Xingcheng Zhou
TUMTraf EMOT: Event-Based Multi-Object Tracking Dataset and Baseline for Traffic Scenarios
Dec 20, 2025Abstract:In Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), multi-object tracking is primarily based on frame-based cameras. However, these cameras tend to perform poorly under dim lighting and high-speed motion conditions. Event cameras, characterized by low latency, high dynamic range and high temporal resolution, have considerable potential to mitigate these issues. Compared to frame-based vision, there are far fewer studies on event-based vision. To address this research gap, we introduce an initial pilot dataset tailored for event-based ITS, covering vehicle and pedestrian detection and tracking. We establish a tracking-by-detection benchmark with a specialized feature extractor based on this dataset, achieving excellent performance.
Safety-Critical Learning for Long-Tail Events: The TUM Traffic Accident Dataset
Aug 20, 2025Abstract:Even though a significant amount of work has been done to increase the safety of transportation networks, accidents still occur regularly. They must be understood as an unavoidable and sporadic outcome of traffic networks. We present the TUM Traffic Accident (TUMTraf-A) dataset, a collection of real-world highway accidents. It contains ten sequences of vehicle crashes at high-speed driving with 294,924 labeled 2D and 93,012 labeled 3D boxes and track IDs within 48,144 labeled frames recorded from four roadside cameras and LiDARs at 10 Hz. The dataset contains ten object classes and is provided in the OpenLABEL format. We propose Accid3nD, an accident detection model that combines a rule-based approach with a learning-based one. Experiments and ablation studies on our dataset show the robustness of our proposed method. The dataset, model, and code are available on our project website: https://tum-traffic-dataset.github.io/tumtraf-a.
Generative AI for Autonomous Driving: Frontiers and Opportunities
May 13, 2025Abstract:Generative Artificial Intelligence (GenAI) constitutes a transformative technological wave that reconfigures industries through its unparalleled capabilities for content creation, reasoning, planning, and multimodal understanding. This revolutionary force offers the most promising path yet toward solving one of engineering's grandest challenges: achieving reliable, fully autonomous driving, particularly the pursuit of Level 5 autonomy. This survey delivers a comprehensive and critical synthesis of the emerging role of GenAI across the autonomous driving stack. We begin by distilling the principles and trade-offs of modern generative modeling, encompassing VAEs, GANs, Diffusion Models, and Large Language Models (LLMs). We then map their frontier applications in image, LiDAR, trajectory, occupancy, video generation as well as LLM-guided reasoning and decision making. We categorize practical applications, such as synthetic data workflows, end-to-end driving strategies, high-fidelity digital twin systems, smart transportation networks, and cross-domain transfer to embodied AI. We identify key obstacles and possibilities such as comprehensive generalization across rare cases, evaluation and safety checks, budget-limited implementation, regulatory compliance, ethical concerns, and environmental effects, while proposing research plans across theoretical assurances, trust metrics, transport integration, and socio-technical influence. By unifying these threads, the survey provides a forward-looking reference for researchers, engineers, and policymakers navigating the convergence of generative AI and advanced autonomous mobility. An actively maintained repository of cited works is available at https://github.com/taco-group/GenAI4AD.
LiDAR-Guided Monocular 3D Object Detection for Long-Range Railway Monitoring
Apr 25, 2025
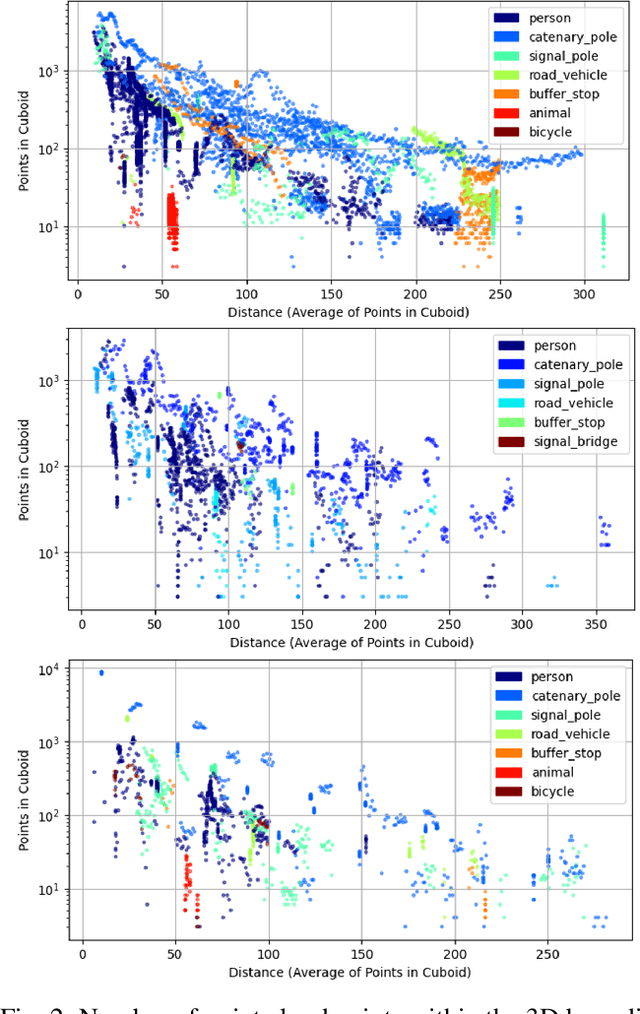


Abstract:Railway systems, particularly in Germany, require high levels of automation to address legacy infrastructure challenges and increase train traffic safely. A key component of automation is robust long-range perception, essential for early hazard detection, such as obstacles at level crossings or pedestrians on tracks. Unlike automotive systems with braking distances of ~70 meters, trains require perception ranges exceeding 1 km. This paper presents an deep-learning-based approach for long-range 3D object detection tailored for autonomous trains. The method relies solely on monocular images, inspired by the Faraway-Frustum approach, and incorporates LiDAR data during training to improve depth estimation. The proposed pipeline consists of four key modules: (1) a modified YOLOv9 for 2.5D object detection, (2) a depth estimation network, and (3-4) dedicated short- and long-range 3D detection heads. Evaluations on the OSDaR23 dataset demonstrate the effectiveness of the approach in detecting objects up to 250 meters. Results highlight its potential for railway automation and outline areas for future improvement.
OpenDriveVLA: Towards End-to-end Autonomous Driving with Large Vision Language Action Model
Mar 30, 2025



Abstract:We present OpenDriveVLA, a Vision-Language Action (VLA) model designed for end-to-end autonomous driving. OpenDriveVLA builds upon open-source pre-trained large Vision-Language Models (VLMs) to generate reliable driving actions, conditioned on 3D environmental perception, ego vehicle states, and driver commands. To bridge the modality gap between driving visual representations and language embeddings, we propose a hierarchical vision-language alignment process, projecting both 2D and 3D structured visual tokens into a unified semantic space. Besides, OpenDriveVLA models the dynamic relationships between the ego vehicle, surrounding agents, and static road elements through an autoregressive agent-env-ego interaction process, ensuring both spatially and behaviorally informed trajectory planning. Extensive experiments on the nuScenes dataset demonstrate that OpenDriveVLA achieves state-of-the-art results across open-loop trajectory planning and driving-related question-answering tasks. Qualitative analyses further illustrate OpenDriveVLA's superior capability to follow high-level driving commands and robustly generate trajectories under challenging scenarios, highlighting its potential for next-generation end-to-end autonomous driving. We will release our code to facilitate further research in this domain.
Towards Vision Zero: The Accid3nD Dataset
Mar 15, 2025



Abstract:Even though a significant amount of work has been done to increase the safety of transportation networks, accidents still occur regularly. They must be understood as unavoidable and sporadic outcomes of traffic networks. No public dataset contains 3D annotations of real-world accidents recorded from roadside sensors. We present the Accid3nD dataset, a collection of real-world highway accidents in different weather and lighting conditions. It contains vehicle crashes at high-speed driving with 2,634,233 labeled 2D bounding boxes, instance masks, and 3D bounding boxes with track IDs. In total, the dataset contains 111,945 labeled frames recorded from four roadside cameras and LiDARs at 25 Hz. The dataset contains six object classes and is provided in the OpenLABEL format. We propose an accident detection model that combines a rule-based approach with a learning-based one. Experiments and ablation studies on our dataset show the robustness of our proposed method. The dataset, model, and code are available on our website: https://accident-dataset.github.io.
TUMTraffic-VideoQA: A Benchmark for Unified Spatio-Temporal Video Understanding in Traffic Scenes
Feb 04, 2025



Abstract:We present TUMTraffic-VideoQA, a novel dataset and benchmark designed for spatio-temporal video understanding in complex roadside traffic scenarios. The dataset comprises 1,000 videos, featuring 85,000 multiple-choice QA pairs, 2,300 object captioning, and 5,700 object grounding annotations, encompassing diverse real-world conditions such as adverse weather and traffic anomalies. By incorporating tuple-based spatio-temporal object expressions, TUMTraffic-VideoQA unifies three essential tasks-multiple-choice video question answering, referred object captioning, and spatio-temporal object grounding-within a cohesive evaluation framework. We further introduce the TUMTraffic-Qwen baseline model, enhanced with visual token sampling strategies, providing valuable insights into the challenges of fine-grained spatio-temporal reasoning. Extensive experiments demonstrate the dataset's complexity, highlight the limitations of existing models, and position TUMTraffic-VideoQA as a robust foundation for advancing research in intelligent transportation systems. The dataset and benchmark are publicly available to facilitate further exploration.
WARM-3D: A Weakly-Supervised Sim2Real Domain Adaptation Framework for Roadside Monocular 3D Object Detection
Jul 30, 2024



Abstract:Existing roadside perception systems are limited by the absence of publicly available, large-scale, high-quality 3D datasets. Exploring the use of cost-effective, extensive synthetic datasets offers a viable solution to tackle this challenge and enhance the performance of roadside monocular 3D detection. In this study, we introduce the TUMTraf Synthetic Dataset, offering a diverse and substantial collection of high-quality 3D data to augment scarce real-world datasets. Besides, we present WARM-3D, a concise yet effective framework to aid the Sim2Real domain transfer for roadside monocular 3D detection. Our method leverages cheap synthetic datasets and 2D labels from an off-the-shelf 2D detector for weak supervision. We show that WARM-3D significantly enhances performance, achieving a +12.40% increase in mAP 3D over the baseline with only pseudo-2D supervision. With 2D GT as weak labels, WARM-3D even reaches performance close to the Oracle baseline. Moreover, WARM-3D improves the ability of 3D detectors to unseen sample recognition across various real-world environments, highlighting its potential for practical applications.
GraphRelate3D: Context-Dependent 3D Object Detection with Inter-Object Relationship Graphs
May 10, 2024



Abstract:Accurate and effective 3D object detection is critical for ensuring the driving safety of autonomous vehicles. Recently, state-of-the-art two-stage 3D object detectors have exhibited promising performance. However, these methods refine proposals individually, ignoring the rich contextual information in the object relationships between the neighbor proposals. In this study, we introduce an object relation module, consisting of a graph generator and a graph neural network (GNN), to learn the spatial information from certain patterns to improve 3D object detection. Specifically, we create an inter-object relationship graph based on proposals in a frame via the graph generator to connect each proposal with its neighbor proposals. Afterward, the GNN module extracts edge features from the generated graph and iteratively refines proposal features with the captured edge features. Ultimately, we leverage the refined features as input to the detection head to obtain detection results. Our approach improves upon the baseline PV-RCNN on the KITTI validation set for the car class across easy, moderate, and hard difficulty levels by 0.82%, 0.74%, and 0.58%, respectively. Additionally, our method outperforms the baseline by more than 1% under the moderate and hard levels BEV AP on the test server.
PointCompress3D -- A Point Cloud Compression Framework for Roadside LiDARs in Intelligent Transportation Systems
May 02, 2024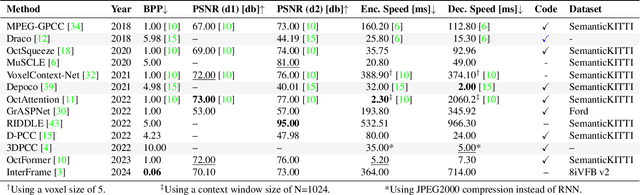

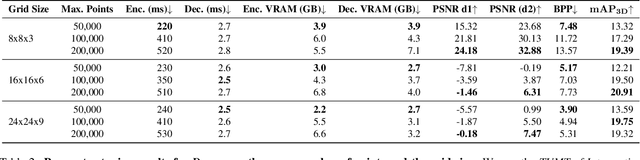
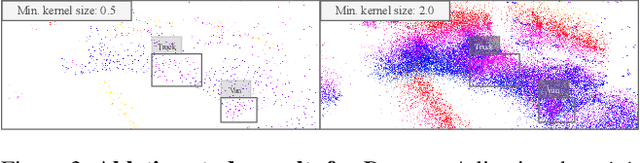
Abstract:In the context of Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITS), efficient data compression is crucial for managing large-scale point cloud data acquired by roadside LiDAR sensors. The demand for efficient storage, streaming, and real-time object detection capabilities for point cloud data is substantial. This work introduces PointCompress3D, a novel point cloud compression framework tailored specifically for roadside LiDARs. Our framework addresses the challenges of compressing high-resolution point clouds while maintaining accuracy and compatibility with roadside LiDAR sensors. We adapt, extend, integrate, and evaluate three cutting-edge compression methods using our real-world-based TUMTraf dataset family. We achieve a frame rate of 10 FPS while keeping compression sizes below 105 Kb, a reduction of 50 times, and maintaining object detection performance on par with the original data. In extensive experiments and ablation studies, we finally achieved a PSNR d2 of 94.46 and a BPP of 6.54 on our dataset. Future work includes the deployment on the live system. The code is available on our project website: https://pointcompress3d.github.io.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge