Yihuan Mao
MOORe: Model-based Offline-to-Online Reinforcement Learning
Jan 25, 2022



Abstract:With the success of offline reinforcement learning (RL), offline trained RL policies have the potential to be further improved when deployed online. A smooth transfer of the policy matters in safe real-world deployment. Besides, fast adaptation of the policy plays a vital role in practical online performance improvement. To tackle these challenges, we propose a simple yet efficient algorithm, Model-based Offline-to-Online Reinforcement learning (MOORe), which employs a prioritized sampling scheme that can dynamically adjust the offline and online data for smooth and efficient online adaptation of the policy. We provide a theoretical foundation for our algorithms design. Experiment results on the D4RL benchmark show that our algorithm smoothly transfers from offline to online stages while enabling sample-efficient online adaption, and also significantly outperforms existing methods.
SEIHAI: A Sample-efficient Hierarchical AI for the MineRL Competition
Nov 17, 2021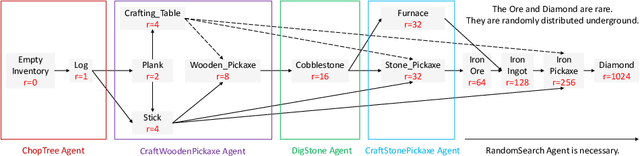
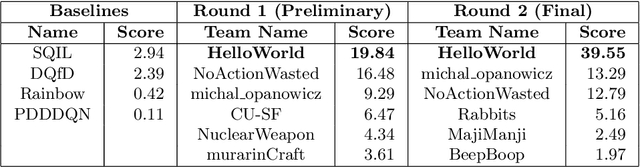

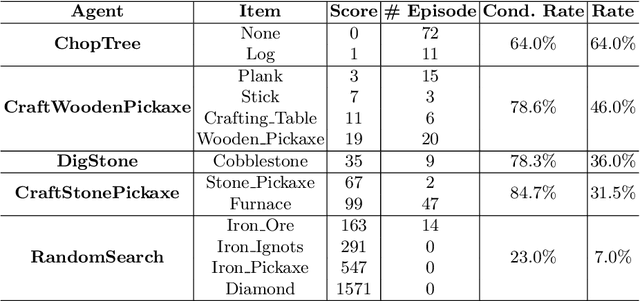
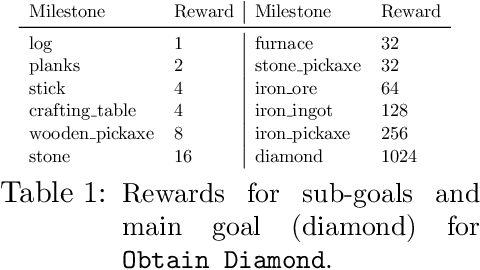
Abstract:The MineRL competition is designed for the development of reinforcement learning and imitation learning algorithms that can efficiently leverage human demonstrations to drastically reduce the number of environment interactions needed to solve the complex \emph{ObtainDiamond} task with sparse rewards. To address the challenge, in this paper, we present \textbf{SEIHAI}, a \textbf{S}ample-\textbf{e}ff\textbf{i}cient \textbf{H}ierarchical \textbf{AI}, that fully takes advantage of the human demonstrations and the task structure. Specifically, we split the task into several sequentially dependent subtasks, and train a suitable agent for each subtask using reinforcement learning and imitation learning. We further design a scheduler to select different agents for different subtasks automatically. SEIHAI takes the first place in the preliminary and final of the NeurIPS-2020 MineRL competition.
Towards robust and domain agnostic reinforcement learning competitions
Jun 07, 2021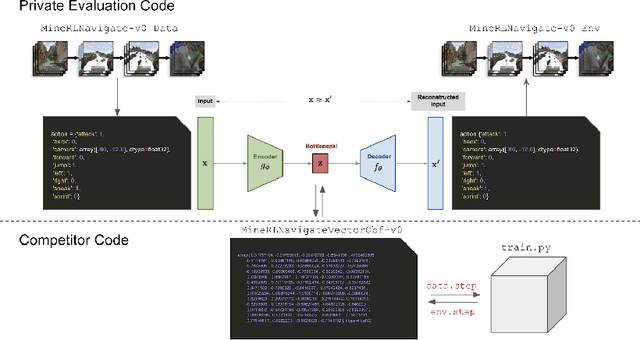
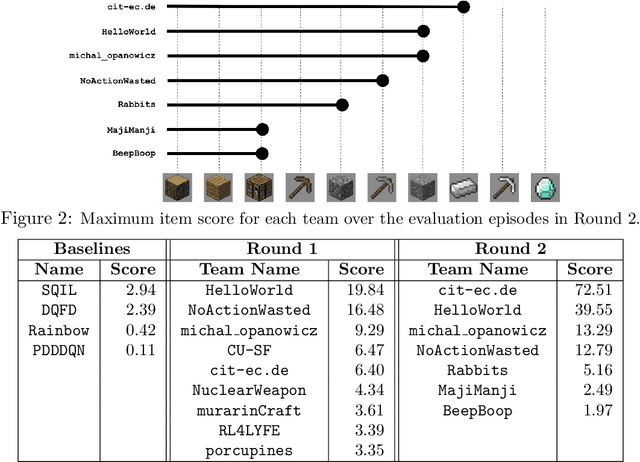
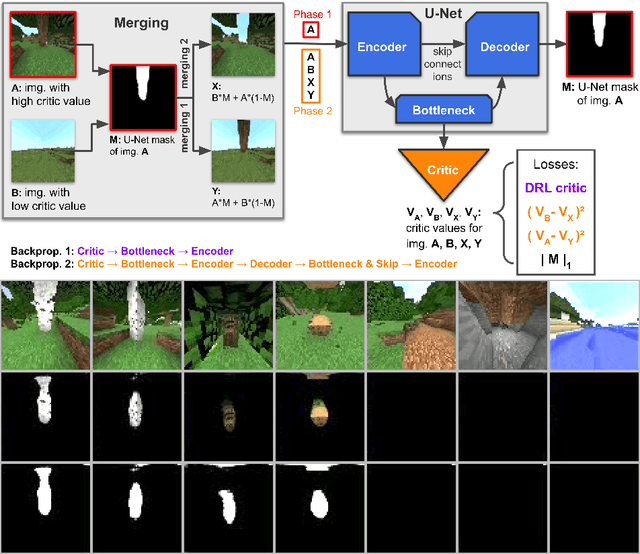
Abstract:Reinforcement learning competitions have formed the basis for standard research benchmarks, galvanized advances in the state-of-the-art, and shaped the direction of the field. Despite this, a majority of challenges suffer from the same fundamental problems: participant solutions to the posed challenge are usually domain-specific, biased to maximally exploit compute resources, and not guaranteed to be reproducible. In this paper, we present a new framework of competition design that promotes the development of algorithms that overcome these barriers. We propose four central mechanisms for achieving this end: submission retraining, domain randomization, desemantization through domain obfuscation, and the limitation of competition compute and environment-sample budget. To demonstrate the efficacy of this design, we proposed, organized, and ran the MineRL 2020 Competition on Sample-Efficient Reinforcement Learning. In this work, we describe the organizational outcomes of the competition and show that the resulting participant submissions are reproducible, non-specific to the competition environment, and sample/resource efficient, despite the difficult competition task.
LadaBERT: Lightweight Adaptation of BERT through Hybrid Model Compression
Apr 08, 2020



Abstract:BERT is a cutting-edge language representation model pre-trained by a large corpus, which achieves superior performances on various natural language understanding tasks. However, a major blocking issue of applying BERT to online services is that it is memory-intensive and leads to unsatisfactory latency of user requests, raising the necessity of model compression. Existing solutions leverage the knowledge distillation framework to learn a smaller model that imitates the behaviors of BERT. However, the training procedure of knowledge distillation is expensive itself as it requires sufficient training data to imitate the teacher model. In this paper, we address this issue by proposing a hybrid solution named LadaBERT (Lightweight adaptation of BERT through hybrid model compression), which combines the advantages of different model compression methods, including weight pruning, matrix factorization and knowledge distillation. LadaBERT achieves state-of-the-art accuracy on various public datasets while the training overheads can be reduced by an order of magnitude.
CrowdPose: Efficient Crowded Scenes Pose Estimation and A New Benchmark
Dec 02, 2018
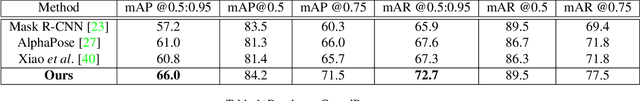
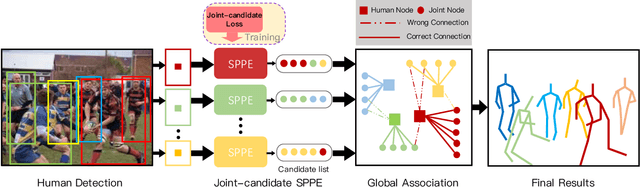
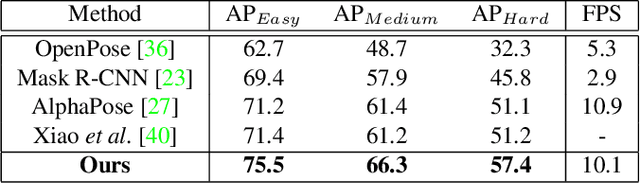
Abstract:Multi-person pose estimation is fundamental to many computer vision tasks and has made significant progress in recent years. However, few previous methods explored the problem of pose estimation in crowded scenes while it remains challenging and inevitable in many scenarios. Moreover, current benchmarks cannot provide an appropriate evaluation for such cases. In this paper, we propose a novel and efficient method to tackle the problem of pose estimation in the crowd and a new dataset to better evaluate algorithms. Our model consists of two key components: joint-candidate single person pose estimation (SPPE) and global maximum joints association. With multi-peak prediction for each joint and global association using graph model, our method is robust to inevitable interference in crowded scenes and very efficient in inference. The proposed method surpasses the state-of-the-art methods on CrowdPose dataset by 4.8 mAP and results on MSCOCO dataset demonstrate the generalization ability of our method. Source code and dataset will be made publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge