Weiqin Zhao
Aligning Knowledge Concepts to Whole Slide Images for Precise Histopathology Image Analysis
Nov 27, 2024Abstract:Due to the large size and lack of fine-grained annotation, Whole Slide Images (WSIs) analysis is commonly approached as a Multiple Instance Learning (MIL) problem. However, previous studies only learn from training data, posing a stark contrast to how human clinicians teach each other and reason about histopathologic entities and factors. Here we present a novel knowledge concept-based MIL framework, named ConcepPath to fill this gap. Specifically, ConcepPath utilizes GPT-4 to induce reliable diseasespecific human expert concepts from medical literature, and incorporate them with a group of purely learnable concepts to extract complementary knowledge from training data. In ConcepPath, WSIs are aligned to these linguistic knowledge concepts by utilizing pathology vision-language model as the basic building component. In the application of lung cancer subtyping, breast cancer HER2 scoring, and gastric cancer immunotherapy-sensitive subtyping task, ConcepPath significantly outperformed previous SOTA methods which lack the guidance of human expert knowledge.
Free Lunch in Pathology Foundation Model: Task-specific Model Adaptation with Concept-Guided Feature Enhancement
Nov 15, 2024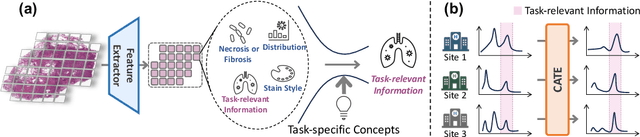
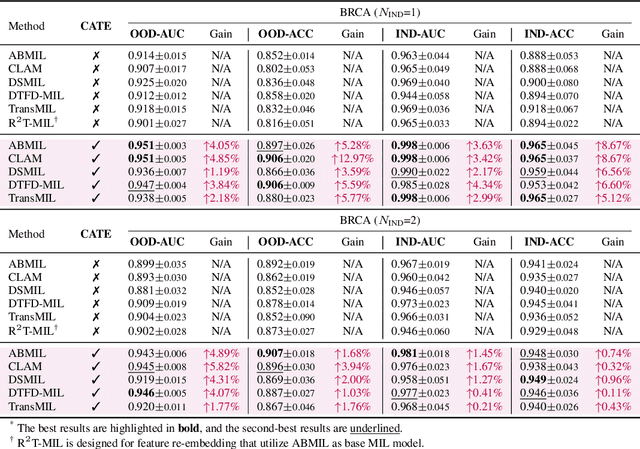
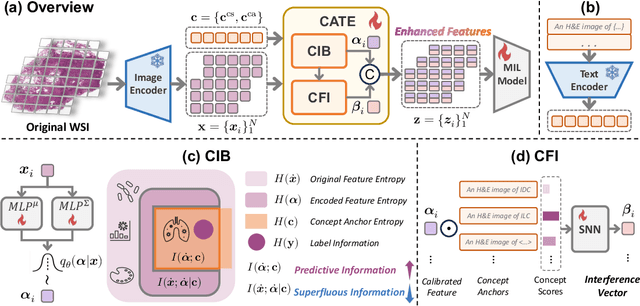
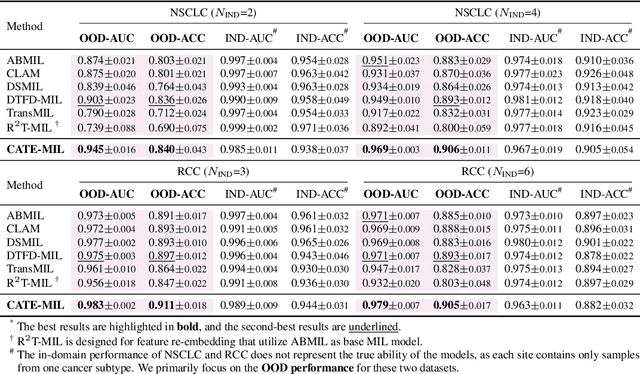
Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) analysis is gaining prominence within the medical imaging field. Recent advances in pathology foundation models have shown the potential to extract powerful feature representations from WSIs for downstream tasks. However, these foundation models are usually designed for general-purpose pathology image analysis and may not be optimal for specific downstream tasks or cancer types. In this work, we present Concept Anchor-guided Task-specific Feature Enhancement (CATE), an adaptable paradigm that can boost the expressivity and discriminativeness of pathology foundation models for specific downstream tasks. Based on a set of task-specific concepts derived from the pathology vision-language model with expert-designed prompts, we introduce two interconnected modules to dynamically calibrate the generic image features extracted by foundation models for certain tasks or cancer types. Specifically, we design a Concept-guided Information Bottleneck module to enhance task-relevant characteristics by maximizing the mutual information between image features and concept anchors while suppressing superfluous information. Moreover, a Concept-Feature Interference module is proposed to utilize the similarity between calibrated features and concept anchors to further generate discriminative task-specific features. The extensive experiments on public WSI datasets demonstrate that CATE significantly enhances the performance and generalizability of MIL models. Additionally, heatmap and umap visualization results also reveal the effectiveness and interpretability of CATE. The source code is available at https://github.com/HKU-MedAI/CATE.
HIGT: Hierarchical Interaction Graph-Transformer for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Sep 14, 2023



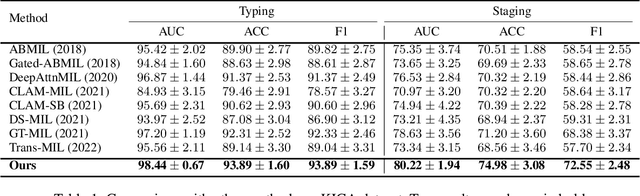
Abstract:In computation pathology, the pyramid structure of gigapixel Whole Slide Images (WSIs) has recently been studied for capturing various information from individual cell interactions to tissue microenvironments. This hierarchical structure is believed to be beneficial for cancer diagnosis and prognosis tasks. However, most previous hierarchical WSI analysis works (1) only characterize local or global correlations within the WSI pyramids and (2) use only unidirectional interaction between different resolutions, leading to an incomplete picture of WSI pyramids. To this end, this paper presents a novel Hierarchical Interaction Graph-Transformer (i.e., HIGT) for WSI analysis. With Graph Neural Network and Transformer as the building commons, HIGT can learn both short-range local information and long-range global representation of the WSI pyramids. Considering that the information from different resolutions is complementary and can benefit each other during the learning process, we further design a novel Bidirectional Interaction block to establish communication between different levels within the WSI pyramids. Finally, we aggregate both coarse-grained and fine-grained features learned from different levels together for slide-level prediction. We evaluate our methods on two public WSI datasets from TCGA projects, i.e., kidney carcinoma (KICA) and esophageal carcinoma (ESCA). Experimental results show that our HIGT outperforms both hierarchical and non-hierarchical state-of-the-art methods on both tumor subtyping and staging tasks.
ConSlide: Asynchronous Hierarchical Interaction Transformer with Breakup-Reorganize Rehearsal for Continual Whole Slide Image Analysis
Aug 25, 2023



Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) analysis has become increasingly important in the medical imaging community, enabling automated and objective diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic-response prediction. However, in clinical practice, the ever-evolving environment hamper the utility of WSI analysis models. In this paper, we propose the FIRST continual learning framework for WSI analysis, named ConSlide, to tackle the challenges of enormous image size, utilization of hierarchical structure, and catastrophic forgetting by progressive model updating on multiple sequential datasets. Our framework contains three key components. The Hierarchical Interaction Transformer (HIT) is proposed to model and utilize the hierarchical structural knowledge of WSI. The Breakup-Reorganize (BuRo) rehearsal method is developed for WSI data replay with efficient region storing buffer and WSI reorganizing operation. The asynchronous updating mechanism is devised to encourage the network to learn generic and specific knowledge respectively during the replay stage, based on a nested cross-scale similarity learning (CSSL) module. We evaluated the proposed ConSlide on four public WSI datasets from TCGA projects. It performs best over other state-of-the-art methods with a fair WSI-based continual learning setting and achieves a better trade-off of the overall performance and forgetting on previous task
MulGT: Multi-task Graph-Transformer with Task-aware Knowledge Injection and Domain Knowledge-driven Pooling for Whole Slide Image Analysis
Feb 21, 2023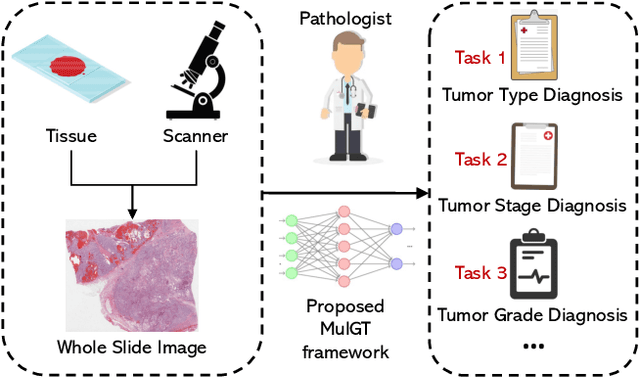
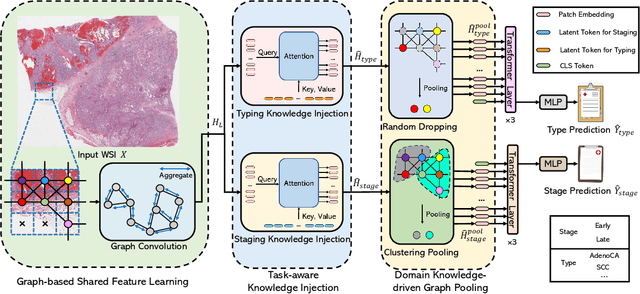
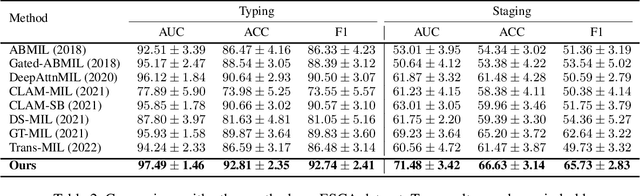
Abstract:Whole slide image (WSI) has been widely used to assist automated diagnosis under the deep learning fields. However, most previous works only discuss the SINGLE task setting which is not aligned with real clinical setting, where pathologists often conduct multiple diagnosis tasks simultaneously. Also, it is commonly recognized that the multi-task learning paradigm can improve learning efficiency by exploiting commonalities and differences across multiple tasks. To this end, we present a novel multi-task framework (i.e., MulGT) for WSI analysis by the specially designed Graph-Transformer equipped with Task-aware Knowledge Injection and Domain Knowledge-driven Graph Pooling modules. Basically, with the Graph Neural Network and Transformer as the building commons, our framework is able to learn task-agnostic low-level local information as well as task-specific high-level global representation. Considering that different tasks in WSI analysis depend on different features and properties, we also design a novel Task-aware Knowledge Injection module to transfer the task-shared graph embedding into task-specific feature spaces to learn more accurate representation for different tasks. Further, we elaborately design a novel Domain Knowledge-driven Graph Pooling module for each task to improve both the accuracy and robustness of different tasks by leveraging different diagnosis patterns of multiple tasks. We evaluated our method on two public WSI datasets from TCGA projects, i.e., esophageal carcinoma and kidney carcinoma. Experimental results show that our method outperforms single-task counterparts and the state-of-theart methods on both tumor typing and staging tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge