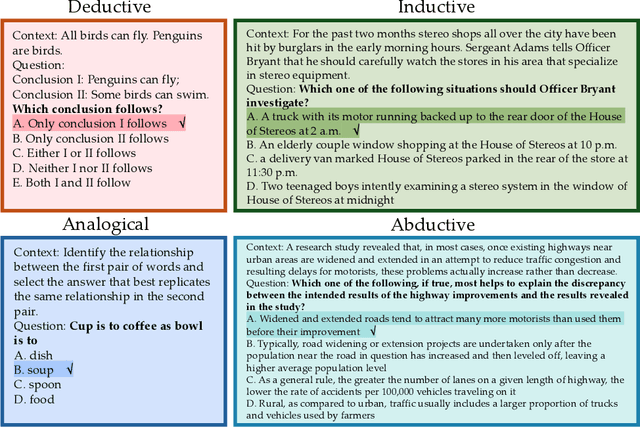
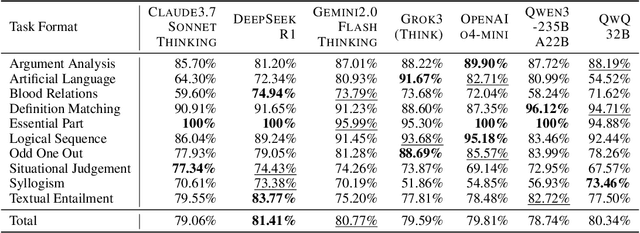
Abstract:Large reasoning models, often post-trained on long chain-of-thought (long CoT) data with reinforcement learning, achieve state-of-the-art performance on mathematical, coding, and domain-specific reasoning benchmarks. However, their logical reasoning capabilities - fundamental to human cognition and independent of domain knowledge - remain understudied. To address this gap, we introduce LogiEval, a holistic benchmark for evaluating logical reasoning in large reasoning models. LogiEval spans diverse reasoning types (deductive, inductive, analogical, and abductive) and task formats (e.g., logical sequence, argument analysis), sourced from high-quality human examinations (e.g., LSAT, GMAT). Our experiments demonstrate that modern reasoning models excel at 4-choice argument analysis problems and analogical reasoning, surpassing human performance, yet exhibit uneven capabilities across reasoning types and formats, highlighting limitations in their generalization. Our analysis reveals that human performance does not mirror model failure distributions. To foster further research, we curate LogiEval-Hard, a challenging subset identified through a novel screening paradigm where small-model failures (Qwen3-30B-A3B) reliably predict difficulties for larger models. Modern models show striking, consistent failures on LogiEval-Hard. This demonstrates that fundamental reasoning bottlenecks persist across model scales, and establishes LogiEval-Hard as both a diagnostic tool and a rigorous testbed for advancing logical reasoning in LLMs.
Logical Reasoning in Large Language Models: A Survey
Feb 13, 2025
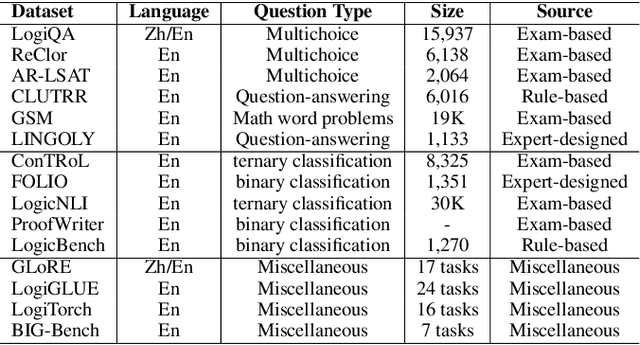

Abstract:With the emergence of advanced reasoning models like OpenAI o3 and DeepSeek-R1, large language models (LLMs) have demonstrated remarkable reasoning capabilities. However, their ability to perform rigorous logical reasoning remains an open question. This survey synthesizes recent advancements in logical reasoning within LLMs, a critical area of AI research. It outlines the scope of logical reasoning in LLMs, its theoretical foundations, and the benchmarks used to evaluate reasoning proficiency. We analyze existing capabilities across different reasoning paradigms - deductive, inductive, abductive, and analogical - and assess strategies to enhance reasoning performance, including data-centric tuning, reinforcement learning, decoding strategies, and neuro-symbolic approaches. The review concludes with future directions, emphasizing the need for further exploration to strengthen logical reasoning in AI systems.
Break the Chain: Large Language Models Can be Shortcut Reasoners
Jun 04, 2024
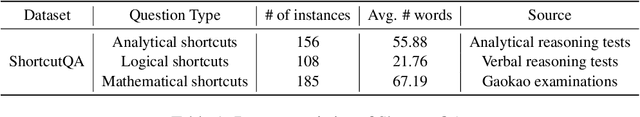
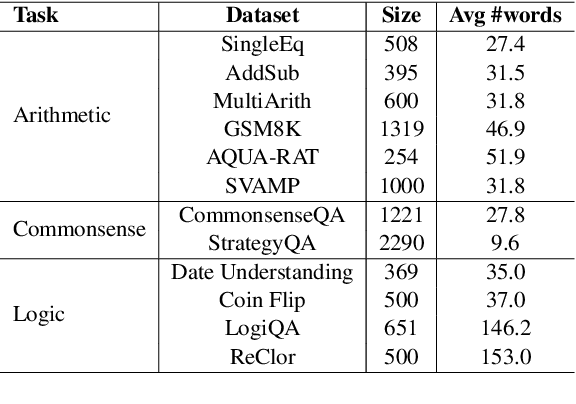
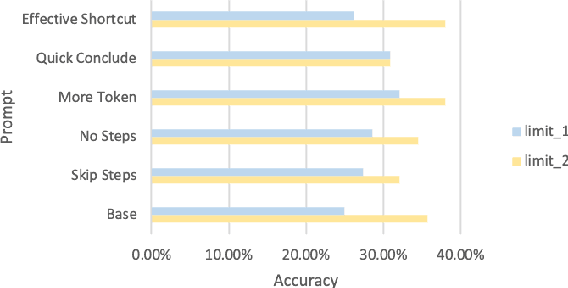
Abstract:Recent advancements in Chain-of-Thought (CoT) reasoning utilize complex modules but are hampered by high token consumption, limited applicability, and challenges in reproducibility. This paper conducts a critical evaluation of CoT prompting, extending beyond arithmetic to include complex logical and commonsense reasoning tasks, areas where standard CoT methods fall short. We propose the integration of human-like heuristics and shortcuts into language models (LMs) through "break the chain" strategies. These strategies disrupt traditional CoT processes using controlled variables to assess their efficacy. Additionally, we develop innovative zero-shot prompting strategies that encourage the use of shortcuts, enabling LMs to quickly exploit reasoning clues and bypass detailed procedural steps. Our comprehensive experiments across various LMs, both commercial and open-source, reveal that LMs maintain effective performance with "break the chain" strategies. We also introduce ShortcutQA, a dataset specifically designed to evaluate reasoning through shortcuts, compiled from competitive tests optimized for heuristic reasoning tasks such as forward/backward reasoning and simplification. Our analysis confirms that ShortcutQA not only poses a robust challenge to LMs but also serves as an essential benchmark for enhancing reasoning efficiency in AI.
Logic Agent: Enhancing Validity with Logic Rule Invocation
Apr 28, 2024Abstract:Chain-of-Thought (CoT) prompting has emerged as a pivotal technique for augmenting the inferential capabilities of language models during reasoning tasks. Despite its advancements, CoT often grapples with challenges in validating reasoning validity and ensuring informativeness. Addressing these limitations, this paper introduces the Logic Agent (LA), an agent-based framework aimed at enhancing the validity of reasoning processes in Large Language Models (LLMs) through strategic logic rule invocation. Unlike conventional approaches, LA transforms LLMs into logic agents that dynamically apply propositional logic rules, initiating the reasoning process by converting natural language inputs into structured logic forms. The logic agent leverages a comprehensive set of predefined functions to systematically navigate the reasoning process. This methodology not only promotes the structured and coherent generation of reasoning constructs but also significantly improves their interpretability and logical coherence. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate LA's capacity to scale effectively across various model sizes, markedly improving the precision of complex reasoning across diverse tasks.
LogiCoT: Logical Chain-of-Thought Instruction-Tuning Data Collection with GPT-4
May 20, 2023Abstract:Generative Pre-trained Transformer 4 (GPT-4) demonstrates impressive chain-of-thought reasoning ability. Recent work on self-instruction tuning, such as Alpaca, has focused on enhancing the general proficiency of models. These instructions enable the model to achieve performance comparable to GPT-3.5 on general tasks like open-domain text generation and paraphrasing. However, they fall short of helping the model handle complex reasoning tasks. To bridge the gap, this paper presents LogiCoT, a new instruction-tuning dataset for Logical Chain-of-Thought reasoning with GPT-4. We elaborate on the process of harvesting instructions for prompting GPT-4 to generate chain-of-thought rationales. LogiCoT serves as an instruction set for teaching models of logical reasoning and elicits general reasoning skills.
Evaluating the Logical Reasoning Ability of ChatGPT and GPT-4
Apr 20, 2023



Abstract:Harnessing logical reasoning ability is a comprehensive natural language understanding endeavor. With the release of Generative Pretrained Transformer 4 (GPT-4), highlighted as "advanced" at reasoning tasks, we are eager to learn the GPT-4 performance on various logical reasoning tasks. This report analyses multiple logical reasoning datasets, with popular benchmarks like LogiQA and ReClor, and newly-released datasets like AR-LSAT. We test the multi-choice reading comprehension and natural language inference tasks with benchmarks requiring logical reasoning. We further construct a logical reasoning out-of-distribution dataset to investigate the robustness of ChatGPT and GPT-4. We also make a performance comparison between ChatGPT and GPT-4. Experiment results show that ChatGPT performs significantly better than the RoBERTa fine-tuning method on most logical reasoning benchmarks. With early access to the GPT-4 API we are able to conduct intense experiments on the GPT-4 model. The results show GPT-4 yields even higher performance on most logical reasoning datasets. Among benchmarks, ChatGPT and GPT-4 do relatively well on well-known datasets like LogiQA and ReClor. However, the performance drops significantly when handling newly released and out-of-distribution datasets. Logical reasoning remains challenging for ChatGPT and GPT-4, especially on out-of-distribution and natural language inference datasets. We release the prompt-style logical reasoning datasets as a benchmark suite and name it LogiEval.
GLUE-X: Evaluating Natural Language Understanding Models from an Out-of-distribution Generalization Perspective
Nov 15, 2022



Abstract:Pre-trained language models (PLMs) improve the model generalization by leveraging massive data as the training corpus in the pre-training phase. However, currently, the out-of-distribution (OOD) generalization becomes a generally ill-posed problem, even for the large-scale PLMs in natural language understanding tasks, which prevents the deployment of NLP methods in the real world. To facilitate the research in this direction, this paper makes the first attempt to establish a unified benchmark named GLUE-X, highlighting the importance of OOD robustness and providing insights on how to measure the robustness of a model and how to improve it. To this end, we collect 13 publicly available datasets as OOD test data, and conduct evaluations on 8 classic NLP tasks over \emph{18} popularly used models. Our findings confirm that the OOD accuracy in NLP tasks needs to be paid more attention to since the significant performance decay compared to ID accuracy has been found in all settings.
Solving Aspect Category Sentiment Analysis as a Text Generation Task
Oct 14, 2021



Abstract:Aspect category sentiment analysis has attracted increasing research attention. The dominant methods make use of pre-trained language models by learning effective aspect category-specific representations, and adding specific output layers to its pre-trained representation. We consider a more direct way of making use of pre-trained language models, by casting the ACSA tasks into natural language generation tasks, using natural language sentences to represent the output. Our method allows more direct use of pre-trained knowledge in seq2seq language models by directly following the task setting during pre-training. Experiments on several benchmarks show that our method gives the best reported results, having large advantages in few-shot and zero-shot settings.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge