Yuxiao Wang
Structure-Aware Decoding Mechanisms for Complex Entity Extraction with Large-Scale Language Models
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a structure-aware decoding method based on large language models to address the difficulty of traditional approaches in maintaining both semantic integrity and structural consistency in nested and overlapping entity extraction tasks. The method introduces a candidate span generation mechanism and structured attention modeling to achieve unified modeling of entity boundaries, hierarchical relationships, and cross-dependencies. The model first uses a pretrained language model to obtain context-aware semantic representations, then captures multi-granular entity span features through candidate representation combinations, and introduces hierarchical structural constraints during decoding to ensure consistency between semantics and structure. To enhance stability in complex scenarios, the model jointly optimizes classification loss and structural consistency loss, maintaining high recognition accuracy under multi-entity co-occurrence and long-sentence dependency conditions. Experiments conducted on the ACE 2005 dataset demonstrate significant improvements in Accuracy, Precision, Recall, and F1-Score, particularly in nested and overlapping entity recognition, where the model shows stronger boundary localization and structural modeling capability. This study verifies the effectiveness of structure-aware decoding in complex semantic extraction tasks, provides a new perspective for developing language models with hierarchical understanding, and establishes a methodological foundation for high-precision information extraction.
Structural Priors and Modular Adapters in the Composable Fine-Tuning Algorithm of Large-Scale Models
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:This paper proposes a composable fine-tuning method that integrates graph structural priors with modular adapters to address the high computational cost and structural instability faced by large-scale pre-trained models in multi-task adaptation. The method introduces a relation matrix to model dependencies among tasks, explicitly encoding correlations between nodes and paths into graph structural priors, which provide unified structural constraints for adapter weight allocation and path selection. Modular adapters are embedded into different layers through low-rank mapping and a pluggable mechanism, enabling efficient cross-task composition and reuse under prior guidance. This mechanism not only improves parameter efficiency and training stability but also alleviates path conflicts and redundant computation in multi-task scenarios. Furthermore, experiments on hyperparameter sensitivity, environmental sensitivity, and data sensitivity are conducted to systematically analyze key factors such as routing temperature, gating thresholds, and relation matrix regularization strength, verifying the consistency and superior performance of the method under structural constraints. The results demonstrate that the proposed framework significantly enhances task prediction accuracy, adapter weight allocation precision, and overall computational efficiency while maintaining model lightweight design, highlighting the synergistic advantages of graph priors and modular mechanisms in composable fine-tuning.
QueryCraft: Transformer-Guided Query Initialization for Enhanced Human-Object Interaction Detection
Aug 12, 2025Abstract:Human-Object Interaction (HOI) detection aims to localize human-object pairs and recognize their interactions in images. Although DETR-based methods have recently emerged as the mainstream framework for HOI detection, they still suffer from a key limitation: Randomly initialized queries lack explicit semantics, leading to suboptimal detection performance. To address this challenge, we propose QueryCraft, a novel plug-and-play HOI detection framework that incorporates semantic priors and guided feature learning through transformer-based query initialization. Central to our approach is \textbf{ACTOR} (\textbf{A}ction-aware \textbf{C}ross-modal \textbf{T}ransf\textbf{OR}mer), a cross-modal Transformer encoder that jointly attends to visual regions and textual prompts to extract action-relevant features. Rather than merely aligning modalities, ACTOR leverages language-guided attention to infer interaction semantics and produce semantically meaningful query representations. To further enhance object-level query quality, we introduce a \textbf{P}erceptual \textbf{D}istilled \textbf{Q}uery \textbf{D}ecoder (\textbf{PDQD}), which distills object category awareness from a pre-trained detector to serve as object query initiation. This dual-branch query initialization enables the model to generate more interpretable and effective queries for HOI detection. Extensive experiments on HICO-Det and V-COCO benchmarks demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance and strong generalization. Code will be released upon publication.
Prompt Guidance and Human Proximal Perception for HOT Prediction with Regional Joint Loss
Jul 02, 2025Abstract:The task of Human-Object conTact (HOT) detection involves identifying the specific areas of the human body that are touching objects. Nevertheless, current models are restricted to just one type of image, often leading to too much segmentation in areas with little interaction, and struggling to maintain category consistency within specific regions. To tackle this issue, a HOT framework, termed \textbf{P3HOT}, is proposed, which blends \textbf{P}rompt guidance and human \textbf{P}roximal \textbf{P}erception. To begin with, we utilize a semantic-driven prompt mechanism to direct the network's attention towards the relevant regions based on the correlation between image and text. Then a human proximal perception mechanism is employed to dynamically perceive key depth range around the human, using learnable parameters to effectively eliminate regions where interactions are not expected. Calculating depth resolves the uncertainty of the overlap between humans and objects in a 2D perspective, providing a quasi-3D viewpoint. Moreover, a Regional Joint Loss (RJLoss) has been created as a new loss to inhibit abnormal categories in the same area. A new evaluation metric called ``AD-Acc.'' is introduced to address the shortcomings of existing methods in addressing negative samples. Comprehensive experimental results demonstrate that our approach achieves state-of-the-art performance in four metrics across two benchmark datasets. Specifically, our model achieves an improvement of \textbf{0.7}$\uparrow$, \textbf{2.0}$\uparrow$, \textbf{1.6}$\uparrow$, and \textbf{11.0}$\uparrow$ in SC-Acc., mIoU, wIoU, and AD-Acc. metrics, respectively, on the HOT-Annotated dataset. Code is available at https://github.com/YuxiaoWang-AI/P3HOT.
OpenVidVRD: Open-Vocabulary Video Visual Relation Detection via Prompt-Driven Semantic Space Alignment
Mar 12, 2025Abstract:The video visual relation detection (VidVRD) task is to identify objects and their relationships in videos, which is challenging due to the dynamic content, high annotation costs, and long-tailed distribution of relations. Visual language models (VLMs) help explore open-vocabulary visual relation detection tasks, yet often overlook the connections between various visual regions and their relations. Moreover, using VLMs to directly identify visual relations in videos poses significant challenges because of the large disparity between images and videos. Therefore, we propose a novel open-vocabulary VidVRD framework, termed OpenVidVRD, which transfers VLMs' rich knowledge and powerful capabilities to improve VidVRD tasks through prompt learning. Specificall y, We use VLM to extract text representations from automatically generated region captions based on the video's regions. Next, we develop a spatiotemporal refiner module to derive object-level relationship representations in the video by integrating cross-modal spatiotemporal complementary information. Furthermore, a prompt-driven strategy to align semantic spaces is employed to harness the semantic understanding of VLMs, enhancing the overall generalization ability of OpenVidVRD. Extensive experiments conducted on the VidVRD and VidOR public datasets show that the proposed model outperforms existing methods.
Pruning for Sparse Diffusion Models based on Gradient Flow
Jan 16, 2025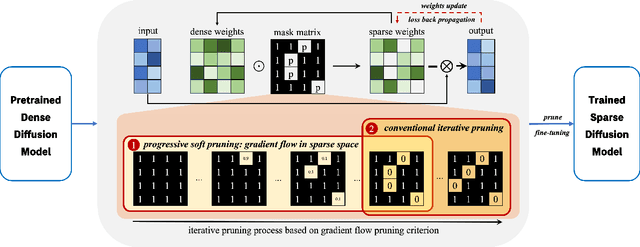
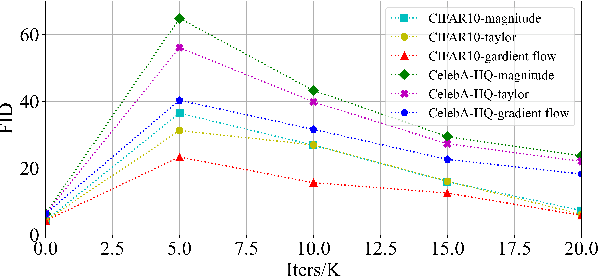
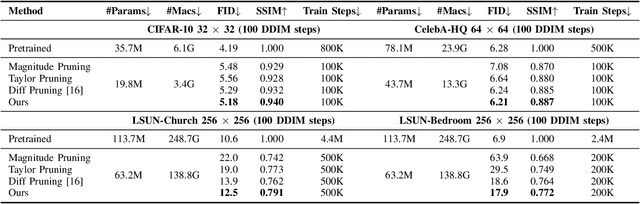
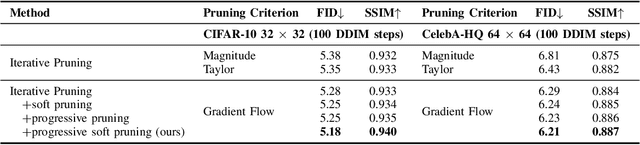
Abstract:Diffusion Models (DMs) have impressive capabilities among generation models, but are limited to slower inference speeds and higher computational costs. Previous works utilize one-shot structure pruning to derive lightweight DMs from pre-trained ones, but this approach often leads to a significant drop in generation quality and may result in the removal of crucial weights. Thus we propose a iterative pruning method based on gradient flow, including the gradient flow pruning process and the gradient flow pruning criterion. We employ a progressive soft pruning strategy to maintain the continuity of the mask matrix and guide it along the gradient flow of the energy function based on the pruning criterion in sparse space, thereby avoiding the sudden information loss typically caused by one-shot pruning. Gradient-flow based criterion prune parameters whose removal increases the gradient norm of loss function and can enable fast convergence for a pruned model in iterative pruning stage. Our extensive experiments on widely used datasets demonstrate that our method achieves superior performance in efficiency and consistency with pre-trained models.
Precision-Enhanced Human-Object Contact Detection via Depth-Aware Perspective Interaction and Object Texture Restoration
Dec 13, 2024



Abstract:Human-object contact (HOT) is designed to accurately identify the areas where humans and objects come into contact. Current methods frequently fail to account for scenarios where objects are frequently blocking the view, resulting in inaccurate identification of contact areas. To tackle this problem, we suggest using a perspective interaction HOT detector called PIHOT, which utilizes a depth map generation model to offer depth information of humans and objects related to the camera, thereby preventing false interaction detection. Furthermore, we use mask dilatation and object restoration techniques to restore the texture details in covered areas, improve the boundaries between objects, and enhance the perception of humans interacting with objects. Moreover, a spatial awareness perception is intended to concentrate on the characteristic features close to the points of contact. The experimental results show that the PIHOT algorithm achieves state-of-the-art performance on three benchmark datasets for HOT detection tasks. Compared to the most recent DHOT, our method enjoys an average improvement of 13%, 27.5%, 16%, and 18.5% on SC-Acc., C-Acc., mIoU, and wIoU metrics, respectively.
A Review of Human-Object Interaction Detection
Aug 20, 2024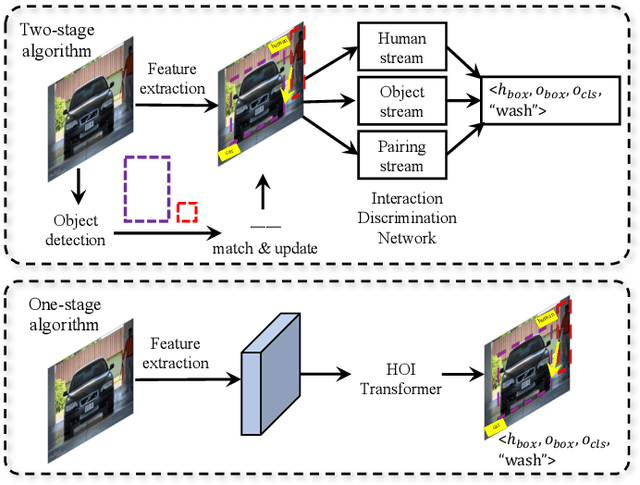
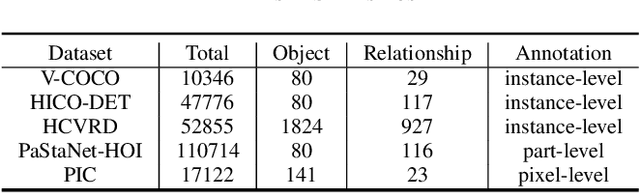
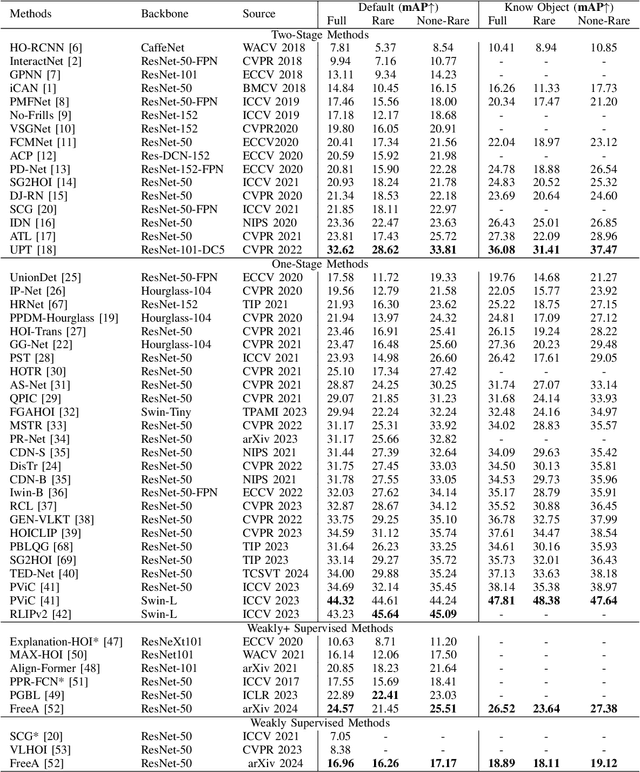
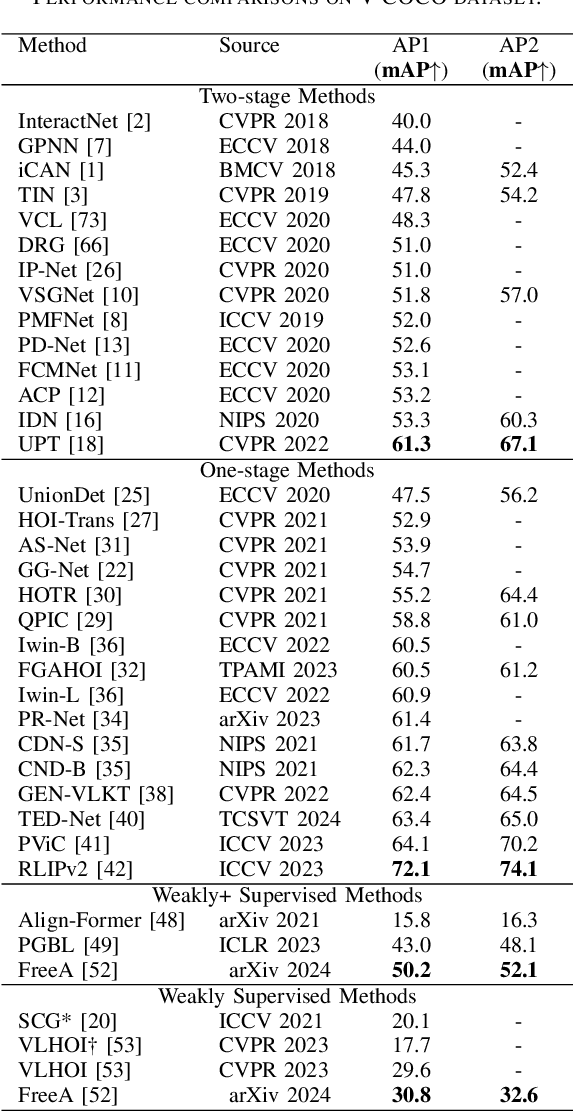
Abstract:Human-object interaction (HOI) detection plays a key role in high-level visual understanding, facilitating a deep comprehension of human activities. Specifically, HOI detection aims to locate the humans and objects involved in interactions within images or videos and classify the specific interactions between them. The success of this task is influenced by several key factors, including the accurate localization of human and object instances, as well as the correct classification of object categories and interaction relationships. This paper systematically summarizes and discusses the recent work in image-based HOI detection. First, the mainstream datasets involved in HOI relationship detection are introduced. Furthermore, starting with two-stage methods and end-to-end one-stage detection approaches, this paper comprehensively discusses the current developments in image-based HOI detection, analyzing the strengths and weaknesses of these two methods. Additionally, the advancements of zero-shot learning, weakly supervised learning, and the application of large-scale language models in HOI detection are discussed. Finally, the current challenges in HOI detection are outlined, and potential research directions and future trends are explored.
Imagen 3
Aug 13, 2024Abstract:We introduce Imagen 3, a latent diffusion model that generates high quality images from text prompts. We describe our quality and responsibility evaluations. Imagen 3 is preferred over other state-of-the-art (SOTA) models at the time of evaluation. In addition, we discuss issues around safety and representation, as well as methods we used to minimize the potential harm of our models.
S4TP: Social-Suitable and Safety-Sensitive Trajectory Planning for Autonomous Vehicles
Apr 18, 2024



Abstract:In public roads, autonomous vehicles (AVs) face the challenge of frequent interactions with human-driven vehicles (HDVs), which render uncertain driving behavior due to varying social characteristics among humans. To effectively assess the risks prevailing in the vicinity of AVs in social interactive traffic scenarios and achieve safe autonomous driving, this article proposes a social-suitable and safety-sensitive trajectory planning (S4TP) framework. Specifically, S4TP integrates the Social-Aware Trajectory Prediction (SATP) and Social-Aware Driving Risk Field (SADRF) modules. SATP utilizes Transformers to effectively encode the driving scene and incorporates an AV's planned trajectory during the prediction decoding process. SADRF assesses the expected surrounding risk degrees during AVs-HDVs interactions, each with different social characteristics, visualized as two-dimensional heat maps centered on the AV. SADRF models the driving intentions of the surrounding HDVs and predicts trajectories based on the representation of vehicular interactions. S4TP employs an optimization-based approach for motion planning, utilizing the predicted HDVs'trajectories as input. With the integration of SADRF, S4TP executes real-time online optimization of the planned trajectory of AV within lowrisk regions, thus improving the safety and the interpretability of the planned trajectory. We have conducted comprehensive tests of the proposed method using the SMARTS simulator. Experimental results in complex social scenarios, such as unprotected left turn intersections, merging, cruising, and overtaking, validate the superiority of our proposed S4TP in terms of safety and rationality. S4TP achieves a pass rate of 100% across all scenarios, surpassing the current state-of-the-art methods Fanta of 98.25% and Predictive-Decision of 94.75%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge