Zuhong Liu
Passage Segmentation of Documents for Extractive Question Answering
Jan 17, 2025Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has proven effective in open-domain question answering. However, the chunking process, which is essential to this pipeline, often receives insufficient attention relative to retrieval and synthesis components. This study emphasizes the critical role of chunking in improving the performance of both dense passage retrieval and the end-to-end RAG pipeline. We then introduce the Logits-Guided Multi-Granular Chunker (LGMGC), a novel framework that splits long documents into contextualized, self-contained chunks of varied granularity. Our experimental results, evaluated on two benchmark datasets, demonstrate that LGMGC not only improves the retrieval step but also outperforms existing chunking methods when integrated into a RAG pipeline.
FedRSU: Federated Learning for Scene Flow Estimation on Roadside Units
Jan 23, 2024Abstract:Roadside unit (RSU) can significantly improve the safety and robustness of autonomous vehicles through Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) communication. Currently, the usage of a single RSU mainly focuses on real-time inference and V2X collaboration, while neglecting the potential value of the high-quality data collected by RSU sensors. Integrating the vast amounts of data from numerous RSUs can provide a rich source of data for model training. However, the absence of ground truth annotations and the difficulty of transmitting enormous volumes of data are two inevitable barriers to fully exploiting this hidden value. In this paper, we introduce FedRSU, an innovative federated learning framework for self-supervised scene flow estimation. In FedRSU, we present a recurrent self-supervision training paradigm, where for each RSU, the scene flow prediction of points at every timestamp can be supervised by its subsequent future multi-modality observation. Another key component of FedRSU is federated learning, where multiple devices collaboratively train an ML model while keeping the training data local and private. With the power of the recurrent self-supervised learning paradigm, FL is able to leverage innumerable underutilized data from RSU. To verify the FedRSU framework, we construct a large-scale multi-modality dataset RSU-SF. The dataset consists of 17 RSU clients, covering various scenarios, modalities, and sensor settings. Based on RSU-SF, we show that FedRSU can greatly improve model performance in ITS and provide a comprehensive benchmark under diverse FL scenarios. To the best of our knowledge, we provide the first real-world LiDAR-camera multi-modal dataset and benchmark for the FL community.
Self-Supervised Bird's Eye View Motion Prediction with Cross-Modality Signals
Jan 21, 2024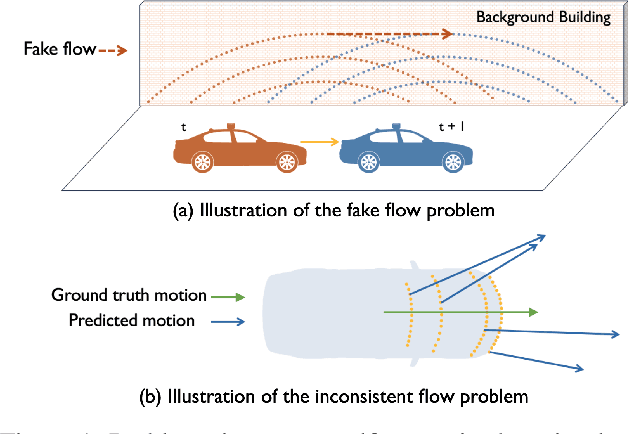
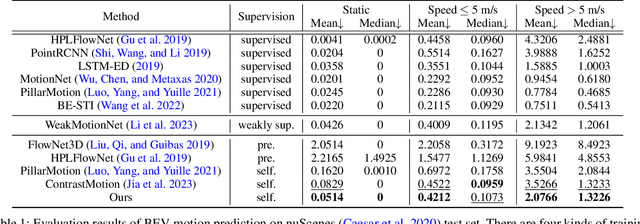
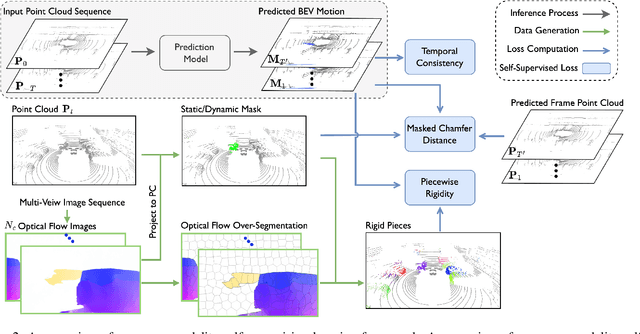
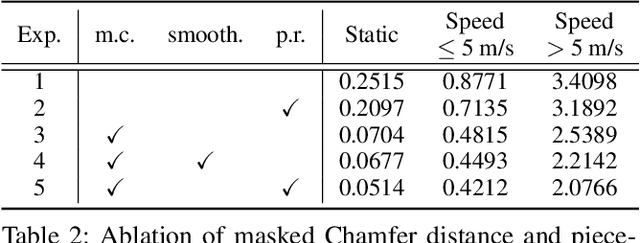
Abstract:Learning the dense bird's eye view (BEV) motion flow in a self-supervised manner is an emerging research for robotics and autonomous driving. Current self-supervised methods mainly rely on point correspondences between point clouds, which may introduce the problems of fake flow and inconsistency, hindering the model's ability to learn accurate and realistic motion. In this paper, we introduce a novel cross-modality self-supervised training framework that effectively addresses these issues by leveraging multi-modality data to obtain supervision signals. We design three innovative supervision signals to preserve the inherent properties of scene motion, including the masked Chamfer distance loss, the piecewise rigidity loss, and the temporal consistency loss. Through extensive experiments, we demonstrate that our proposed self-supervised framework outperforms all previous self-supervision methods for the motion prediction task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge