Philip Davidson
FaceFolds: Meshed Radiance Manifolds for Efficient Volumetric Rendering of Dynamic Faces
Apr 22, 2024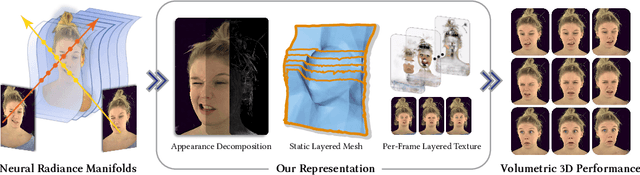

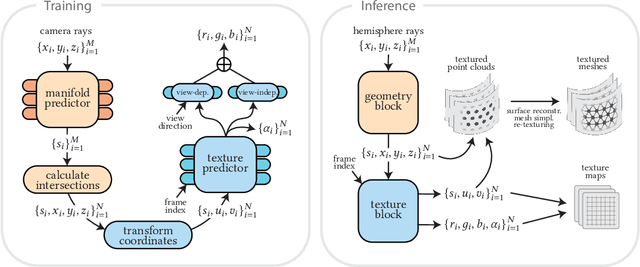
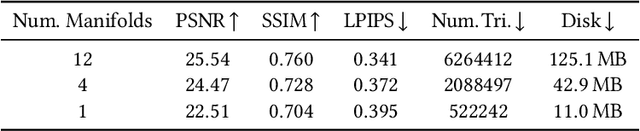
Abstract:3D rendering of dynamic face captures is a challenging problem, and it demands improvements on several fronts$\unicode{x2014}$photorealism, efficiency, compatibility, and configurability. We present a novel representation that enables high-quality volumetric rendering of an actor's dynamic facial performances with minimal compute and memory footprint. It runs natively on commodity graphics soft- and hardware, and allows for a graceful trade-off between quality and efficiency. Our method utilizes recent advances in neural rendering, particularly learning discrete radiance manifolds to sparsely sample the scene to model volumetric effects. We achieve efficient modeling by learning a single set of manifolds for the entire dynamic sequence, while implicitly modeling appearance changes as temporal canonical texture. We export a single layered mesh and view-independent RGBA texture video that is compatible with legacy graphics renderers without additional ML integration. We demonstrate our method by rendering dynamic face captures of real actors in a game engine, at comparable photorealism to state-of-the-art neural rendering techniques at previously unseen frame rates.
Sandwiched Compression: Repurposing Standard Codecs with Neural Network Wrappers
Feb 08, 2024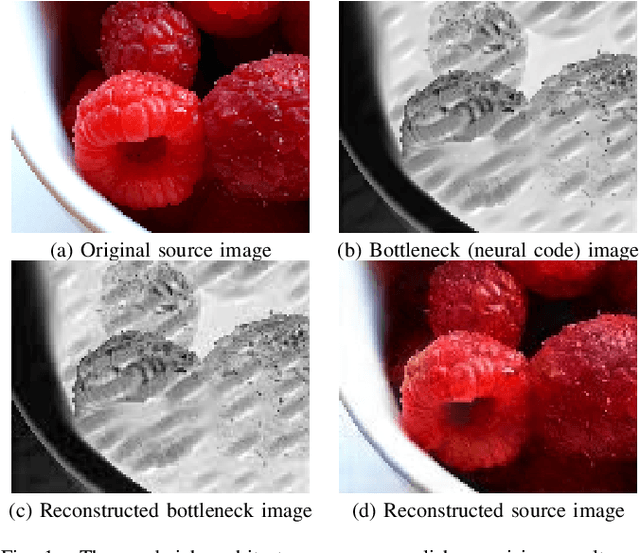
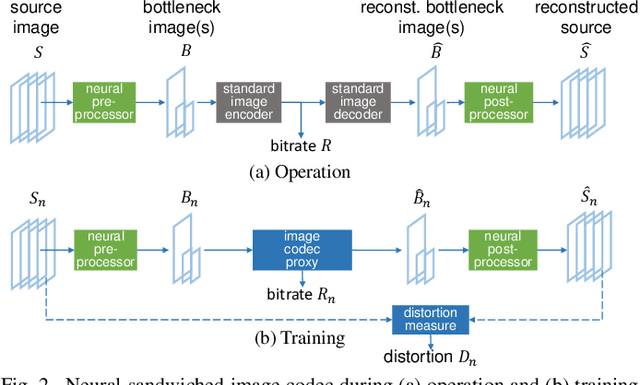
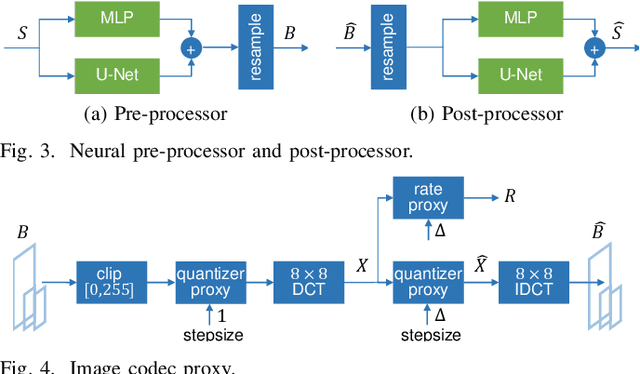
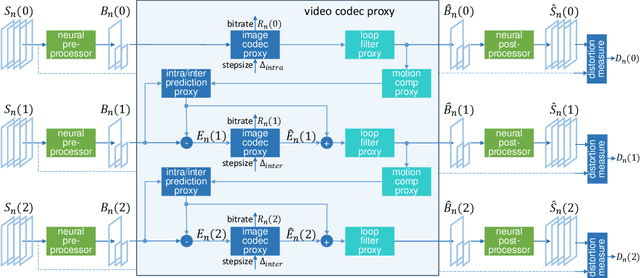
Abstract:We propose sandwiching standard image and video codecs between pre- and post-processing neural networks. The networks are jointly trained through a differentiable codec proxy to minimize a given rate-distortion loss. This sandwich architecture not only improves the standard codec's performance on its intended content, it can effectively adapt the codec to other types of image/video content and to other distortion measures. Essentially, the sandwich learns to transmit ``neural code images'' that optimize overall rate-distortion performance even when the overall problem is well outside the scope of the codec's design. Through a variety of examples, we apply the sandwich architecture to sources with different numbers of channels, higher resolution, higher dynamic range, and perceptual distortion measures. The results demonstrate substantial improvements (up to 9 dB gains or up to 30\% bitrate reductions) compared to alternative adaptations. We derive VQ equivalents for the sandwich, establish optimality properties, and design differentiable codec proxies approximating current standard codecs. We further analyze model complexity, visual quality under perceptual metrics, as well as sandwich configurations that offer interesting potentials in image/video compression and streaming.
Neural Light Transport for Relighting and View Synthesis
Aug 20, 2020

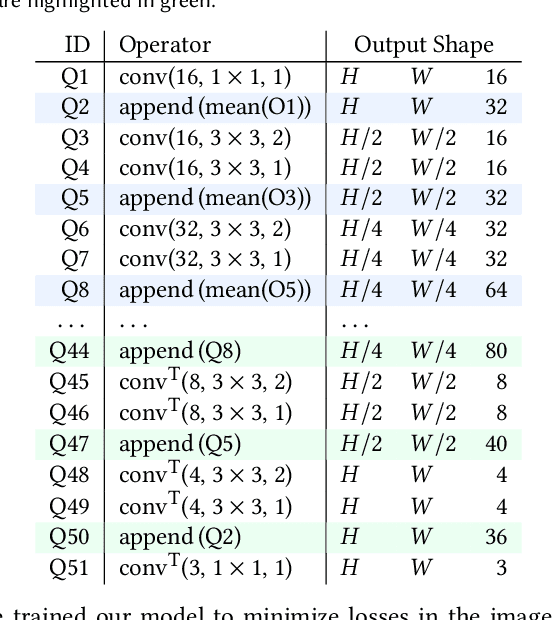
Abstract:The light transport (LT) of a scene describes how it appears under different lighting and viewing directions, and complete knowledge of a scene's LT enables the synthesis of novel views under arbitrary lighting. In this paper, we focus on image-based LT acquisition, primarily for human bodies within a light stage setup. We propose a semi-parametric approach to learn a neural representation of LT that is embedded in the space of a texture atlas of known geometric properties, and model all non-diffuse and global LT as residuals added to a physically-accurate diffuse base rendering. In particular, we show how to fuse previously seen observations of illuminants and views to synthesize a new image of the same scene under a desired lighting condition from a chosen viewpoint. This strategy allows the network to learn complex material effects (such as subsurface scattering) and global illumination, while guaranteeing the physical correctness of the diffuse LT (such as hard shadows). With this learned LT, one can relight the scene photorealistically with a directional light or an HDRI map, synthesize novel views with view-dependent effects, or do both simultaneously, all in a unified framework using a set of sparse, previously seen observations. Qualitative and quantitative experiments demonstrate that our neural LT (NLT) outperforms state-of-the-art solutions for relighting and view synthesis, without separate treatment for both problems that prior work requires.
Deep Implicit Volume Compression
May 18, 2020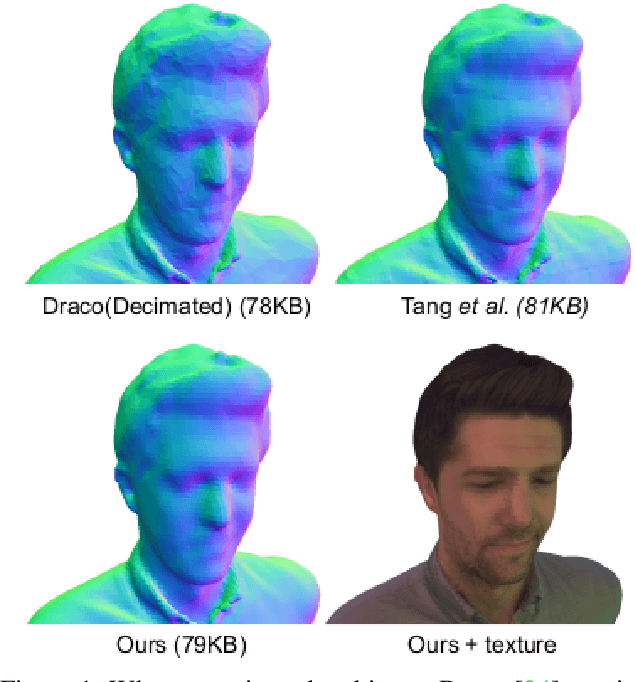

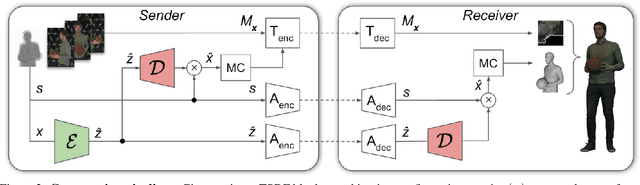
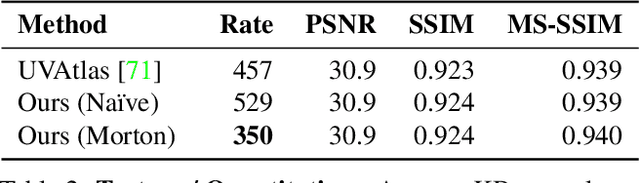
Abstract:We describe a novel approach for compressing truncated signed distance fields (TSDF) stored in 3D voxel grids, and their corresponding textures. To compress the TSDF, our method relies on a block-based neural network architecture trained end-to-end, achieving state-of-the-art rate-distortion trade-off. To prevent topological errors, we losslessly compress the signs of the TSDF, which also upper bounds the reconstruction error by the voxel size. To compress the corresponding texture, we designed a fast block-based UV parameterization, generating coherent texture maps that can be effectively compressed using existing video compression algorithms. We demonstrate the performance of our algorithms on two 4D performance capture datasets, reducing bitrate by 66% for the same distortion, or alternatively reducing the distortion by 50% for the same bitrate, compared to the state-of-the-art.
Volumetric Capture of Humans with a Single RGBD Camera via Semi-Parametric Learning
May 29, 2019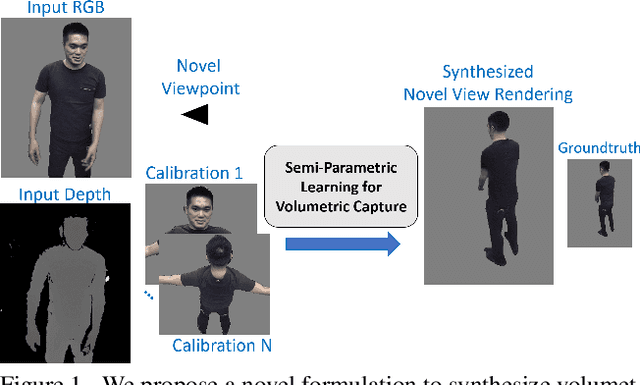
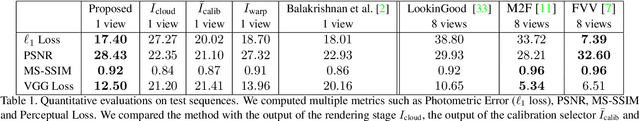
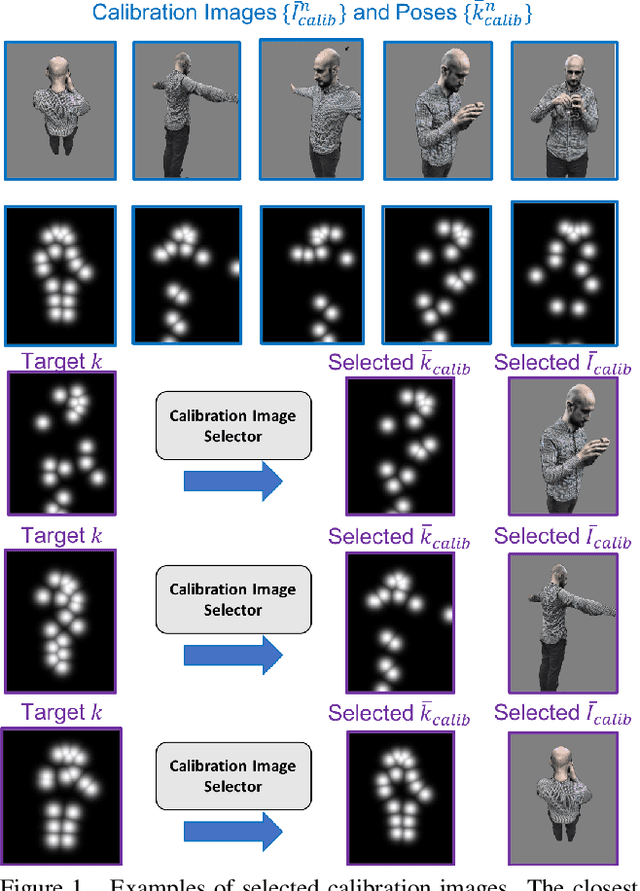
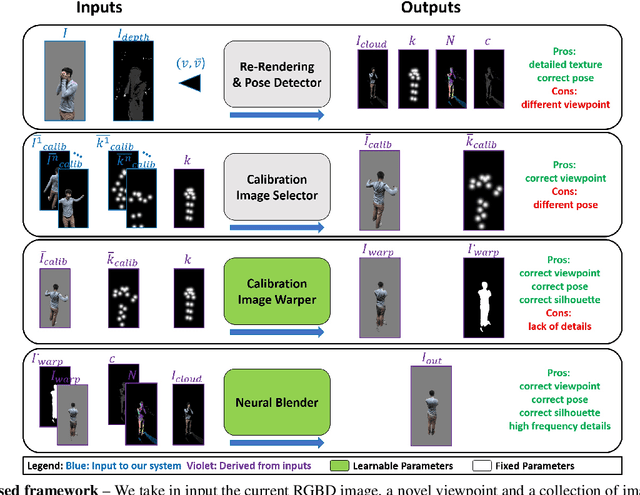
Abstract:Volumetric (4D) performance capture is fundamental for AR/VR content generation. Whereas previous work in 4D performance capture has shown impressive results in studio settings, the technology is still far from being accessible to a typical consumer who, at best, might own a single RGBD sensor. Thus, in this work, we propose a method to synthesize free viewpoint renderings using a single RGBD camera. The key insight is to leverage previously seen "calibration" images of a given user to extrapolate what should be rendered in a novel viewpoint from the data available in the sensor. Given these past observations from multiple viewpoints, and the current RGBD image from a fixed view, we propose an end-to-end framework that fuses both these data sources to generate novel renderings of the performer. We demonstrate that the method can produce high fidelity images, and handle extreme changes in subject pose and camera viewpoints. We also show that the system generalizes to performers not seen in the training data. We run exhaustive experiments demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed semi-parametric model (i.e. calibration images available to the neural network) compared to other state of the art machine learned solutions. Further, we compare the method with more traditional pipelines that employ multi-view capture. We show that our framework is able to achieve compelling results, with substantially less infrastructure than previously required.
LookinGood: Enhancing Performance Capture with Real-time Neural Re-Rendering
Nov 12, 2018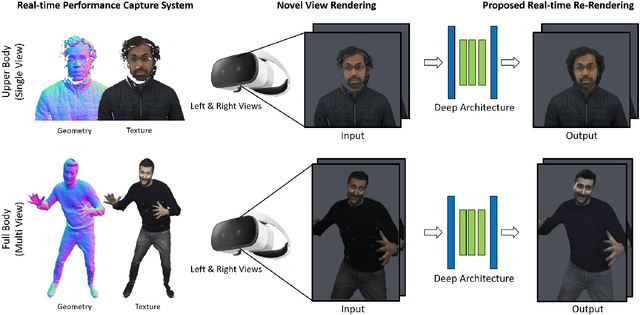
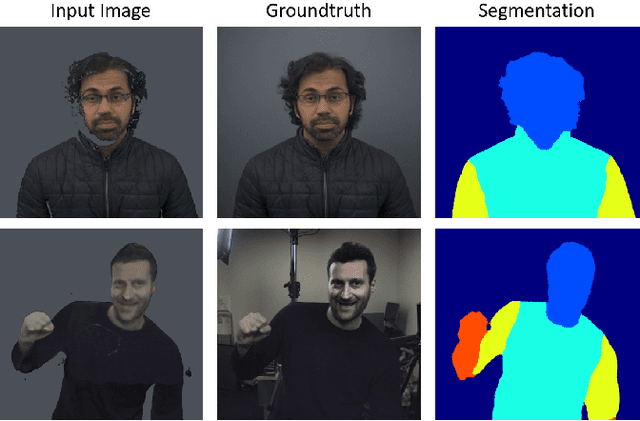
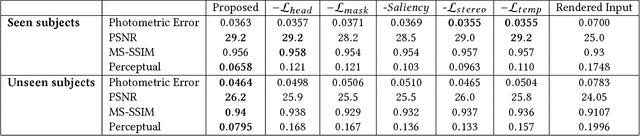
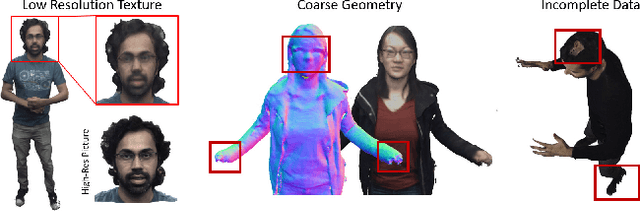

Abstract:Motivated by augmented and virtual reality applications such as telepresence, there has been a recent focus in real-time performance capture of humans under motion. However, given the real-time constraint, these systems often suffer from artifacts in geometry and texture such as holes and noise in the final rendering, poor lighting, and low-resolution textures. We take the novel approach to augment such real-time performance capture systems with a deep architecture that takes a rendering from an arbitrary viewpoint, and jointly performs completion, super resolution, and denoising of the imagery in real-time. We call this approach neural (re-)rendering, and our live system "LookinGood". Our deep architecture is trained to produce high resolution and high quality images from a coarse rendering in real-time. First, we propose a self-supervised training method that does not require manual ground-truth annotation. We contribute a specialized reconstruction error that uses semantic information to focus on relevant parts of the subject, e.g. the face. We also introduce a salient reweighing scheme of the loss function that is able to discard outliers. We specifically design the system for virtual and augmented reality headsets where the consistency between the left and right eye plays a crucial role in the final user experience. Finally, we generate temporally stable results by explicitly minimizing the difference between two consecutive frames. We tested the proposed system in two different scenarios: one involving a single RGB-D sensor, and upper body reconstruction of an actor, the second consisting of full body 360 degree capture. Through extensive experimentation, we demonstrate how our system generalizes across unseen sequences and subjects. The supplementary video is available at http://youtu.be/Md3tdAKoLGU.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge