Zhenge Jia
A 10.60 $μ$W 150 GOPS Mixed-Bit-Width Sparse CNN Accelerator for Life-Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmia Detection
Oct 22, 2024



Abstract:This paper proposes an ultra-low power, mixed-bit-width sparse convolutional neural network (CNN) accelerator to accelerate ventricular arrhythmia (VA) detection. The chip achieves 50% sparsity in a quantized 1D CNN using a sparse processing element (SPE) architecture. Measurement on the prototype chip TSMC 40nm CMOS low-power (LP) process for the VA classification task demonstrates that it consumes 10.60 $\mu$W of power while achieving a performance of 150 GOPS and a diagnostic accuracy of 99.95%. The computation power density is only 0.57 $\mu$W/mm$^2$, which is 14.23X smaller than state-of-the-art works, making it highly suitable for implantable and wearable medical devices.
Rethinking Medical Anomaly Detection in Brain MRI: An Image Quality Assessment Perspective
Aug 15, 2024



Abstract:Reconstruction-based methods, particularly those leveraging autoencoders, have been widely adopted to perform anomaly detection in brain MRI. While most existing works try to improve detection accuracy by proposing new model structures or algorithms, we tackle the problem through image quality assessment, an underexplored perspective in the field. We propose a fusion quality loss function that combines Structural Similarity Index Measure loss with l1 loss, offering a more comprehensive evaluation of reconstruction quality. Additionally, we introduce a data pre-processing strategy that enhances the average intensity ratio (AIR) between normal and abnormal regions, further improving the distinction of anomalies. By fusing the aforementioned two methods, we devise the image quality assessment (IQA) approach. The proposed IQA approach achieves significant improvements (>10%) in terms of Dice coefficient (DICE) and Area Under the Precision-Recall Curve (AUPRC) on the BraTS21 (T2, FLAIR) and MSULB datasets when compared with state-of-the-art methods. These results highlight the importance of invoking the comprehensive image quality assessment in medical anomaly detection and provide a new perspective for future research in this field.
Empirical Guidelines for Deploying LLMs onto Resource-constrained Edge Devices
Jun 06, 2024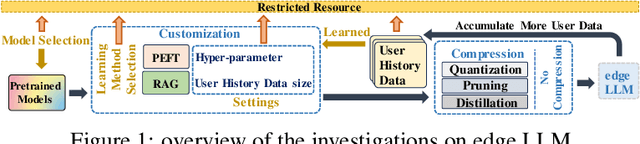
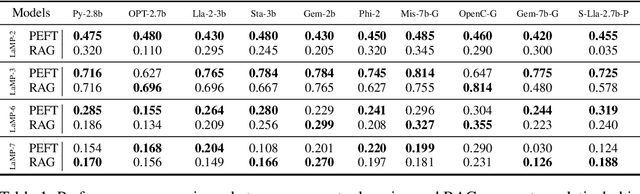
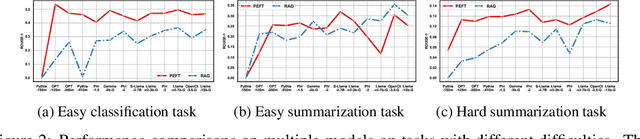
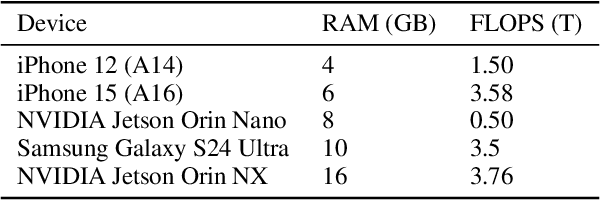
Abstract:The scaling laws have become the de facto guidelines for designing large language models (LLMs), but they were studied under the assumption of unlimited computing resources for both training and inference. As LLMs are increasingly used as personalized intelligent assistants, their customization (i.e., learning through fine-tuning) and deployment onto resource-constrained edge devices will become more and more prevalent. An urging but open question is how a resource-constrained computing environment would affect the design choices for a personalized LLM. We study this problem empirically in this work. In particular, we consider the tradeoffs among a number of key design factors and their intertwined impacts on learning efficiency and accuracy. The factors include the learning methods for LLM customization, the amount of personalized data used for learning customization, the types and sizes of LLMs, the compression methods of LLMs, the amount of time afforded to learn, and the difficulty levels of the target use cases. Through extensive experimentation and benchmarking, we draw a number of surprisingly insightful guidelines for deploying LLMs onto resource-constrained devices. For example, an optimal choice between parameter learning and RAG may vary depending on the difficulty of the downstream task, the longer fine-tuning time does not necessarily help the model, and a compressed LLM may be a better choice than an uncompressed LLM to learn from limited personalized data.
Robust Implementation of Retrieval-Augmented Generation on Edge-based Computing-in-Memory Architectures
May 07, 2024



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) deployed on edge devices learn through fine-tuning and updating a certain portion of their parameters. Although such learning methods can be optimized to reduce resource utilization, the overall required resources remain a heavy burden on edge devices. Instead, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG), a resource-efficient LLM learning method, can improve the quality of the LLM-generated content without updating model parameters. However, the RAG-based LLM may involve repetitive searches on the profile data in every user-LLM interaction. This search can lead to significant latency along with the accumulation of user data. Conventional efforts to decrease latency result in restricting the size of saved user data, thus reducing the scalability of RAG as user data continuously grows. It remains an open question: how to free RAG from the constraints of latency and scalability on edge devices? In this paper, we propose a novel framework to accelerate RAG via Computing-in-Memory (CiM) architectures. It accelerates matrix multiplications by performing in-situ computation inside the memory while avoiding the expensive data transfer between the computing unit and memory. Our framework, Robust CiM-backed RAG (RoCR), utilizing a novel contrastive learning-based training method and noise-aware training, can enable RAG to efficiently search profile data with CiM. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work utilizing CiM to accelerate RAG.
Enabling On-Device Large Language Model Personalization with Self-Supervised Data Selection and Synthesis
Dec 02, 2023Abstract:After a large language model (LLM) is deployed on edge devices, it is desirable for these devices to learn from user-generated conversation data to generate user-specific and personalized responses in real-time. However, user-generated data usually contains sensitive and private information, and uploading such data to the cloud for annotation is not preferred if not prohibited. While it is possible to obtain annotation locally by directly asking users to provide preferred responses, such annotations have to be sparse to not affect user experience. In addition, the storage of edge devices is usually too limited to enable large-scale fine-tuning with full user-generated data. It remains an open question how to enable on-device LLM personalization, considering sparse annotation and limited on-device storage. In this paper, we propose a novel framework to select and store the most representative data online in a self-supervised way. Such data has a small memory footprint and allows infrequent requests of user annotations for further fine-tuning. To enhance fine-tuning quality, multiple semantically similar pairs of question texts and expected responses are generated using the LLM. Our experiments show that the proposed framework achieves the best user-specific content-generating capability (accuracy) and fine-tuning speed (performance) compared with vanilla baselines. To the best of our knowledge, this is the very first on-device LLM personalization framework.
TinyML Design Contest for Life-Threatening Ventricular Arrhythmia Detection
May 23, 2023



Abstract:The first ACM/IEEE TinyML Design Contest (TDC) held at the 41st International Conference on Computer-Aided Design (ICCAD) in 2022 is a challenging, multi-month, research and development competition. TDC'22 focuses on real-world medical problems that require the innovation and implementation of artificial intelligence/machine learning (AI/ML) algorithms on implantable devices. The challenge problem of TDC'22 is to develop a novel AI/ML-based real-time detection algorithm for life-threatening ventricular arrhythmia over low-power microcontrollers utilized in Implantable Cardioverter-Defibrillators (ICDs). The dataset contains more than 38,000 5-second intracardiac electrograms (IEGMs) segments over 8 different types of rhythm from 90 subjects. The dedicated hardware platform is NUCLEO-L432KC manufactured by STMicroelectronics. TDC'22, which is open to multi-person teams world-wide, attracted more than 150 teams from over 50 organizations. This paper first presents the medical problem, dataset, and evaluation procedure in detail. It further demonstrates and discusses the designs developed by the leading teams as well as representative results. This paper concludes with the direction of improvement for the future TinyML design for health monitoring applications.
BiTrackGAN: Cascaded CycleGANs to Constraint Face Aging
Apr 22, 2023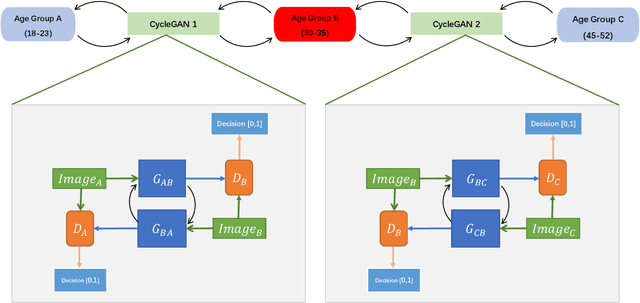
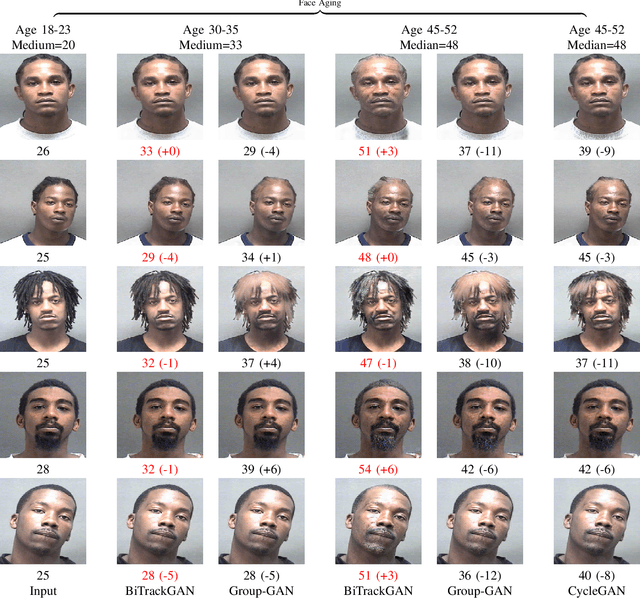

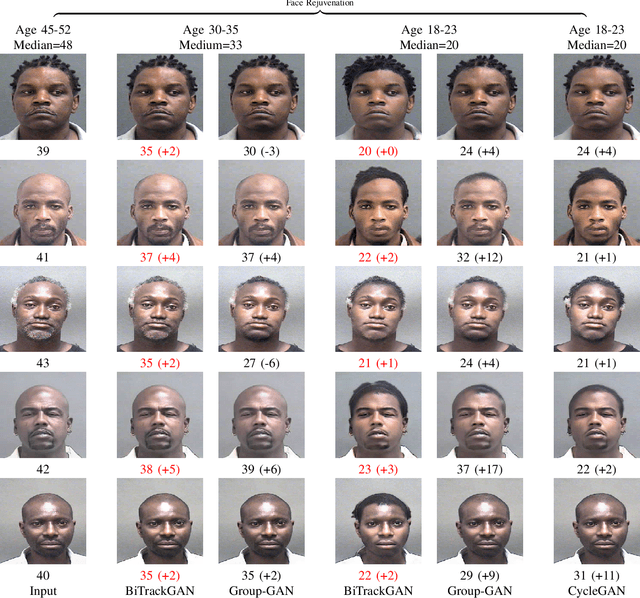
Abstract:With the increased accuracy of modern computer vision technology, many access control systems are equipped with face recognition functions for faster identification. In order to maintain high recognition accuracy, it is necessary to keep the face database up-to-date. However, it is impractical to collect the latest facial picture of the system's user through human effort. Thus, we propose a bottom-up training method for our proposed network to address this challenge. Essentially, our proposed network is a translation pipeline that cascades two CycleGAN blocks (a widely used unpaired image-to-image translation generative adversarial network) called BiTrackGAN. By bottom-up training, it induces an ideal intermediate state between these two CycleGAN blocks, namely the constraint mechanism. Experimental results show that BiTrackGAN achieves more reasonable and diverse cross-age facial synthesis than other CycleGAN-related methods. As far as we know, it is a novel and effective constraint mechanism for more reason and accurate aging synthesis through the CycleGAN approach.
Development of A Real-time POCUS Image Quality Assessment and Acquisition Guidance System
Dec 19, 2022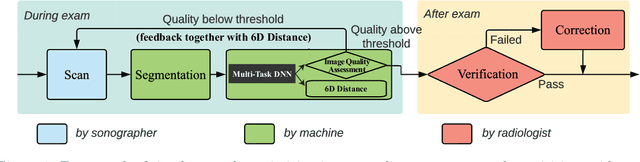
Abstract:Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is one of the most commonly applied tools for cardiac function imaging in the clinical routine of the emergency department and pediatric intensive care unit. The prior studies demonstrate that AI-assisted software can guide nurses or novices without prior sonography experience to acquire POCUS by recognizing the interest region, assessing image quality, and providing instructions. However, these AI algorithms cannot simply replace the role of skilled sonographers in acquiring diagnostic-quality POCUS. Unlike chest X-ray, CT, and MRI, which have standardized imaging protocols, POCUS can be acquired with high inter-observer variability. Though being with variability, they are usually all clinically acceptable and interpretable. In challenging clinical environments, sonographers employ novel heuristics to acquire POCUS in complex scenarios. To help novice learners to expedite the training process while reducing the dependency on experienced sonographers in the curriculum implementation, We will develop a framework to perform real-time AI-assisted quality assessment and probe position guidance to provide training process for novice learners with less manual intervention.
Personalized Deep Learning for Ventricular Arrhythmias Detection on Medical IoT Systems
Aug 18, 2020



Abstract:Life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias (VA) are the leading cause of sudden cardiac death (SCD), which is the most significant cause of natural death in the US. The implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a small device implanted to patients under high risk of SCD as a preventive treatment. The ICD continuously monitors the intracardiac rhythm and delivers shock when detecting the life-threatening VA. Traditional methods detect VA by setting criteria on the detected rhythm. However, those methods suffer from a high inappropriate shock rate and require a regular follow-up to optimize criteria parameters for each ICD recipient. To ameliorate the challenges, we propose the personalized computing framework for deep learning based VA detection on medical IoT systems. The system consists of intracardiac and surface rhythm monitors, and the cloud platform for data uploading, diagnosis, and CNN model personalization. We equip the system with real-time inference on both intracardiac and surface rhythm monitors. To improve the detection accuracy, we enable the monitors to detect VA collaboratively by proposing the cooperative inference. We also introduce the CNN personalization for each patient based on the computing framework to tackle the unlabeled and limited rhythm data problem. When compared with the traditional detection algorithm, the proposed method achieves comparable accuracy on VA rhythm detection and 6.6% reduction in inappropriate shock rate, while the average inference latency is kept at 71ms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge