Z. Morley Mao
RLBoost: Harvesting Preemptible Resources for Cost-Efficient Reinforcement Learning on LLMs
Oct 22, 2025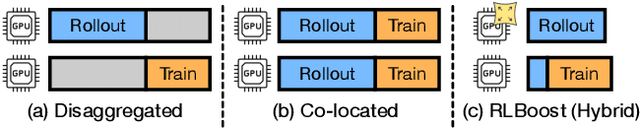
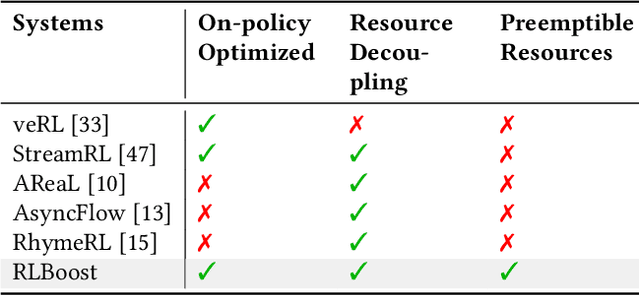
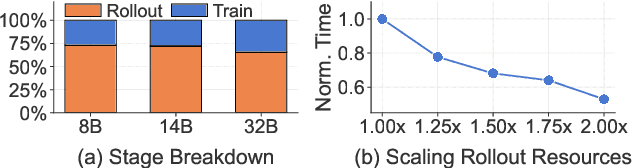
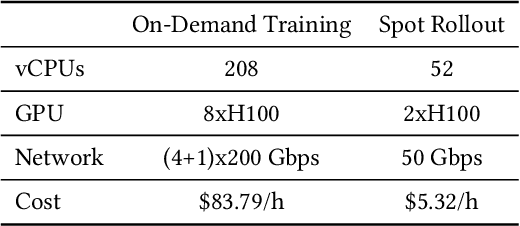
Abstract:Reinforcement learning (RL) has become essential for unlocking advanced reasoning capabilities in large language models (LLMs). RL workflows involve interleaving rollout and training stages with fundamentally different resource requirements. Rollout typically dominates overall execution time, yet scales efficiently through multiple independent instances. In contrast, training requires tightly-coupled GPUs with full-mesh communication. Existing RL frameworks fall into two categories: co-located and disaggregated architectures. Co-located ones fail to address this resource tension by forcing both stages to share the same GPUs. Disaggregated architectures, without modifications of well-established RL algorithms, suffer from resource under-utilization. Meanwhile, preemptible GPU resources, i.e., spot instances on public clouds and spare capacity in production clusters, present significant cost-saving opportunities for accelerating RL workflows, if efficiently harvested for rollout. In this paper, we present RLBoost, a systematic solution for cost-efficient RL training that harvests preemptible GPU resources. Our key insight is that rollout's stateless and embarrassingly parallel nature aligns perfectly with preemptible and often fragmented resources. To efficiently utilize these resources despite frequent and unpredictable availability changes, RLBoost adopts a hybrid architecture with three key techniques: (1) adaptive rollout offload to dynamically adjust workloads on the reserved (on-demand) cluster, (2) pull-based weight transfer that quickly provisions newly available instances, and (3) token-level response collection and migration for efficient preemption handling and continuous load balancing. Extensive experiments show RLBoost increases training throughput by 1.51x-1.97x while improving cost efficiency by 28%-49% compared to using only on-demand GPU resources.
TC-LoRA: Temporally Modulated Conditional LoRA for Adaptive Diffusion Control
Oct 10, 2025
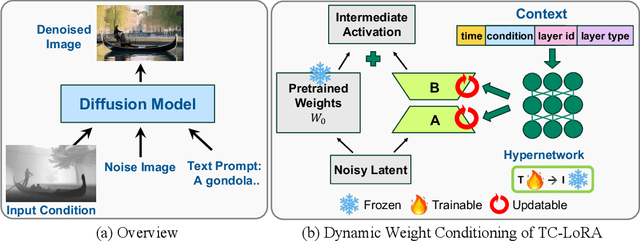


Abstract:Current controllable diffusion models typically rely on fixed architectures that modify intermediate activations to inject guidance conditioned on a new modality. This approach uses a static conditioning strategy for a dynamic, multi-stage denoising process, limiting the model's ability to adapt its response as the generation evolves from coarse structure to fine detail. We introduce TC-LoRA (Temporally Modulated Conditional LoRA), a new paradigm that enables dynamic, context-aware control by conditioning the model's weights directly. Our framework uses a hypernetwork to generate LoRA adapters on-the-fly, tailoring weight modifications for the frozen backbone at each diffusion step based on time and the user's condition. This mechanism enables the model to learn and execute an explicit, adaptive strategy for applying conditional guidance throughout the entire generation process. Through experiments on various data domains, we demonstrate that this dynamic, parametric control significantly enhances generative fidelity and adherence to spatial conditions compared to static, activation-based methods. TC-LoRA establishes an alternative approach in which the model's conditioning strategy is modified through a deeper functional adaptation of its weights, allowing control to align with the dynamic demands of the task and generative stage.
SwingArena: Competitive Programming Arena for Long-context GitHub Issue Solving
May 29, 2025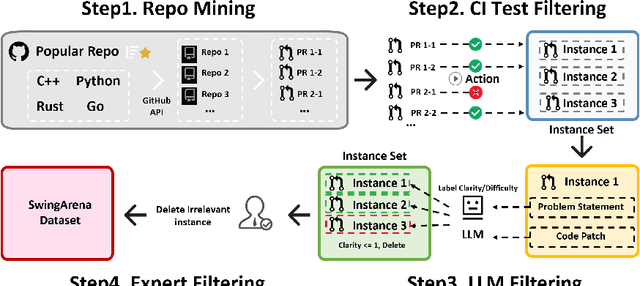
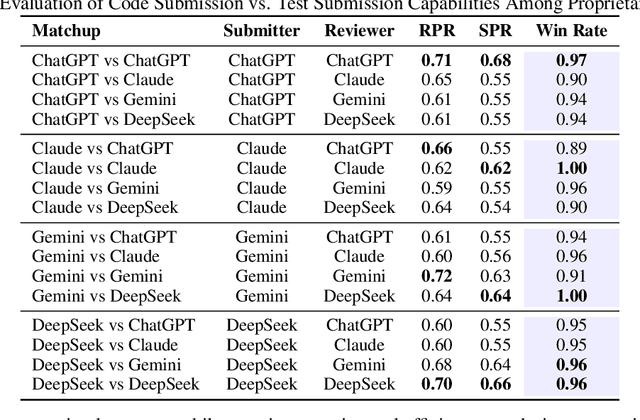
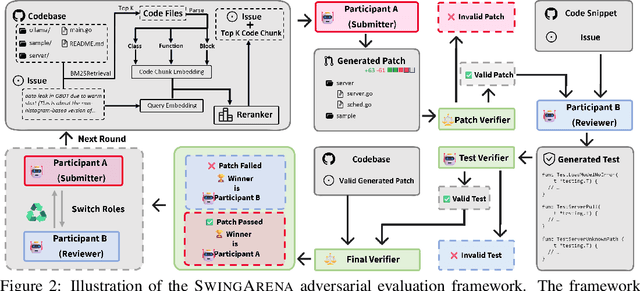
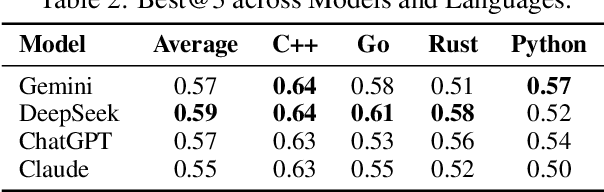
Abstract:We present SwingArena, a competitive evaluation framework for Large Language Models (LLMs) that closely mirrors real-world software development workflows. Unlike traditional static benchmarks, SwingArena models the collaborative process of software iteration by pairing LLMs as submitters, who generate patches, and reviewers, who create test cases and verify the patches through continuous integration (CI) pipelines. To support these interactive evaluations, we introduce a retrieval-augmented code generation (RACG) module that efficiently handles long-context challenges by providing syntactically and semantically relevant code snippets from large codebases, supporting multiple programming languages (C++, Python, Rust, and Go). This enables the framework to scale across diverse tasks and contexts while respecting token limitations. Our experiments, using over 400 high-quality real-world GitHub issues selected from a pool of 2,300 issues, show that models like GPT-4o excel at aggressive patch generation, whereas DeepSeek and Gemini prioritize correctness in CI validation. SwingArena presents a scalable and extensible methodology for evaluating LLMs in realistic, CI-driven software development settings. More details are available on our project page: swing-bench.github.io
HeterMoE: Efficient Training of Mixture-of-Experts Models on Heterogeneous GPUs
Apr 04, 2025Abstract:The Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) architecture has become increasingly popular as a method to scale up large language models (LLMs). To save costs, heterogeneity-aware training solutions have been proposed to utilize GPU clusters made up of both newer and older-generation GPUs. However, existing solutions are agnostic to the performance characteristics of different MoE model components (i.e., attention and expert) and do not fully utilize each GPU's compute capability. In this paper, we introduce HeterMoE, a system to efficiently train MoE models on heterogeneous GPUs. Our key insight is that newer GPUs significantly outperform older generations on attention due to architectural advancements, while older GPUs are still relatively efficient for experts. HeterMoE disaggregates attention and expert computation, where older GPUs are only assigned with expert modules. Through the proposed zebra parallelism, HeterMoE overlaps the computation on different GPUs, in addition to employing an asymmetric expert assignment strategy for fine-grained load balancing to minimize GPU idle time. Our evaluation shows that HeterMoE achieves up to 2.3x speed-up compared to existing MoE training systems, and 1.4x compared to an optimally balanced heterogeneity-aware solution. HeterMoE efficiently utilizes older GPUs by maintaining 95% training throughput on average, even with half of the GPUs in a homogeneous A40 cluster replaced with V100.
FATH: Authentication-based Test-time Defense against Indirect Prompt Injection Attacks
Oct 28, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have been widely deployed as the backbone with additional tools and text information for real-world applications. However, integrating external information into LLM-integrated applications raises significant security concerns. Among these, prompt injection attacks are particularly threatening, where malicious instructions injected in the external text information can exploit LLMs to generate answers as the attackers desire. While both training-time and test-time defense methods have been developed to mitigate such attacks, the unaffordable training costs associated with training-time methods and the limited effectiveness of existing test-time methods make them impractical. This paper introduces a novel test-time defense strategy, named Formatting AuThentication with Hash-based tags (FATH). Unlike existing approaches that prevent LLMs from answering additional instructions in external text, our method implements an authentication system, requiring LLMs to answer all received instructions with a security policy and selectively filter out responses to user instructions as the final output. To achieve this, we utilize hash-based authentication tags to label each response, facilitating accurate identification of responses according to the user's instructions and improving the robustness against adaptive attacks. Comprehensive experiments demonstrate that our defense method can effectively defend against indirect prompt injection attacks, achieving state-of-the-art performance under Llama3 and GPT3.5 models across various attack methods. Our code is released at: https://github.com/Jayfeather1024/FATH
Cocoon: Robust Multi-Modal Perception with Uncertainty-Aware Sensor Fusion
Oct 16, 2024
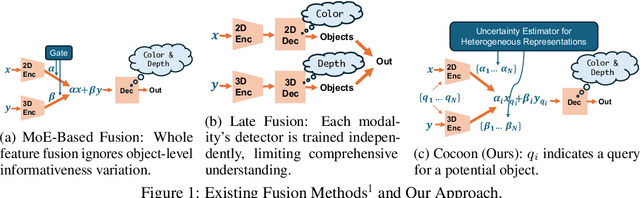
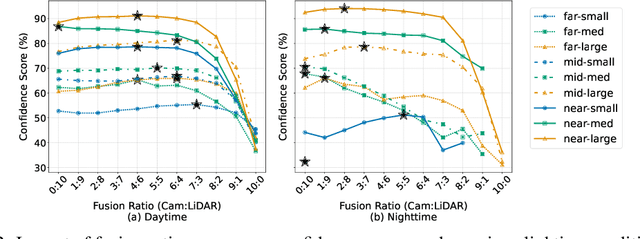
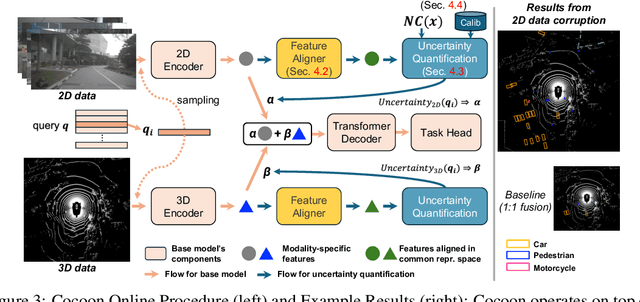
Abstract:An important paradigm in 3D object detection is the use of multiple modalities to enhance accuracy in both normal and challenging conditions, particularly for long-tail scenarios. To address this, recent studies have explored two directions of adaptive approaches: MoE-based adaptive fusion, which struggles with uncertainties arising from distinct object configurations, and late fusion for output-level adaptive fusion, which relies on separate detection pipelines and limits comprehensive understanding. In this work, we introduce Cocoon, an object- and feature-level uncertainty-aware fusion framework. The key innovation lies in uncertainty quantification for heterogeneous representations, enabling fair comparison across modalities through the introduction of a feature aligner and a learnable surrogate ground truth, termed feature impression. We also define a training objective to ensure that their relationship provides a valid metric for uncertainty quantification. Cocoon consistently outperforms existing static and adaptive methods in both normal and challenging conditions, including those with natural and artificial corruptions. Furthermore, we show the validity and efficacy of our uncertainty metric across diverse datasets.
Compute Or Load KV Cache? Why Not Both?
Oct 04, 2024



Abstract:Recent advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs) have significantly increased context window sizes, enabling sophisticated applications but also introducing substantial computational overheads, particularly computing key-value (KV) cache in the prefill stage. Prefix caching has emerged to save GPU power in this scenario, which saves KV cache at disks and reuse them across multiple queries. However, traditional prefix caching mechanisms often suffer from substantial latency because the speed of loading KV cache from disks to GPU memory is bottlenecked by the throughput of I/O devices. To optimize the latency of long-context prefill, we propose Cake, a novel KV cache loader, which employs a bidirectional parallelized KV cache generation strategy. Upon receiving a prefill task, Cake simultaneously and dynamically loads saved KV cache from prefix cache locations and computes KV cache on local GPUs, maximizing the utilization of available computation and I/O bandwidth resources. Additionally, Cake automatically adapts to diverse system statuses without manual parameter. tuning. In experiments on various prompt datasets, GPUs, and I/O devices, Cake offers up to 68.1% Time To First Token (TTFT) reduction compare with compute-only method and 94.6% TTFT reduction compare with I/O-only method.
Safeguard is a Double-edged Sword: Denial-of-service Attack on Large Language Models
Oct 03, 2024



Abstract:Safety is a paramount concern of large language models (LLMs) in their open deployment. To this end, safeguard methods aim to enforce the ethical and responsible use of LLMs through safety alignment or guardrail mechanisms. However, we found that the malicious attackers could exploit false positives of safeguards, i.e., fooling the safeguard model to block safe content mistakenly, leading to a new denial-of-service (DoS) attack on LLMs. Specifically, by software or phishing attacks on user client software, attackers insert a short, seemingly innocuous adversarial prompt into to user prompt templates in configuration files; thus, this prompt appears in final user requests without visibility in the user interface and is not trivial to identify. By designing an optimization process that utilizes gradient and attention information, our attack can automatically generate seemingly safe adversarial prompts, approximately only 30 characters long, that universally block over 97\% of user requests on Llama Guard 3. The attack presents a new dimension of evaluating LLM safeguards focusing on false positives, fundamentally different from the classic jailbreak.
AutoSpec: Automated Generation of Neural Network Specifications
Sep 17, 2024



Abstract:The increasing adoption of neural networks in learning-augmented systems highlights the importance of model safety and robustness, particularly in safety-critical domains. Despite progress in the formal verification of neural networks, current practices require users to manually define model specifications -- properties that dictate expected model behavior in various scenarios. This manual process, however, is prone to human error, limited in scope, and time-consuming. In this paper, we introduce AutoSpec, the first framework to automatically generate comprehensive and accurate specifications for neural networks in learning-augmented systems. We also propose the first set of metrics for assessing the accuracy and coverage of model specifications, establishing a benchmark for future comparisons. Our evaluation across four distinct applications shows that AutoSpec outperforms human-defined specifications as well as two baseline approaches introduced in this study.
Adaptive Skeleton Graph Decoding
Feb 19, 2024



Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) have seen significant adoption for natural language tasks, owing their success to massive numbers of model parameters (e.g., 70B+); however, LLM inference incurs significant computation and memory costs. Recent approaches propose parallel decoding strategies, such as Skeleton-of-Thought (SoT), to improve performance by breaking prompts down into sub-problems that can be decoded in parallel; however, they often suffer from reduced response quality. Our key insight is that we can request additional information, specifically dependencies and difficulty, when generating the sub-problems to improve both response quality and performance. In this paper, we propose Skeleton Graph Decoding (SGD), which uses dependencies exposed between sub-problems to support information forwarding between dependent sub-problems for improved quality while exposing parallelization opportunities for decoding independent sub-problems. Additionally, we leverage difficulty estimates for each sub-problem to select an appropriately-sized model, improving performance without significantly reducing quality. Compared to standard autoregressive generation and SoT, SGD achieves a 1.69x speedup while improving quality by up to 51%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge