Yuzheng Hu
Michael Pokorny
OPUS: Towards Efficient and Principled Data Selection in Large Language Model Pre-training in Every Iteration
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:As high-quality public text approaches exhaustion, a phenomenon known as the Data Wall, pre-training is shifting from more tokens to better tokens. However, existing methods either rely on heuristic static filters that ignore training dynamics, or use dynamic yet optimizer-agnostic criteria based on raw gradients. We propose OPUS (Optimizer-induced Projected Utility Selection), a dynamic data selection framework that defines utility in the optimizer-induced update space. OPUS scores candidates by projecting their effective updates, shaped by modern optimizers, onto a target direction derived from a stable, in-distribution proxy. To ensure scalability, we employ Ghost technique with CountSketch for computational efficiency, and Boltzmann sampling for data diversity, incurring only 4.7\% additional compute overhead. OPUS achieves remarkable results across diverse corpora, quality tiers, optimizers, and model scales. In pre-training of GPT-2 Large/XL on FineWeb and FineWeb-Edu with 30B tokens, OPUS outperforms industrial-level baselines and even full 200B-token training. Moreover, when combined with industrial-level static filters, OPUS further improves pre-training efficiency, even with lower-quality data. Furthermore, in continued pre-training of Qwen3-8B-Base on SciencePedia, OPUS achieves superior performance using only 0.5B tokens compared to full training with 3B tokens, demonstrating significant data efficiency gains in specialized domains.
Taming Hyperparameter Sensitivity in Data Attribution: Practical Selection Without Costly Retraining
May 30, 2025Abstract:Data attribution methods, which quantify the influence of individual training data points on a machine learning model, have gained increasing popularity in data-centric applications in modern AI. Despite a recent surge of new methods developed in this space, the impact of hyperparameter tuning in these methods remains under-explored. In this work, we present the first large-scale empirical study to understand the hyperparameter sensitivity of common data attribution methods. Our results show that most methods are indeed sensitive to certain key hyperparameters. However, unlike typical machine learning algorithms -- whose hyperparameters can be tuned using computationally-cheap validation metrics -- evaluating data attribution performance often requires retraining models on subsets of training data, making such metrics prohibitively costly for hyperparameter tuning. This poses a critical open challenge for the practical application of data attribution methods. To address this challenge, we advocate for better theoretical understandings of hyperparameter behavior to inform efficient tuning strategies. As a case study, we provide a theoretical analysis of the regularization term that is critical in many variants of influence function methods. Building on this analysis, we propose a lightweight procedure for selecting the regularization value without model retraining, and validate its effectiveness across a range of standard data attribution benchmarks. Overall, our study identifies a fundamental yet overlooked challenge in the practical application of data attribution, and highlights the importance of careful discussion on hyperparameter selection in future method development.
A Snapshot of Influence: A Local Data Attribution Framework for Online Reinforcement Learning
May 25, 2025Abstract:Online reinforcement learning (RL) excels in complex, safety-critical domains, yet it faces challenges such as sample inefficiency, training instability, and a lack of interpretability. Data attribution offers a principled way to trace model behavior back to individual training samples. However, in online RL, each training sample not only drives policy updates but also influences future data collection, violating the fixed dataset assumption in existing attribution methods. In this paper, we initiate the study of data attribution for online RL, focusing on the widely used Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) algorithm. We start by establishing a local attribution framework, interpreting model checkpoints with respect to the records in the recent training buffer. We design two target functions, capturing agent action and cumulative return respectively, and measure each record's contribution through gradient similarity between its training loss and these targets. We demonstrate the power of this framework through three concrete applications: diagnosis of learning, temporal analysis of behavior formation, and targeted intervention during training. Leveraging this framework, we further propose an algorithm, iterative influence-based filtering (IIF), for online RL training that iteratively performs experience filtering to refine policy updates. Across standard RL benchmarks (classic control, navigation, locomotion) to RLHF for large language models, IIF reduces sample complexity, speeds up training, and achieves higher returns. Overall, these results advance interpretability, efficiency, and effectiveness of online RL.
MergeBench: A Benchmark for Merging Domain-Specialized LLMs
May 16, 2025Abstract:Model merging provides a scalable alternative to multi-task training by combining specialized finetuned models through parameter arithmetic, enabling efficient deployment without the need for joint training or access to all task data. While recent methods have shown promise, existing evaluations are limited in both model scale and task diversity, leaving open questions about their applicability to large, domain-specialized LLMs. To tackle the challenges, we introduce MergeBench, a comprehensive evaluation suite designed to assess model merging at scale. MergeBench builds on state-of-the-art open-source language models, including Llama and Gemma families at 2B to 9B scales, and covers five key domains: instruction following, mathematics, multilingual understanding, coding and safety. We standardize finetuning and evaluation protocols, and assess eight representative merging methods across multi-task performance, forgetting and runtime efficiency. Based on extensive experiments, we provide practical guidelines for algorithm selection and share insights showing that model merging tends to perform better on stronger base models, with techniques such as merging coefficient tuning and sparsification improving knowledge retention. However, several challenges remain, including the computational cost on large models, the gap for in-domain performance compared to multi-task models, and the underexplored role of model merging in standard LLM training pipelines. We hope MergeBench provides a foundation for future research to advance the understanding and practical application of model merging. We open source our code at \href{https://github.com/uiuctml/MergeBench}{https://github.com/uiuctml/MergeBench}.
Empirical Privacy Variance
Mar 16, 2025Abstract:We propose the notion of empirical privacy variance and study it in the context of differentially private fine-tuning of language models. Specifically, we show that models calibrated to the same $(\varepsilon, \delta)$-DP guarantee using DP-SGD with different hyperparameter configurations can exhibit significant variations in empirical privacy, which we quantify through the lens of memorization. We investigate the generality of this phenomenon across multiple dimensions and discuss why it is surprising and relevant. Through regression analysis, we examine how individual and composite hyperparameters influence empirical privacy. The results reveal a no-free-lunch trade-off: existing practices of hyperparameter tuning in DP-SGD, which focus on optimizing utility under a fixed privacy budget, often come at the expense of empirical privacy. To address this, we propose refined heuristics for hyperparameter selection that explicitly account for empirical privacy, showing that they are both precise and practically useful. Finally, we take preliminary steps to understand empirical privacy variance. We propose two hypotheses, identify limitations in existing techniques like privacy auditing, and outline open questions for future research.
Humanity's Last Exam
Jan 24, 2025Abstract:Benchmarks are important tools for tracking the rapid advancements in large language model (LLM) capabilities. However, benchmarks are not keeping pace in difficulty: LLMs now achieve over 90\% accuracy on popular benchmarks like MMLU, limiting informed measurement of state-of-the-art LLM capabilities. In response, we introduce Humanity's Last Exam (HLE), a multi-modal benchmark at the frontier of human knowledge, designed to be the final closed-ended academic benchmark of its kind with broad subject coverage. HLE consists of 3,000 questions across dozens of subjects, including mathematics, humanities, and the natural sciences. HLE is developed globally by subject-matter experts and consists of multiple-choice and short-answer questions suitable for automated grading. Each question has a known solution that is unambiguous and easily verifiable, but cannot be quickly answered via internet retrieval. State-of-the-art LLMs demonstrate low accuracy and calibration on HLE, highlighting a significant gap between current LLM capabilities and the expert human frontier on closed-ended academic questions. To inform research and policymaking upon a clear understanding of model capabilities, we publicly release HLE at https://lastexam.ai.
Most Influential Subset Selection: Challenges, Promises, and Beyond
Sep 25, 2024Abstract:How can we attribute the behaviors of machine learning models to their training data? While the classic influence function sheds light on the impact of individual samples, it often fails to capture the more complex and pronounced collective influence of a set of samples. To tackle this challenge, we study the Most Influential Subset Selection (MISS) problem, which aims to identify a subset of training samples with the greatest collective influence. We conduct a comprehensive analysis of the prevailing approaches in MISS, elucidating their strengths and weaknesses. Our findings reveal that influence-based greedy heuristics, a dominant class of algorithms in MISS, can provably fail even in linear regression. We delineate the failure modes, including the errors of influence function and the non-additive structure of the collective influence. Conversely, we demonstrate that an adaptive version of these heuristics which applies them iteratively, can effectively capture the interactions among samples and thus partially address the issues. Experiments on real-world datasets corroborate these theoretical findings, and further demonstrate that the merit of adaptivity can extend to more complex scenarios such as classification tasks and non-linear neural networks. We conclude our analysis by emphasizing the inherent trade-off between performance and computational efficiency, questioning the use of additive metrics such as the linear datamodeling score, and offering a range of discussions.
Localize-and-Stitch: Efficient Model Merging via Sparse Task Arithmetic
Aug 24, 2024Abstract:Model merging offers an effective strategy to combine the strengths of multiple finetuned models into a unified model that preserves the specialized capabilities of each. Existing methods merge models in a global manner, performing arithmetic operations across all model parameters. However, such global merging often leads to task interference, degrading the performance of the merged model. In this work, we introduce Localize-and-Stitch, a novel approach that merges models in a localized way. Our algorithm works in two steps: i) Localization: identify tiny ($1\%$ of the total parameters) localized regions in the finetuned models containing essential skills for the downstream tasks, and ii) Stitching: reintegrate only these essential regions back into the pretrained model for task synergy. We demonstrate that our approach effectively locates sparse regions responsible for finetuned performance, and the localized regions could be treated as compact and interpretable representations of the finetuned models (tasks). Empirically, we evaluate our method on various vision and language benchmarks, showing that it outperforms existing model merging methods under different data availability scenarios. Beyond strong empirical performance, our algorithm also facilitates model compression and preserves pretrained knowledge, enabling flexible and continual skill composition from multiple finetuned models with minimal storage and computational overhead. Our code is available at https://github.com/yifei-he/Localize-and-Stitch.
HPL-ViT: A Unified Perception Framework for Heterogeneous Parallel LiDARs in V2V
Sep 27, 2023



Abstract:To develop the next generation of intelligent LiDARs, we propose a novel framework of parallel LiDARs and construct a hardware prototype in our experimental platform, DAWN (Digital Artificial World for Natural). It emphasizes the tight integration of physical and digital space in LiDAR systems, with networking being one of its supported core features. In the context of autonomous driving, V2V (Vehicle-to-Vehicle) technology enables efficient information sharing between different agents which significantly promotes the development of LiDAR networks. However, current research operates under an ideal situation where all vehicles are equipped with identical LiDAR, ignoring the diversity of LiDAR categories and operating frequencies. In this paper, we first utilize OpenCDA and RLS (Realistic LiDAR Simulation) to construct a novel heterogeneous LiDAR dataset named OPV2V-HPL. Additionally, we present HPL-ViT, a pioneering architecture designed for robust feature fusion in heterogeneous and dynamic scenarios. It uses a graph-attention Transformer to extract domain-specific features for each agent, coupled with a cross-attention mechanism for the final fusion. Extensive experiments on OPV2V-HPL demonstrate that HPL-ViT achieves SOTA (state-of-the-art) performance in all settings and exhibits outstanding generalization capabilities.
Revisiting Scalarization in Multi-Task Learning: A Theoretical Perspective
Aug 27, 2023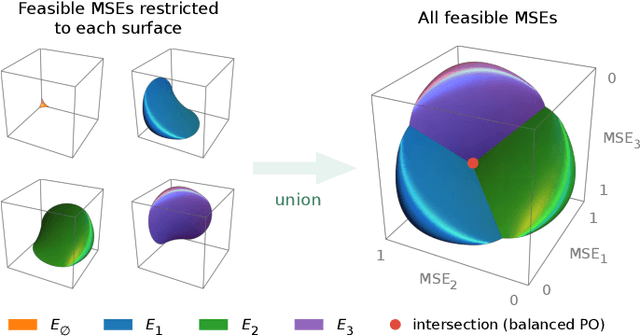

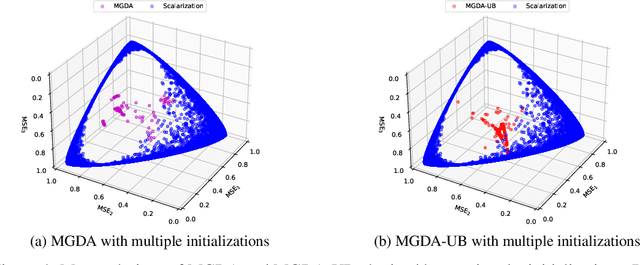

Abstract:Linear scalarization, i.e., combining all loss functions by a weighted sum, has been the default choice in the literature of multi-task learning (MTL) since its inception. In recent years, there is a surge of interest in developing Specialized Multi-Task Optimizers (SMTOs) that treat MTL as a multi-objective optimization problem. However, it remains open whether there is a fundamental advantage of SMTOs over scalarization. In fact, heated debates exist in the community comparing these two types of algorithms, mostly from an empirical perspective. To approach the above question, in this paper, we revisit scalarization from a theoretical perspective. We focus on linear MTL models and study whether scalarization is capable of fully exploring the Pareto front. Our findings reveal that, in contrast to recent works that claimed empirical advantages of scalarization, scalarization is inherently incapable of full exploration, especially for those Pareto optimal solutions that strike the balanced trade-offs between multiple tasks. More concretely, when the model is under-parametrized, we reveal a multi-surface structure of the feasible region and identify necessary and sufficient conditions for full exploration. This leads to the conclusion that scalarization is in general incapable of tracing out the Pareto front. Our theoretical results partially answer the open questions in Xin et al. (2021), and provide a more intuitive explanation on why scalarization fails beyond non-convexity. We additionally perform experiments on a real-world dataset using both scalarization and state-of-the-art SMTOs. The experimental results not only corroborate our theoretical findings, but also unveil the potential of SMTOs in finding balanced solutions, which cannot be achieved by scalarization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge