Hongwei Hu
MeetBench-XL: Calibrated Multi-Dimensional Evaluation and Learned Dual-Policy Agents for Real-Time Meetings
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:Enterprise meeting environments require AI assistants that handle diverse operational tasks, from rapid fact checking during live discussions to cross meeting analysis for strategic planning, under strict latency, cost, and privacy constraints. Existing meeting benchmarks mainly focus on simplified question answering and fail to reflect real world enterprise workflows, where queries arise organically from multi stakeholder collaboration, span long temporal contexts, and require tool augmented reasoning. We address this gap through a grounded dataset and a learned agent framework. First, we introduce MeetAll, a bilingual and multimodal corpus derived from 231 enterprise meetings totaling 140 hours. Questions are injected using an enterprise informed protocol validated by domain expert review and human discriminability studies. Unlike purely synthetic benchmarks, this protocol is grounded in four enterprise critical dimensions: cognitive load, temporal context span, domain expertise, and actionable task execution, calibrated through interviews with stakeholders across finance, healthcare, and technology sectors. Second, we propose MeetBench XL, a multi dimensional evaluation protocol aligned with human judgment that measures factual fidelity, intent alignment, response efficiency, structural clarity, and completeness. Third, we present MeetMaster XL, a learned dual policy agent that jointly optimizes query routing between fast and slow reasoning paths and tool invocation, including retrieval, cross meeting aggregation, and web search. A lightweight classifier enables accurate routing with minimal overhead, achieving a superior quality latency tradeoff over single model baselines. Experiments against commercial systems show consistent gains, supported by ablations, robustness tests, and a real world deployment case study.Resources: https://github.com/huyuelin/MeetBench.
Lightweight High-Fidelity Low-Bitrate Talking Face Compression for 3D Video Conference
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The demand for immersive and interactive communication has driven advancements in 3D video conferencing, yet achieving high-fidelity 3D talking face representation at low bitrates remains a challenge. Traditional 2D video compression techniques fail to preserve fine-grained geometric and appearance details, while implicit neural rendering methods like NeRF suffer from prohibitive computational costs. To address these challenges, we propose a lightweight, high-fidelity, low-bitrate 3D talking face compression framework that integrates FLAME-based parametric modeling with 3DGS neural rendering. Our approach transmits only essential facial metadata in real time, enabling efficient reconstruction with a Gaussian-based head model. Additionally, we introduce a compact representation and compression scheme, including Gaussian attribute compression and MLP optimization, to enhance transmission efficiency. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves superior rate-distortion performance, delivering high-quality facial rendering at extremely low bitrates, making it well-suited for real-time 3D video conferencing applications.
UniDiffGrasp: A Unified Framework Integrating VLM Reasoning and VLM-Guided Part Diffusion for Open-Vocabulary Constrained Grasping with Dual Arms
May 11, 2025Abstract:Open-vocabulary, task-oriented grasping of specific functional parts, particularly with dual arms, remains a key challenge, as current Vision-Language Models (VLMs), while enhancing task understanding, often struggle with precise grasp generation within defined constraints and effective dual-arm coordination. We innovatively propose UniDiffGrasp, a unified framework integrating VLM reasoning with guided part diffusion to address these limitations. UniDiffGrasp leverages a VLM to interpret user input and identify semantic targets (object, part(s), mode), which are then grounded via open-vocabulary segmentation. Critically, the identified parts directly provide geometric constraints for a Constrained Grasp Diffusion Field (CGDF) using its Part-Guided Diffusion, enabling efficient, high-quality 6-DoF grasps without retraining. For dual-arm tasks, UniDiffGrasp defines distinct target regions, applies part-guided diffusion per arm, and selects stable cooperative grasps. Through extensive real-world deployment, UniDiffGrasp achieves grasp success rates of 0.876 in single-arm and 0.767 in dual-arm scenarios, significantly surpassing existing state-of-the-art methods, demonstrating its capability to enable precise and coordinated open-vocabulary grasping in complex real-world scenarios.
Linear Attention Modeling for Learned Image Compression
Feb 09, 2025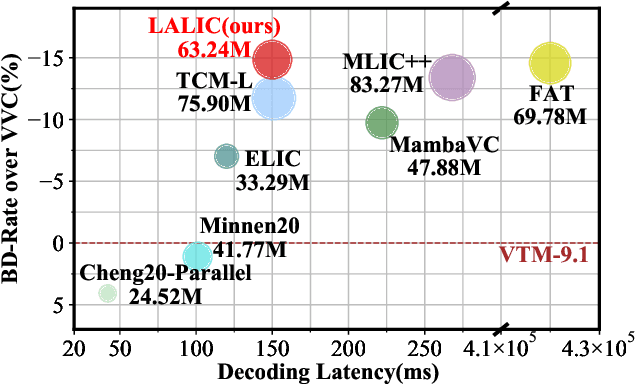



Abstract:Recent years, learned image compression has made tremendous progress to achieve impressive coding efficiency. Its coding gain mainly comes from non-linear neural network-based transform and learnable entropy modeling. However, most of recent focuses have been solely on a strong backbone, and few studies consider the low-complexity design. In this paper, we propose LALIC, a linear attention modeling for learned image compression. Specially, we propose to use Bi-RWKV blocks, by utilizing the Spatial Mix and Channel Mix modules to achieve more compact features extraction, and apply the Conv based Omni-Shift module to adapt to two-dimensional latent representation. Furthermore, we propose a RWKV-based Spatial-Channel ConTeXt model (RWKV-SCCTX), that leverages the Bi-RWKV to modeling the correlation between neighboring features effectively, to further improve the RD performance. To our knowledge, our work is the first work to utilize efficient Bi-RWKV models with linear attention for learned image compression. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves competitive RD performances by outperforming VTM-9.1 by -14.84%, -15.20%, -17.32% in BD-rate on Kodak, Tecnick and CLIC Professional validation datasets.
Chanel-Orderer: A Channel-Ordering Predictor for Tri-Channel Natural Images
Nov 20, 2024



Abstract:This paper shows a proof-of-concept that, given a typical 3-channel images but in a randomly permuted channel order, a model (termed as Chanel-Orderer) with ad-hoc inductive biases in terms of both architecture and loss functions can accurately predict the channel ordering and knows how to make it right. Specifically, Chanel-Orderer learns to score each of the three channels with the priors of object semantics and uses the resulting scores to predict the channel ordering. This brings up benefits into a typical scenario where an \texttt{RGB} image is often mis-displayed in the \texttt{BGR} format and needs to be corrected into the right order. Furthermore, as a byproduct, the resulting model Chanel-Orderer is able to tell whether a given image is a near-gray-scale image (near-monochromatic) or not (polychromatic). Our research suggests that Chanel-Orderer mimics human visual coloring of our physical natural world.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge