Yifeng Shi
Sat2RealCity: Geometry-Aware and Appearance-Controllable 3D Urban Generation from Satellite Imagery
Nov 14, 2025Abstract:Recent advances in generative modeling have substantially enhanced 3D urban generation, enabling applications in digital twins, virtual cities, and large-scale simulations. However, existing methods face two key challenges: (1) the need for large-scale 3D city assets for supervised training, which are difficult and costly to obtain, and (2) reliance on semantic or height maps, which are used exclusively for generating buildings in virtual worlds and lack connection to real-world appearance, limiting the realism and generalizability of generated cities. To address these limitations, we propose Sat2RealCity, a geometry-aware and appearance-controllable framework for 3D urban generation from real-world satellite imagery. Unlike previous city-level generation methods, Sat2RealCity builds generation upon individual building entities, enabling the use of rich priors and pretrained knowledge from 3D object generation while substantially reducing dependence on large-scale 3D city assets. Specifically, (1) we introduce the OSM-based spatial priors strategy to achieve interpretable geometric generation from spatial topology to building instances; (2) we design an appearance-guided controllable modeling mechanism for fine-grained appearance realism and style control; and (3) we construct an MLLM-powered semantic-guided generation pipeline, bridging semantic interpretation and geometric reconstruction. Extensive quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that Sat2RealCity significantly surpasses existing baselines in structural consistency and appearance realism, establishing a strong foundation for real-world aligned 3D urban content creation. The code will be released soon.
DoReMi: A Domain-Representation Mixture Framework for Generalizable 3D Understanding
Nov 14, 2025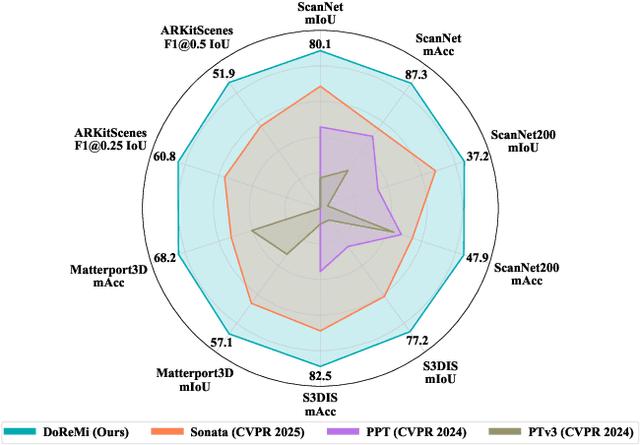
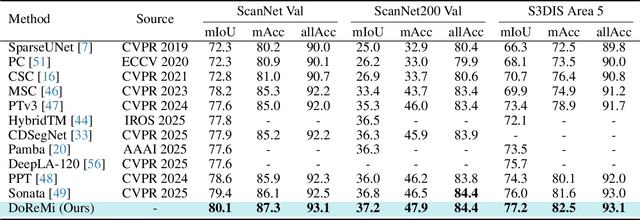
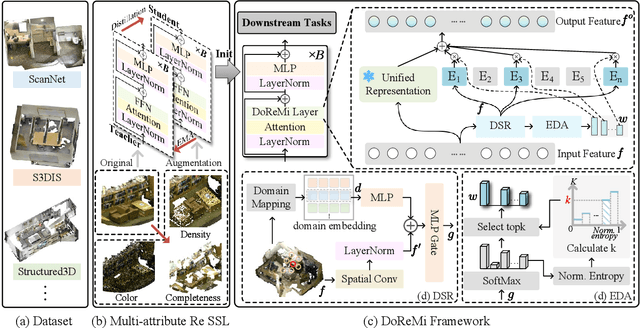
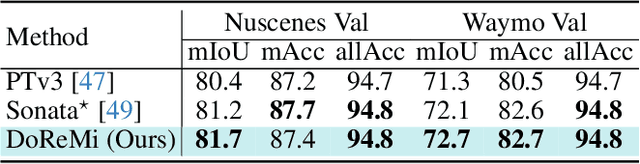
Abstract:The generalization of 3D deep learning across multiple domains remains limited by the limited scale of existing datasets and the high heterogeneity of multi-source point clouds. Point clouds collected from different sensors (e.g., LiDAR scans and mesh-derived point clouds) exhibit substantial discrepancies in density and noise distribution, resulting in negative transfer during multi-domain fusion. Most existing approaches focus exclusively on either domain-aware or domain-general features, overlooking the potential synergy between them. To address this, we propose DoReMi (Domain-Representation Mixture), a Mixture-of-Experts (MoE) framework that jointly models Domain-aware Experts branch and a unified Representation branch to enable cooperative learning between specialized and generalizable knowledge. DoReMi dynamically activates domain-aware expert branch via Domain-Guided Spatial Routing (DSR) for context-aware expert selection and employs Entropy-Controlled Dynamic Allocation (EDA) for stable and efficient expert utilization, thereby adaptively modeling diverse domain distributions. Complemented by a frozen unified representation branch pretrained through robust multi-attribute self-supervised learning, DoReMi preserves cross-domain geometric and structural priors while maintaining global consistency. We evaluate DoReMi across multiple 3D understanding benchmarks. Notably, DoReMi achieves 80.1% mIoU on ScanNet Val and 77.2% mIoU on S3DIS, demonstrating competitive or superior performance compared to existing approaches, and showing strong potential as a foundation framework for future 3D understanding research. The code will be released soon.
RopeBEV: A Multi-Camera Roadside Perception Network in Bird's-Eye-View
Sep 18, 2024



Abstract:Multi-camera perception methods in Bird's-Eye-View (BEV) have gained wide application in autonomous driving. However, due to the differences between roadside and vehicle-side scenarios, there currently lacks a multi-camera BEV solution in roadside. This paper systematically analyzes the key challenges in multi-camera BEV perception for roadside scenarios compared to vehicle-side. These challenges include the diversity in camera poses, the uncertainty in Camera numbers, the sparsity in perception regions, and the ambiguity in orientation angles. In response, we introduce RopeBEV, the first dense multi-camera BEV approach. RopeBEV introduces BEV augmentation to address the training balance issues caused by diverse camera poses. By incorporating CamMask and ROIMask (Region of Interest Mask), it supports variable camera numbers and sparse perception, respectively. Finally, camera rotation embedding is utilized to resolve orientation ambiguity. Our method ranks 1st on the real-world highway dataset RoScenes and demonstrates its practical value on a private urban dataset that covers more than 50 intersections and 600 cameras.
RT-DETRv3: Real-time End-to-End Object Detection with Hierarchical Dense Positive Supervision
Sep 13, 2024



Abstract:RT-DETR is the first real-time end-to-end transformer-based object detector. Its efficiency comes from the framework design and the Hungarian matching. However, compared to dense supervision detectors like the YOLO series, the Hungarian matching provides much sparser supervision, leading to insufficient model training and difficult to achieve optimal results. To address these issues, we proposed a hierarchical dense positive supervision method based on RT-DETR, named RT-DETRv3. Firstly, we introduce a CNN-based auxiliary branch that provides dense supervision that collaborates with the original decoder to enhance the encoder feature representation. Secondly, to address insufficient decoder training, we propose a novel learning strategy involving self-attention perturbation. This strategy diversifies label assignment for positive samples across multiple query groups, thereby enriching positive supervisions. Additionally, we introduce a shared-weight decoder branch for dense positive supervision to ensure more high-quality queries matching each ground truth. Notably, all aforementioned modules are training-only. We conduct extensive experiments to demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach on COCO val2017. RT-DETRv3 significantly outperforms existing real-time detectors, including the RT-DETR series and the YOLO series. For example, RT-DETRv3-R18 achieves 48.1% AP (+1.6%/+1.4%) compared to RT-DETR-R18/RT-DETRv2-R18 while maintaining the same latency. Meanwhile, it requires only half of epochs to attain a comparable performance. Furthermore, RT-DETRv3-R101 can attain an impressive 54.6% AP outperforming YOLOv10-X. Code will be released soon.
Explore the LiDAR-Camera Dynamic Adjustment Fusion for 3D Object Detection
Jul 22, 2024Abstract:Camera and LiDAR serve as informative sensors for accurate and robust autonomous driving systems. However, these sensors often exhibit heterogeneous natures, resulting in distributional modality gaps that present significant challenges for fusion. To address this, a robust fusion technique is crucial, particularly for enhancing 3D object detection. In this paper, we introduce a dynamic adjustment technology aimed at aligning modal distributions and learning effective modality representations to enhance the fusion process. Specifically, we propose a triphase domain aligning module. This module adjusts the feature distributions from both the camera and LiDAR, bringing them closer to the ground truth domain and minimizing differences. Additionally, we explore improved representation acquisition methods for dynamic fusion, which includes modal interaction and specialty enhancement. Finally, an adaptive learning technique that merges the semantics and geometry information for dynamical instance optimization. Extensive experiments in the nuScenes dataset present competitive performance with state-of-the-art approaches. Our code will be released in the future.
ViT-CoMer: Vision Transformer with Convolutional Multi-scale Feature Interaction for Dense Predictions
Mar 15, 2024Abstract:Although Vision Transformer (ViT) has achieved significant success in computer vision, it does not perform well in dense prediction tasks due to the lack of inner-patch information interaction and the limited diversity of feature scale. Most existing studies are devoted to designing vision-specific transformers to solve the above problems, which introduce additional pre-training costs. Therefore, we present a plain, pre-training-free, and feature-enhanced ViT backbone with Convolutional Multi-scale feature interaction, named ViT-CoMer, which facilitates bidirectional interaction between CNN and transformer. Compared to the state-of-the-art, ViT-CoMer has the following advantages: (1) We inject spatial pyramid multi-receptive field convolutional features into the ViT architecture, which effectively alleviates the problems of limited local information interaction and single-feature representation in ViT. (2) We propose a simple and efficient CNN-Transformer bidirectional fusion interaction module that performs multi-scale fusion across hierarchical features, which is beneficial for handling dense prediction tasks. (3) We evaluate the performance of ViT-CoMer across various dense prediction tasks, different frameworks, and multiple advanced pre-training. Notably, our ViT-CoMer-L achieves 64.3% AP on COCO val2017 without extra training data, and 62.1% mIoU on ADE20K val, both of which are comparable to state-of-the-art methods. We hope ViT-CoMer can serve as a new backbone for dense prediction tasks to facilitate future research. The code will be released at https://github.com/Traffic-X/ViT-CoMer.
MonoLSS: Learnable Sample Selection For Monocular 3D Detection
Dec 22, 2023



Abstract:In the field of autonomous driving, monocular 3D detection is a critical task which estimates 3D properties (depth, dimension, and orientation) of objects in a single RGB image. Previous works have used features in a heuristic way to learn 3D properties, without considering that inappropriate features could have adverse effects. In this paper, sample selection is introduced that only suitable samples should be trained to regress the 3D properties. To select samples adaptively, we propose a Learnable Sample Selection (LSS) module, which is based on Gumbel-Softmax and a relative-distance sample divider. The LSS module works under a warm-up strategy leading to an improvement in training stability. Additionally, since the LSS module dedicated to 3D property sample selection relies on object-level features, we further develop a data augmentation method named MixUp3D to enrich 3D property samples which conforms to imaging principles without introducing ambiguity. As two orthogonal methods, the LSS module and MixUp3D can be utilized independently or in conjunction. Sufficient experiments have shown that their combined use can lead to synergistic effects, yielding improvements that transcend the mere sum of their individual applications. Leveraging the LSS module and the MixUp3D, without any extra data, our method named MonoLSS ranks 1st in all three categories (Car, Cyclist, and Pedestrian) on KITTI 3D object detection benchmark, and achieves competitive results on both the Waymo dataset and KITTI-nuScenes cross-dataset evaluation. The code is included in the supplementary material and will be released to facilitate related academic and industrial studies.
DUSA: Decoupled Unsupervised Sim2Real Adaptation for Vehicle-to-Everything Collaborative Perception
Oct 12, 2023Abstract:Vehicle-to-Everything (V2X) collaborative perception is crucial for autonomous driving. However, achieving high-precision V2X perception requires a significant amount of annotated real-world data, which can always be expensive and hard to acquire. Simulated data have raised much attention since they can be massively produced at an extremely low cost. Nevertheless, the significant domain gap between simulated and real-world data, including differences in sensor type, reflectance patterns, and road surroundings, often leads to poor performance of models trained on simulated data when evaluated on real-world data. In addition, there remains a domain gap between real-world collaborative agents, e.g. different types of sensors may be installed on autonomous vehicles and roadside infrastructures with different extrinsics, further increasing the difficulty of sim2real generalization. To take full advantage of simulated data, we present a new unsupervised sim2real domain adaptation method for V2X collaborative detection named Decoupled Unsupervised Sim2Real Adaptation (DUSA). Our new method decouples the V2X collaborative sim2real domain adaptation problem into two sub-problems: sim2real adaptation and inter-agent adaptation. For sim2real adaptation, we design a Location-adaptive Sim2Real Adapter (LSA) module to adaptively aggregate features from critical locations of the feature map and align the features between simulated data and real-world data via a sim/real discriminator on the aggregated global feature. For inter-agent adaptation, we further devise a Confidence-aware Inter-agent Adapter (CIA) module to align the fine-grained features from heterogeneous agents under the guidance of agent-wise confidence maps. Experiments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed DUSA approach on unsupervised sim2real adaptation from the simulated V2XSet dataset to the real-world DAIR-V2X-C dataset.
V2X-Seq: A Large-Scale Sequential Dataset for Vehicle-Infrastructure Cooperative Perception and Forecasting
May 10, 2023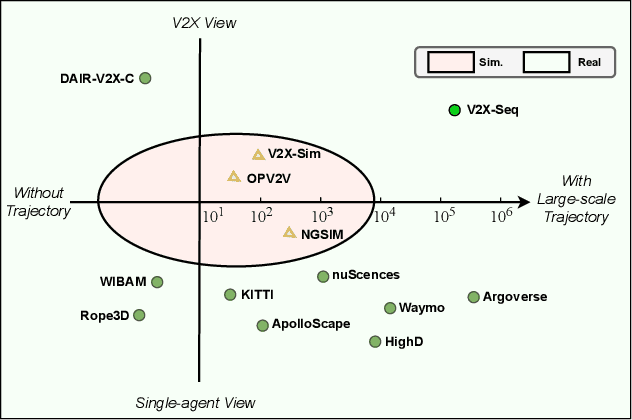
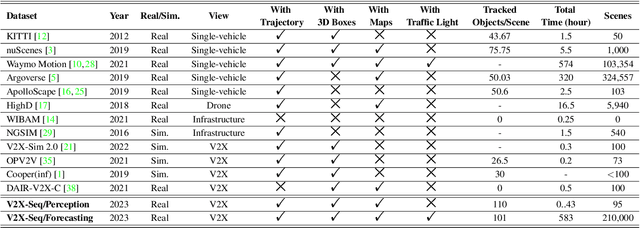
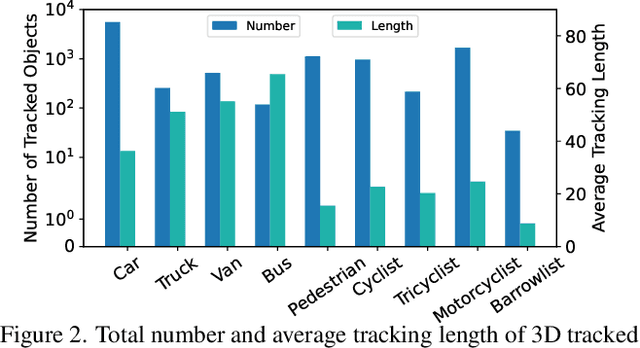
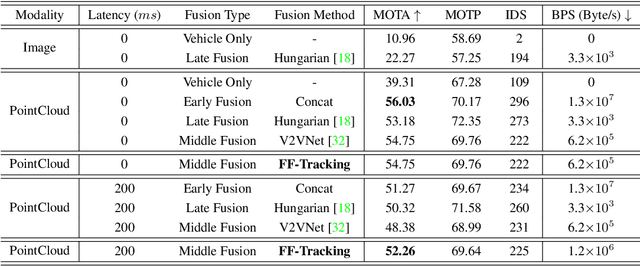
Abstract:Utilizing infrastructure and vehicle-side information to track and forecast the behaviors of surrounding traffic participants can significantly improve decision-making and safety in autonomous driving. However, the lack of real-world sequential datasets limits research in this area. To address this issue, we introduce V2X-Seq, the first large-scale sequential V2X dataset, which includes data frames, trajectories, vector maps, and traffic lights captured from natural scenery. V2X-Seq comprises two parts: the sequential perception dataset, which includes more than 15,000 frames captured from 95 scenarios, and the trajectory forecasting dataset, which contains about 80,000 infrastructure-view scenarios, 80,000 vehicle-view scenarios, and 50,000 cooperative-view scenarios captured from 28 intersections' areas, covering 672 hours of data. Based on V2X-Seq, we introduce three new tasks for vehicle-infrastructure cooperative (VIC) autonomous driving: VIC3D Tracking, Online-VIC Forecasting, and Offline-VIC Forecasting. We also provide benchmarks for the introduced tasks. Find data, code, and more up-to-date information at \href{https://github.com/AIR-THU/DAIR-V2X-Seq}{https://github.com/AIR-THU/DAIR-V2X-Seq}.
Multimodal Understanding Through Correlation Maximization and Minimization
May 04, 2023Abstract:Multimodal learning has mainly focused on learning large models on, and fusing feature representations from, different modalities for better performances on downstream tasks. In this work, we take a detour from this trend and study the intrinsic nature of multimodal data by asking the following questions: 1) Can we learn more structured latent representations of general multimodal data?; and 2) can we intuitively understand, both mathematically and visually, what the latent representations capture? To answer 1), we propose a general and lightweight framework, Multimodal Understanding Through Correlation Maximization and Minimization (MUCMM), that can be incorporated into any large pre-trained network. MUCMM learns both the common and individual representations. The common representations capture what is common between the modalities; the individual representations capture the unique aspect of the modalities. To answer 2), we propose novel scores that summarize the learned common and individual structures and visualize the score gradients with respect to the input, visually discerning what the different representations capture. We further provide mathematical intuitions of the computed gradients in a linear setting, and demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach through a variety of experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge