Yu Fu
Department of Information Security, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan, Hubei, 430033, China
LingLanMiDian: Systematic Evaluation of LLMs on TCM Knowledge and Clinical Reasoning
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) are advancing rapidly in medical NLP, yet Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) with its distinctive ontology, terminology, and reasoning patterns requires domain-faithful evaluation. Existing TCM benchmarks are fragmented in coverage and scale and rely on non-unified or generation-heavy scoring that hinders fair comparison. We present the LingLanMiDian (LingLan) benchmark, a large-scale, expert-curated, multi-task suite that unifies evaluation across knowledge recall, multi-hop reasoning, information extraction, and real-world clinical decision-making. LingLan introduces a consistent metric design, a synonym-tolerant protocol for clinical labels, a per-dataset 400-item Hard subset, and a reframing of diagnosis and treatment recommendation into single-choice decision recognition. We conduct comprehensive, zero-shot evaluations on 14 leading open-source and proprietary LLMs, providing a unified perspective on their strengths and limitations in TCM commonsense knowledge understanding, reasoning, and clinical decision support; critically, the evaluation on Hard subset reveals a substantial gap between current models and human experts in TCM-specialized reasoning. By bridging fundamental knowledge and applied reasoning through standardized evaluation, LingLan establishes a unified, quantitative, and extensible foundation for advancing TCM LLMs and domain-specific medical AI research. All evaluation data and code are available at https://github.com/TCMAI-BJTU/LingLan and http://tcmnlp.com.
Thinking Out of Order: When Output Order Stops Reflecting Reasoning Order in Diffusion Language Models
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Autoregressive (AR) language models enforce a fixed left-to-right generation order, creating a fundamental limitation when the required output structure conflicts with natural reasoning (e.g., producing answers before explanations due to presentation or schema constraints). In such cases, AR models must commit to answers before generating intermediate reasoning, and this rigid constraint forces premature commitment. Masked diffusion language models (MDLMs), which iteratively refine all tokens in parallel, offer a way to decouple computation order from output structure. We validate this capability on GSM8K, Math500, and ReasonOrderQA, a benchmark we introduce with controlled difficulty and order-level evaluation. When prompts request answers before reasoning, AR models exhibit large accuracy gaps compared to standard chain-of-thought ordering (up to 67% relative drop), while MDLMs remain stable ($\leq$14% relative drop), a property we term "order robustness". Using ReasonOrderQA, we present evidence that MDLMs achieve order robustness by stabilizing simpler tokens (e.g., reasoning steps) earlier in the diffusion process than complex ones (e.g., final answers), enabling reasoning tokens to stabilize before answer commitment. Finally, we identify failure conditions where this advantage weakens, outlining the limits required for order robustness.
M4Diffuser: Multi-View Diffusion Policy with Manipulability-Aware Control for Robust Mobile Manipulation
Sep 18, 2025Abstract:Mobile manipulation requires the coordinated control of a mobile base and a robotic arm while simultaneously perceiving both global scene context and fine-grained object details. Existing single-view approaches often fail in unstructured environments due to limited fields of view, exploration, and generalization abilities. Moreover, classical controllers, although stable, struggle with efficiency and manipulability near singularities. To address these challenges, we propose M4Diffuser, a hybrid framework that integrates a Multi-View Diffusion Policy with a novel Reduced and Manipulability-aware QP (ReM-QP) controller for mobile manipulation. The diffusion policy leverages proprioceptive states and complementary camera perspectives with both close-range object details and global scene context to generate task-relevant end-effector goals in the world frame. These high-level goals are then executed by the ReM-QP controller, which eliminates slack variables for computational efficiency and incorporates manipulability-aware preferences for robustness near singularities. Comprehensive experiments in simulation and real-world environments show that M4Diffuser achieves 7 to 56 percent higher success rates and reduces collisions by 3 to 31 percent over baselines. Our approach demonstrates robust performance for smooth whole-body coordination, and strong generalization to unseen tasks, paving the way for reliable mobile manipulation in unstructured environments. Details of the demo and supplemental material are available on our project website https://sites.google.com/view/m4diffuser.
A Survey of Reinforcement Learning for Large Reasoning Models
Sep 10, 2025Abstract:In this paper, we survey recent advances in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for reasoning with Large Language Models (LLMs). RL has achieved remarkable success in advancing the frontier of LLM capabilities, particularly in addressing complex logical tasks such as mathematics and coding. As a result, RL has emerged as a foundational methodology for transforming LLMs into LRMs. With the rapid progress of the field, further scaling of RL for LRMs now faces foundational challenges not only in computational resources but also in algorithm design, training data, and infrastructure. To this end, it is timely to revisit the development of this domain, reassess its trajectory, and explore strategies to enhance the scalability of RL toward Artificial SuperIntelligence (ASI). In particular, we examine research applying RL to LLMs and LRMs for reasoning abilities, especially since the release of DeepSeek-R1, including foundational components, core problems, training resources, and downstream applications, to identify future opportunities and directions for this rapidly evolving area. We hope this review will promote future research on RL for broader reasoning models. Github: https://github.com/TsinghuaC3I/Awesome-RL-for-LRMs
Inverse IFEval: Can LLMs Unlearn Stubborn Training Conventions to Follow Real Instructions?
Sep 04, 2025Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) achieve strong performance on diverse tasks but often exhibit cognitive inertia, struggling to follow instructions that conflict with the standardized patterns learned during supervised fine-tuning (SFT). To evaluate this limitation, we propose Inverse IFEval, a benchmark that measures models Counter-intuitive Abilitytheir capacity to override training-induced biases and comply with adversarial instructions. Inverse IFEval introduces eight types of such challenges, including Question Correction, Intentional Textual Flaws, Code without Comments, and Counterfactual Answering. Using a human-in-the-loop pipeline, we construct a dataset of 1012 high-quality Chinese and English questions across 23 domains, evaluated under an optimized LLM-as-a-Judge framework. Experiments on existing leading LLMs demonstrate the necessity of our proposed Inverse IFEval benchmark. Our findings emphasize that future alignment efforts should not only pursue fluency and factual correctness but also account for adaptability under unconventional contexts. We hope that Inverse IFEval serves as both a diagnostic tool and a foundation for developing methods that mitigate cognitive inertia, reduce overfitting to narrow patterns, and ultimately enhance the instruction-following reliability of LLMs in diverse and unpredictable real-world scenarios.
UniDiffGrasp: A Unified Framework Integrating VLM Reasoning and VLM-Guided Part Diffusion for Open-Vocabulary Constrained Grasping with Dual Arms
May 11, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary, task-oriented grasping of specific functional parts, particularly with dual arms, remains a key challenge, as current Vision-Language Models (VLMs), while enhancing task understanding, often struggle with precise grasp generation within defined constraints and effective dual-arm coordination. We innovatively propose UniDiffGrasp, a unified framework integrating VLM reasoning with guided part diffusion to address these limitations. UniDiffGrasp leverages a VLM to interpret user input and identify semantic targets (object, part(s), mode), which are then grounded via open-vocabulary segmentation. Critically, the identified parts directly provide geometric constraints for a Constrained Grasp Diffusion Field (CGDF) using its Part-Guided Diffusion, enabling efficient, high-quality 6-DoF grasps without retraining. For dual-arm tasks, UniDiffGrasp defines distinct target regions, applies part-guided diffusion per arm, and selects stable cooperative grasps. Through extensive real-world deployment, UniDiffGrasp achieves grasp success rates of 0.876 in single-arm and 0.767 in dual-arm scenarios, significantly surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating its capability to enable precise and coordinated open-vocabulary grasping in complex real-world scenarios.
Harnessing the Unseen: The Hidden Influence of Intrinsic Knowledge in Long-Context Language Models
Apr 11, 2025



Abstract:Recent advances in long-context models (LCMs), designed to handle extremely long input contexts, primarily focus on utilizing external contextual information, often leaving the influence of large language models' intrinsic knowledge underexplored. In this work, we investigate how this intrinsic knowledge affects content generation and demonstrate that its impact becomes increasingly pronounced as context length extends. Furthermore, we show that the model's ability to utilize intrinsic knowledge, which we call intrinsic retrieval ability, does not improve simultaneously with its ability to leverage contextual knowledge through extrinsic retrieval ability. Moreover, better extrinsic retrieval can interfere with the model's ability to use its own knowledge effectively, limiting its full potential. To bridge this gap, we design a simple yet effective Hybrid Needle-in-a-Haystack test that evaluates models based on their capabilities across both retrieval abilities, rather than solely emphasizing extrinsic retrieval ability. Our experimental results reveal that Qwen-2.5 models significantly outperform Llama-3.1 models, demonstrating superior intrinsic retrieval ability. Moreover, even the more powerful Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct model fails to exhibit better performance under LCM conditions, highlighting the importance of evaluating models from a dual-retrieval perspective.
DATAWEAVER: Authoring Data-Driven Narratives through the Integrated Composition of Visualization and Text
Mar 29, 2025Abstract:Data-driven storytelling has gained prominence in journalism and other data reporting fields. However, the process of creating these stories remains challenging, often requiring the integration of effective visualizations with compelling narratives to form a cohesive, interactive presentation. To help streamline this process, we present an integrated authoring framework and system, DataWeaver, that supports both visualization-to-text and text-to-visualization composition. DataWeaver enables users to create data narratives anchored to data facts derived from "call-out" interactions, i.e., user-initiated highlights of visualization elements that prompt relevant narrative content. In addition to this "vis-to-text" composition, DataWeaver also supports a "text-initiated" approach, generating relevant interactive visualizations from existing narratives. Key findings from an evaluation with 13 participants highlighted the utility and usability of DataWeaver and the effectiveness of its integrated authoring framework. The evaluation also revealed opportunities to enhance the framework by refining filtering mechanisms and visualization recommendations and better support authoring creativity by introducing advanced customization options.
MetaXCR: Reinforcement-Based Meta-Transfer Learning for Cross-Lingual Commonsense Reasoning
Mar 09, 2025
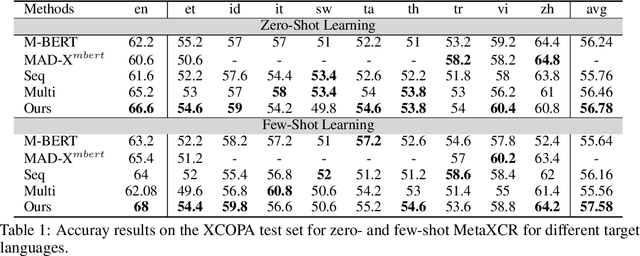

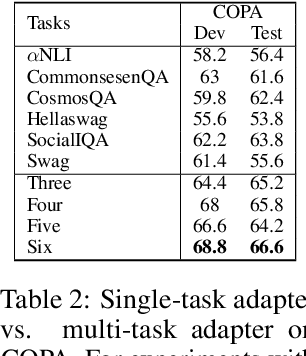
Abstract:Commonsense reasoning (CR) has been studied in many pieces of domain and has achieved great progress with the aid of large datasets. Unfortunately, most existing CR datasets are built in English, so most previous work focus on English. Furthermore, as the annotation of commonsense reasoning is costly, it is impossible to build a large dataset for every novel task. Therefore, there are growing appeals for Cross-lingual Low-Resource Commonsense Reasoning, which aims to leverage diverse existed English datasets to help the model adapt to new cross-lingual target datasets with limited labeled data. In this paper, we propose a multi-source adapter for cross-lingual low-resource Commonsense Reasoning (MetaXCR). In this framework, we first extend meta learning by incorporating multiple training datasets to learn a generalized task adapters across different tasks. Then, we further introduce a reinforcement-based sampling strategy to help the model sample the source task that is the most helpful to the target task. Finally, we introduce two types of cross-lingual meta-adaption methods to enhance the performance of models on target languages. Extensive experiments demonstrate MetaXCR is superior over state-of-the-arts, while being trained with fewer parameters than other work.
Vector Copula Variational Inference and Dependent Block Posterior Approximations
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Variational inference (VI) is a popular method to estimate statistical and econometric models. The key to VI is the selection of a tractable density to approximate the Bayesian posterior. For large and complex models a common choice is to assume independence between multivariate blocks in a partition of the parameter space. While this simplifies the problem it can reduce accuracy. This paper proposes using vector copulas to capture dependence between the blocks parsimoniously. Tailored multivariate marginals are constructed using learnable cyclically monotone transformations. We call the resulting joint distribution a ``dependent block posterior'' approximation. Vector copula models are suggested that make tractable and flexible variational approximations. They allow for differing marginals, numbers of blocks, block sizes and forms of between block dependence. They also allow for solution of the variational optimization using fast and efficient stochastic gradient methods. The efficacy and versatility of the approach is demonstrated using four different statistical models and 16 datasets which have posteriors that are challenging to approximate. In all cases, our method produces more accurate posterior approximations than benchmark VI methods that either assume block independence or factor-based dependence, at limited additional computational cost.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge