Yun-Ta Tsai
Cross-Camera Convolutional Color Constancy
Nov 24, 2020



Abstract:We present "Cross-Camera Convolutional Color Constancy" (C5), a learning-based method, trained on images from multiple cameras, that accurately estimates a scene's illuminant color from raw images captured by a new camera previously unseen during training. C5 is a hypernetwork-like extension of the convolutional color constancy (CCC) approach: C5 learns to generate the weights of a CCC model that is then evaluated on the input image, with the CCC weights dynamically adapted to different input content. Unlike prior cross-camera color constancy models, which are usually designed to be agnostic to the spectral properties of test-set images from unobserved cameras, C5 approaches this problem through the lens of transductive inference: additional unlabeled images are provided as input to the model at test time, which allows the model to calibrate itself to the spectral properties of the test-set camera during inference. C5 achieves state-of-the-art accuracy for cross-camera color constancy on several datasets, is fast to evaluate (~7 and ~90 ms per image on a GPU or CPU, respectively), and requires little memory (~2 MB), and, thus, is a practical solution to the problem of calibration-free automatic white balance for mobile photography.
Light Stage Super-Resolution: Continuous High-Frequency Relighting
Oct 17, 2020



Abstract:The light stage has been widely used in computer graphics for the past two decades, primarily to enable the relighting of human faces. By capturing the appearance of the human subject under different light sources, one obtains the light transport matrix of that subject, which enables image-based relighting in novel environments. However, due to the finite number of lights in the stage, the light transport matrix only represents a sparse sampling on the entire sphere. As a consequence, relighting the subject with a point light or a directional source that does not coincide exactly with one of the lights in the stage requires interpolation and resampling the images corresponding to nearby lights, and this leads to ghosting shadows, aliased specularities, and other artifacts. To ameliorate these artifacts and produce better results under arbitrary high-frequency lighting, this paper proposes a learning-based solution for the "super-resolution" of scans of human faces taken from a light stage. Given an arbitrary "query" light direction, our method aggregates the captured images corresponding to neighboring lights in the stage, and uses a neural network to synthesize a rendering of the face that appears to be illuminated by a "virtual" light source at the query location. This neural network must circumvent the inherent aliasing and regularity of the light stage data that was used for training, which we accomplish through the use of regularized traditional interpolation methods within our network. Our learned model is able to produce renderings for arbitrary light directions that exhibit realistic shadows and specular highlights, and is able to generalize across a wide variety of subjects.
Neural Light Transport for Relighting and View Synthesis
Aug 20, 2020
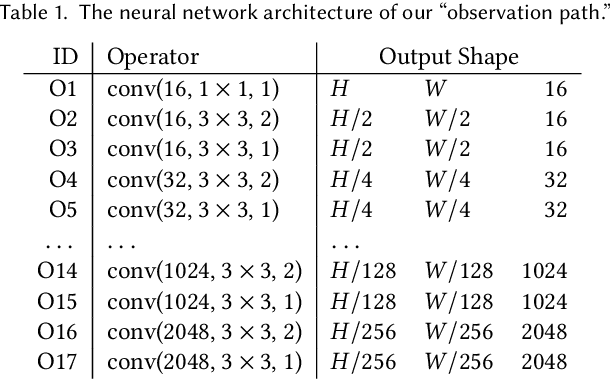

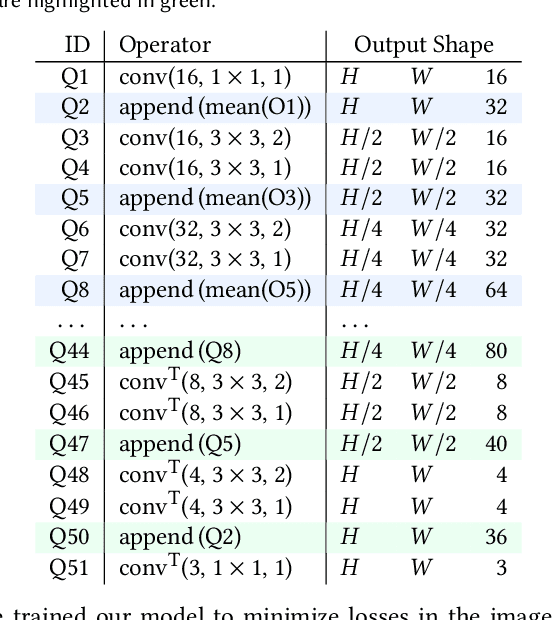
Abstract:The light transport (LT) of a scene describes how it appears under different lighting and viewing directions, and complete knowledge of a scene's LT enables the synthesis of novel views under arbitrary lighting. In this paper, we focus on image-based LT acquisition, primarily for human bodies within a light stage setup. We propose a semi-parametric approach to learn a neural representation of LT that is embedded in the space of a texture atlas of known geometric properties, and model all non-diffuse and global LT as residuals added to a physically-accurate diffuse base rendering. In particular, we show how to fuse previously seen observations of illuminants and views to synthesize a new image of the same scene under a desired lighting condition from a chosen viewpoint. This strategy allows the network to learn complex material effects (such as subsurface scattering) and global illumination, while guaranteeing the physical correctness of the diffuse LT (such as hard shadows). With this learned LT, one can relight the scene photorealistically with a directional light or an HDRI map, synthesize novel views with view-dependent effects, or do both simultaneously, all in a unified framework using a set of sparse, previously seen observations. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our neural LT (NLT) outperforms state-of-the-art solutions for relighting and view synthesis, without separate treatment for both problems that prior work requires.
Sky Optimization: Semantically aware image processing of skies in low-light photography
Jun 15, 2020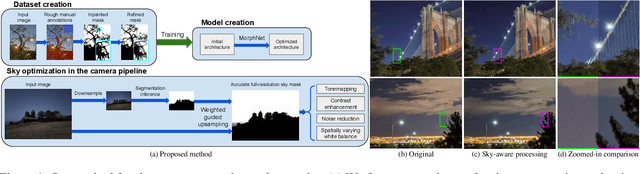
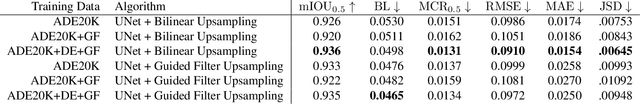
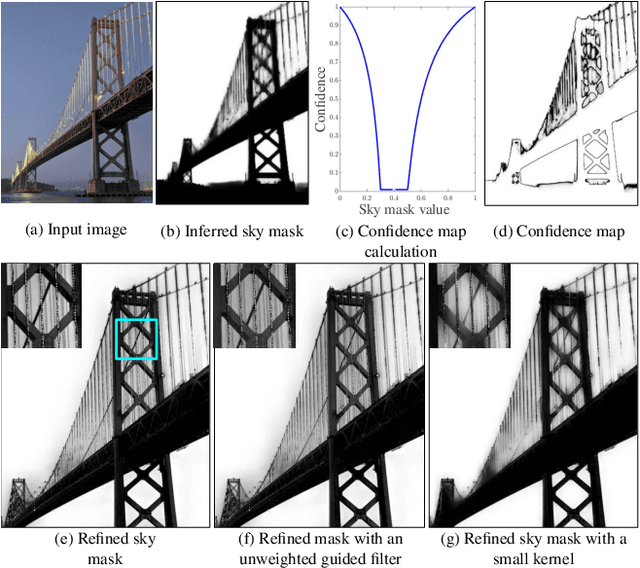
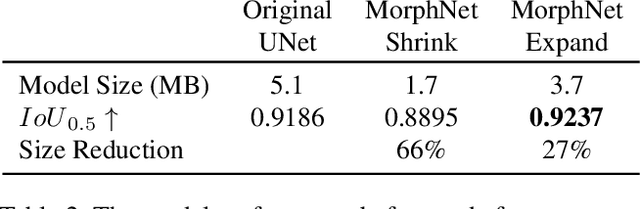
Abstract:The sky is a major component of the appearance of a photograph, and its color and tone can strongly influence the mood of a picture. In nighttime photography, the sky can also suffer from noise and color artifacts. For this reason, there is a strong desire to process the sky in isolation from the rest of the scene to achieve an optimal look. In this work, we propose an automated method, which can run as a part of a camera pipeline, for creating accurate sky alpha-masks and using them to improve the appearance of the sky. Our method performs end-to-end sky optimization in less than half a second per image on a mobile device. We introduce a method for creating an accurate sky-mask dataset that is based on partially annotated images that are inpainted and refined by our modified weighted guided filter. We use this dataset to train a neural network for semantic sky segmentation. Due to the compute and power constraints of mobile devices, sky segmentation is performed at a low image resolution. Our modified weighted guided filter is used for edge-aware upsampling to resize the alpha-mask to a higher resolution. With this detailed mask we automatically apply post-processing steps to the sky in isolation, such as automatic spatially varying white-balance, brightness adjustments, contrast enhancement, and noise reduction.
Portrait Shadow Manipulation
May 20, 2020
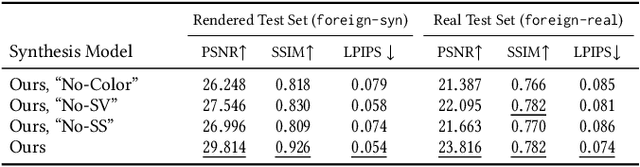
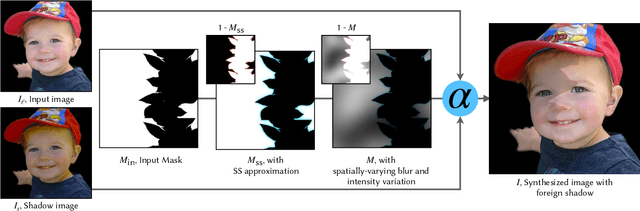
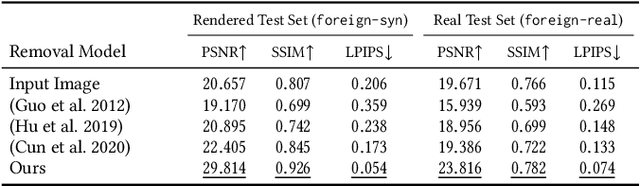
Abstract:Casually-taken portrait photographs often suffer from unflattering lighting and shadowing because of suboptimal conditions in the environment. Aesthetic qualities such as the position and softness of shadows and the lighting ratio between the bright and dark parts of the face are frequently determined by the constraints of the environment rather than by the photographer. Professionals address this issue by adding light shaping tools such as scrims, bounce cards, and flashes. In this paper, we present a computational approach that gives casual photographers some of this control, thereby allowing poorly-lit portraits to be relit post-capture in a realistic and easily-controllable way. Our approach relies on a pair of neural networks---one to remove foreign shadows cast by external objects, and another to soften facial shadows cast by the features of the subject and to add a synthetic fill light to improve the lighting ratio. To train our first network we construct a dataset of real-world portraits wherein synthetic foreign shadows are rendered onto the face, and we show that our network learns to remove those unwanted shadows. To train our second network we use a dataset of Light Stage scans of human subjects to construct input/output pairs of input images harshly lit by a small light source, and variably softened and fill-lit output images of each face. We propose a way to explicitly encode facial symmetry and show that our dataset and training procedure enable the model to generalize to images taken in the wild. Together, these networks enable the realistic and aesthetically pleasing enhancement of shadows and lights in real-world portrait images
Handheld Mobile Photography in Very Low Light
Oct 24, 2019



Abstract:Taking photographs in low light using a mobile phone is challenging and rarely produces pleasing results. Aside from the physical limits imposed by read noise and photon shot noise, these cameras are typically handheld, have small apertures and sensors, use mass-produced analog electronics that cannot easily be cooled, and are commonly used to photograph subjects that move, like children and pets. In this paper we describe a system for capturing clean, sharp, colorful photographs in light as low as 0.3~lux, where human vision becomes monochromatic and indistinct. To permit handheld photography without flash illumination, we capture, align, and combine multiple frames. Our system employs "motion metering", which uses an estimate of motion magnitudes (whether due to handshake or moving objects) to identify the number of frames and the per-frame exposure times that together minimize both noise and motion blur in a captured burst. We combine these frames using robust alignment and merging techniques that are specialized for high-noise imagery. To ensure accurate colors in such low light, we employ a learning-based auto white balancing algorithm. To prevent the photographs from looking like they were shot in daylight, we use tone mapping techniques inspired by illusionistic painting: increasing contrast, crushing shadows to black, and surrounding the scene with darkness. All of these processes are performed using the limited computational resources of a mobile device. Our system can be used by novice photographers to produce shareable pictures in a few seconds based on a single shutter press, even in environments so dim that humans cannot see clearly.
* 22 pages, 27 figures
Single Image Portrait Relighting
May 02, 2019



Abstract:Lighting plays a central role in conveying the essence and depth of the subject in a portrait photograph. Professional photographers will carefully control the lighting in their studio to manipulate the appearance of their subject, while consumer photographers are usually constrained to the illumination of their environment. Though prior works have explored techniques for relighting an image, their utility is usually limited due to requirements of specialized hardware, multiple images of the subject under controlled or known illuminations, or accurate models of geometry and reflectance. To this end, we present a system for portrait relighting: a neural network that takes as input a single RGB image of a portrait taken with a standard cellphone camera in an unconstrained environment, and from that image produces a relit image of that subject as though it were illuminated according to any provided environment map. Our method is trained on a small database of 18 individuals captured under different directional light sources in a controlled light stage setup consisting of a densely sampled sphere of lights. Our proposed technique produces quantitatively superior results on our dataset's validation set compared to prior works, and produces convincing qualitative relighting results on a dataset of hundreds of real-world cellphone portraits. Because our technique can produce a 640 $\times$ 640 image in only 160 milliseconds, it may enable interactive user-facing photographic applications in the future.
* SIGGRAPH 2019 Technical Paper accepted
Fast Fourier Color Constancy
Mar 16, 2017



Abstract:We present Fast Fourier Color Constancy (FFCC), a color constancy algorithm which solves illuminant estimation by reducing it to a spatial localization task on a torus. By operating in the frequency domain, FFCC produces lower error rates than the previous state-of-the-art by 13-20% while being 250-3000 times faster. This unconventional approach introduces challenges regarding aliasing, directional statistics, and preconditioning, which we address. By producing a complete posterior distribution over illuminants instead of a single illuminant estimate, FFCC enables better training techniques, an effective temporal smoothing technique, and richer methods for error analysis. Our implementation of FFCC runs at ~700 frames per second on a mobile device, allowing it to be used as an accurate, real-time, temporally-coherent automatic white balance algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge