Xiangbo Shu
Spatiotemporal-Untrammelled Mixture of Experts for Multi-Person Motion Prediction
Dec 25, 2025Abstract:Comprehensively and flexibly capturing the complex spatio-temporal dependencies of human motion is critical for multi-person motion prediction. Existing methods grapple with two primary limitations: i) Inflexible spatiotemporal representation due to reliance on positional encodings for capturing spatiotemporal information. ii) High computational costs stemming from the quadratic time complexity of conventional attention mechanisms. To overcome these limitations, we propose the Spatiotemporal-Untrammelled Mixture of Experts (ST-MoE), which flexibly explores complex spatio-temporal dependencies in human motion and significantly reduces computational cost. To adaptively mine complex spatio-temporal patterns from human motion, our model incorporates four distinct types of spatiotemporal experts, each specializing in capturing different spatial or temporal dependencies. To reduce the potential computational overhead while integrating multiple experts, we introduce bidirectional spatiotemporal Mamba as experts, each sharing bidirectional temporal and spatial Mamba in distinct combinations to achieve model efficiency and parameter economy. Extensive experiments on four multi-person benchmark datasets demonstrate that our approach not only outperforms state-of-art in accuracy but also reduces model parameter by 41.38% and achieves a 3.6x speedup in training. The code is available at https://github.com/alanyz106/ST-MoE.
MUST: Multi-Scale Structural-Temporal Link Prediction Model for UAV Ad Hoc Networks
May 14, 2025Abstract:Link prediction in unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) ad hoc networks (UANETs) aims to predict the potential formation of future links between UAVs. In adversarial environments where the route information of UAVs is unavailable, predicting future links must rely solely on the observed historical topological information of UANETs. However, the highly dynamic and sparse nature of UANET topologies presents substantial challenges in effectively capturing meaningful structural and temporal patterns for accurate link prediction. Most existing link prediction methods focus on temporal dynamics at a single structural scale while neglecting the effects of sparsity, resulting in insufficient information capture and limited applicability to UANETs. In this paper, we propose a multi-scale structural-temporal link prediction model (MUST) for UANETs. Specifically, we first employ graph attention networks (GATs) to capture structural features at multiple levels, including the individual UAV level, the UAV community level, and the overall network level. Then, we use long short-term memory (LSTM) networks to learn the temporal dynamics of these multi-scale structural features. Additionally, we address the impact of sparsity by introducing a sophisticated loss function during model optimization. We validate the performance of MUST using several UANET datasets generated through simulations. Extensive experimental results demonstrate that MUST achieves state-of-the-art link prediction performance in highly dynamic and sparse UANETs.
Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization for Few-shot Action Recognition
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) aims to recognize novel action categories with few exemplars. Existing methods typically learn frame-level representations independently for each video by designing various inter-frame temporal modeling strategies. However, they neglect explicit relation modeling between videos and tasks, thus failing to capture shared temporal patterns across videos and reuse temporal knowledge from historical tasks. In light of this, we propose HR2G-shot, a Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization framework for FSAR, which unifies three types of relation modeling (inter-frame, inter-video, and inter-task) to learn task-specific temporal patterns from a holistic view. In addition to conducting inter-frame temporal interactions, we further devise two components to respectively explore inter-video and inter-task relationships: i) Inter-video Semantic Correlation (ISC) performs cross-video frame-level interactions in a fine-grained manner, thereby capturing task-specific query features and learning intra- and inter-class temporal correlations among support features; ii) Inter-task Knowledge Transfer (IKT) retrieves and aggregates relevant temporal knowledge from the bank, which stores diverse temporal patterns from historical tasks. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks show that HR2G-shot outperforms current top-leading FSAR methods.
Learning Clustering-based Prototypes for Compositional Zero-shot Learning
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Learning primitive (i.e., attribute and object) concepts from seen compositions is the primary challenge of Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). Existing CZSL solutions typically rely on oversimplified data assumptions, e.g., modeling each primitive with a single centroid primitive representation, ignoring the natural diversities of the attribute (resp. object) when coupled with different objects (resp. attribute). In this work, we develop ClusPro, a robust clustering-based prototype mining framework for CZSL that defines the conceptual boundaries of primitives through a set of diversified prototypes. Specifically, ClusPro conducts within-primitive clustering on the embedding space for automatically discovering and dynamically updating prototypes. These representative prototypes are subsequently used to repaint a well-structured and independent primitive embedding space, ensuring intra-primitive separation and inter-primitive decorrelation through prototype-based contrastive learning and decorrelation learning. Moreover, ClusPro efficiently performs prototype clustering in a non-parametric fashion without the introduction of additional learnable parameters or computational budget during testing. Experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate ClusPro outperforms various top-leading CZSL solutions under both closed-world and open-world settings.
Kernel-Aware Graph Prompt Learning for Few-Shot Anomaly Detection
Dec 23, 2024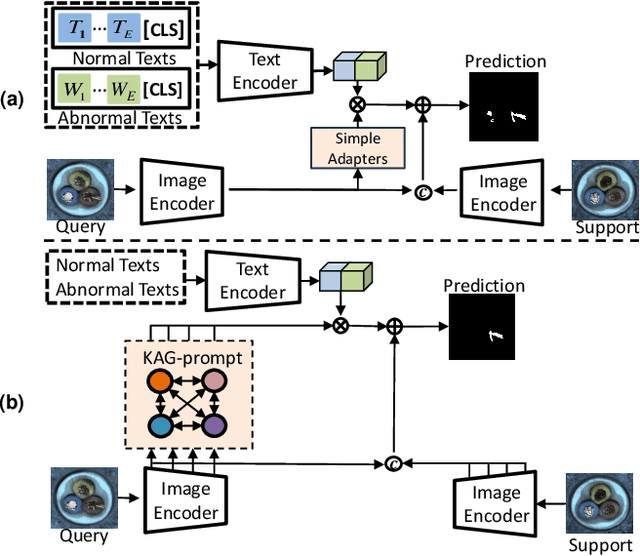
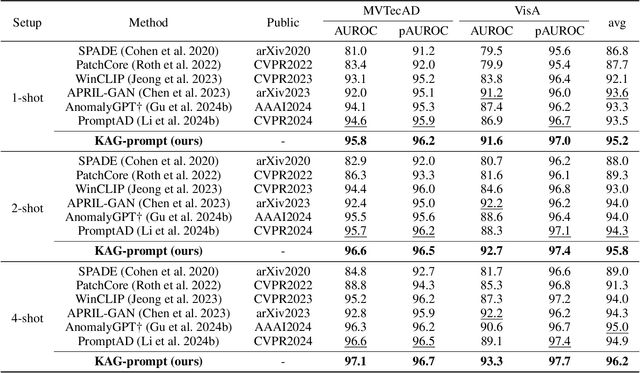
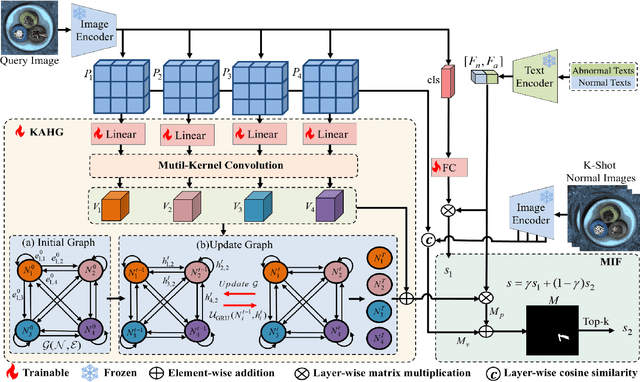
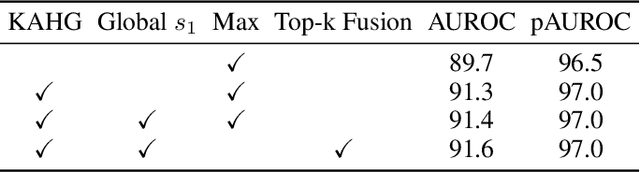
Abstract:Few-shot anomaly detection (FSAD) aims to detect unseen anomaly regions with the guidance of very few normal support images from the same class. Existing FSAD methods usually find anomalies by directly designing complex text prompts to align them with visual features under the prevailing large vision-language model paradigm. However, these methods, almost always, neglect intrinsic contextual information in visual features, e.g., the interaction relationships between different vision layers, which is an important clue for detecting anomalies comprehensively. To this end, we propose a kernel-aware graph prompt learning framework, termed as KAG-prompt, by reasoning the cross-layer relations among visual features for FSAD. Specifically, a kernel-aware hierarchical graph is built by taking the different layer features focusing on anomalous regions of different sizes as nodes, meanwhile, the relationships between arbitrary pairs of nodes stand for the edges of the graph. By message passing over this graph, KAG-prompt can capture cross-layer contextual information, thus leading to more accurate anomaly prediction. Moreover, to integrate the information of multiple important anomaly signals in the prediction map, we propose a novel image-level scoring method based on multi-level information fusion. Extensive experiments on MVTecAD and VisA datasets show that KAG-prompt achieves state-of-the-art FSAD results for image-level/pixel-level anomaly detection. Code is available at https://github.com/CVL-hub/KAG-prompt.git.
EventCrab: Harnessing Frame and Point Synergy for Event-based Action Recognition and Beyond
Nov 27, 2024



Abstract:Event-based Action Recognition (EAR) possesses the advantages of high-temporal resolution capturing and privacy preservation compared with traditional action recognition. Current leading EAR solutions typically follow two regimes: project unconstructed event streams into dense constructed event frames and adopt powerful frame-specific networks, or employ lightweight point-specific networks to handle sparse unconstructed event points directly. However, such two regimes are blind to a fundamental issue: failing to accommodate the unique dense temporal and sparse spatial properties of asynchronous event data. In this article, we present a synergy-aware framework, i.e., EventCrab, that adeptly integrates the "lighter" frame-specific networks for dense event frames with the "heavier" point-specific networks for sparse event points, balancing accuracy and efficiency. Furthermore, we establish a joint frame-text-point representation space to bridge distinct event frames and points. In specific, to better exploit the unique spatiotemporal relationships inherent in asynchronous event points, we devise two strategies for the "heavier" point-specific embedding: i) a Spiking-like Context Learner (SCL) that extracts contextualized event points from raw event streams. ii) an Event Point Encoder (EPE) that further explores event-point long spatiotemporal features in a Hilbert-scan way. Experiments on four datasets demonstrate the significant performance of our proposed EventCrab, particularly gaining improvements of 5.17% on SeAct and 7.01% on HARDVS.
FTMoMamba: Motion Generation with Frequency and Text State Space Models
Nov 26, 2024Abstract:Diffusion models achieve impressive performance in human motion generation. However, current approaches typically ignore the significance of frequency-domain information in capturing fine-grained motions within the latent space (e.g., low frequencies correlate with static poses, and high frequencies align with fine-grained motions). Additionally, there is a semantic discrepancy between text and motion, leading to inconsistency between the generated motions and the text descriptions. In this work, we propose a novel diffusion-based FTMoMamba framework equipped with a Frequency State Space Model (FreqSSM) and a Text State Space Model (TextSSM). Specifically, to learn fine-grained representation, FreqSSM decomposes sequences into low-frequency and high-frequency components, guiding the generation of static pose (e.g., sits, lay) and fine-grained motions (e.g., transition, stumble), respectively. To ensure the consistency between text and motion, TextSSM encodes text features at the sentence level, aligning textual semantics with sequential features. Extensive experiments show that FTMoMamba achieves superior performance on the text-to-motion generation task, especially gaining the lowest FID of 0.181 (rather lower than 0.421 of MLD) on the HumanML3D dataset.
UnitedVLN: Generalizable Gaussian Splatting for Continuous Vision-Language Navigation
Nov 25, 2024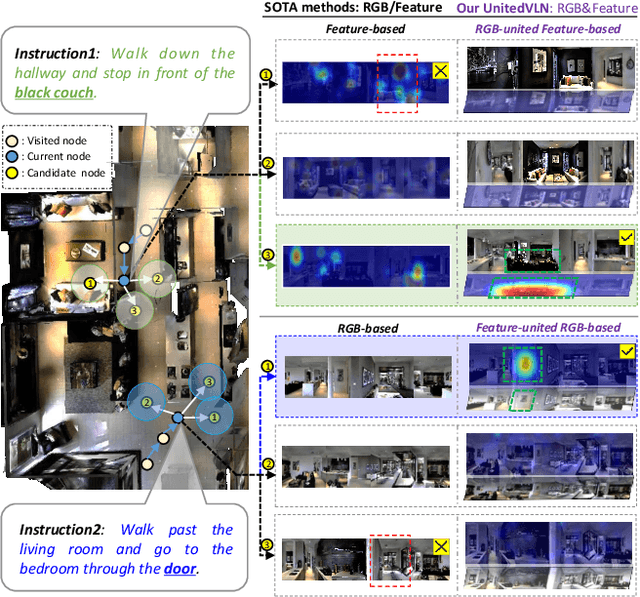
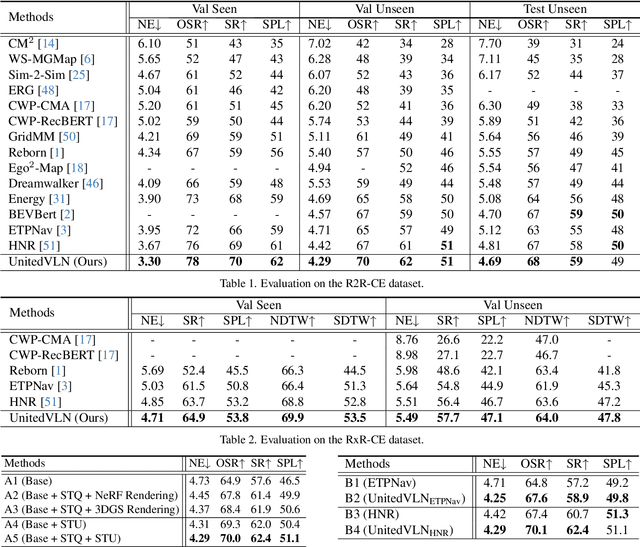
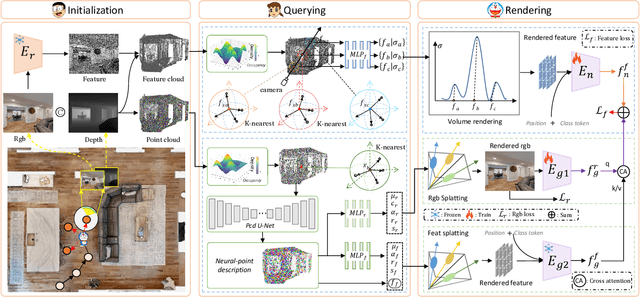
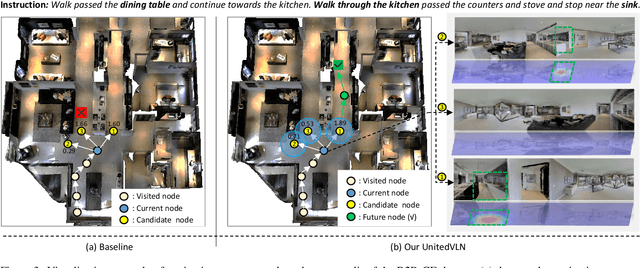
Abstract:Vision-and-Language Navigation (VLN), where an agent follows instructions to reach a target destination, has recently seen significant advancements. In contrast to navigation in discrete environments with predefined trajectories, VLN in Continuous Environments (VLN-CE) presents greater challenges, as the agent is free to navigate any unobstructed location and is more vulnerable to visual occlusions or blind spots. Recent approaches have attempted to address this by imagining future environments, either through predicted future visual images or semantic features, rather than relying solely on current observations. However, these RGB-based and feature-based methods lack intuitive appearance-level information or high-level semantic complexity crucial for effective navigation. To overcome these limitations, we introduce a novel, generalizable 3DGS-based pre-training paradigm, called UnitedVLN, which enables agents to better explore future environments by unitedly rendering high-fidelity 360 visual images and semantic features. UnitedVLN employs two key schemes: search-then-query sampling and separate-then-united rendering, which facilitate efficient exploitation of neural primitives, helping to integrate both appearance and semantic information for more robust navigation. Extensive experiments demonstrate that UnitedVLN outperforms state-of-the-art methods on existing VLN-CE benchmarks.
FedMLLM: Federated Fine-tuning MLLM on Multimodal Heterogeneity Data
Nov 22, 2024



Abstract:Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) have made significant advancements, demonstrating powerful capabilities in processing and understanding multimodal data. Fine-tuning MLLMs with Federated Learning (FL) allows for expanding the training data scope by including private data sources, thereby enhancing their practical applicability in privacy-sensitive domains. However, current research remains in the early stage, particularly in addressing the \textbf{multimodal heterogeneities} in real-world applications. In this paper, we introduce a benchmark for evaluating various downstream tasks in the federated fine-tuning of MLLMs within multimodal heterogeneous scenarios, laying the groundwork for the research in the field. Our benchmark encompasses two datasets, five comparison baselines, and four multimodal scenarios, incorporating over ten types of modal heterogeneities. To address the challenges posed by modal heterogeneity, we develop a general FedMLLM framework that integrates four representative FL methods alongside two modality-agnostic strategies. Extensive experimental results show that our proposed FL paradigm improves the performance of MLLMs by broadening the range of training data and mitigating multimodal heterogeneity. Code is available at https://github.com/1xbq1/FedMLLM
GrokLST: Towards High-Resolution Benchmark and Toolkit for Land Surface Temperature Downscaling
Sep 30, 2024



Abstract:Land Surface Temperature (LST) is a critical parameter for environmental studies, but obtaining high-resolution LST data remains challenging due to the spatio-temporal trade-off in satellite remote sensing. Guided LST downscaling has emerged as a solution, but current methods often neglect spatial non-stationarity and lack a open-source ecosystem for deep learning methods. To address these limitations, we propose the Modality-Conditional Large Selective Kernel (MoCoLSK) Networks, a novel architecture that dynamically fuses multi-modal data through modality-conditioned projections. MoCoLSK re-engineers our previous LSKNet to achieve a confluence of dynamic receptive field adjustment and multi-modal feature integration, leading to enhanced LST prediction accuracy. Furthermore, we establish the GrokLST project, a comprehensive open-source ecosystem featuring the GrokLST dataset, a high-resolution benchmark, and the GrokLST toolkit, an open-source PyTorch-based toolkit encapsulating MoCoLSK alongside 40+ state-of-the-art approaches. Extensive experimental results validate MoCoLSK's effectiveness in capturing complex dependencies and subtle variations within multispectral data, outperforming existing methods in LST downscaling. Our code, dataset, and toolkit are available at https://github.com/GrokCV/GrokLST.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge