Hongyu Qu
See the Text: From Tokenization to Visual Reading
Oct 21, 2025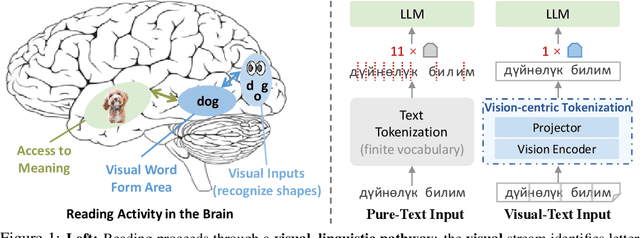

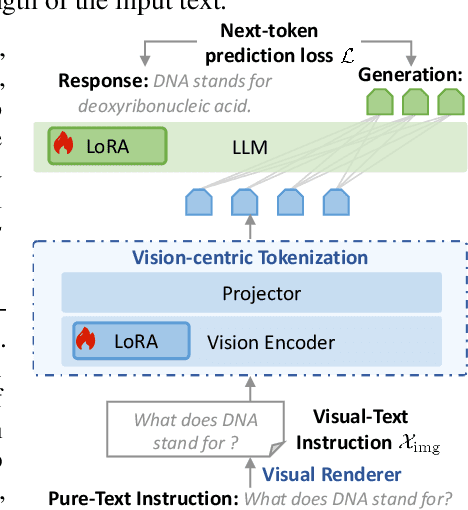
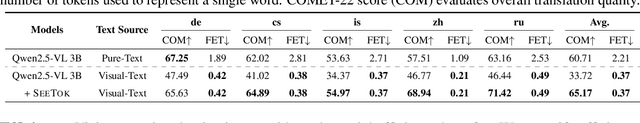
Abstract:People see text. Humans read by recognizing words as visual objects, including their shapes, layouts, and patterns, before connecting them to meaning, which enables us to handle typos, distorted fonts, and various scripts effectively. Modern large language models (LLMs), however, rely on subword tokenization, fragmenting text into pieces from a fixed vocabulary. While effective for high-resource languages, this approach over-segments low-resource languages, yielding long, linguistically meaningless sequences and inflating computation. In this work, we challenge this entrenched paradigm and move toward a vision-centric alternative. Our method, SeeTok, renders text as images (visual-text) and leverages pretrained multimodal LLMs to interpret them, reusing strong OCR and text-vision alignment abilities learned from large-scale multimodal training. Across three different language tasks, SeeTok matches or surpasses subword tokenizers while requiring 4.43 times fewer tokens and reducing FLOPs by 70.5%, with additional gains in cross-lingual generalization, robustness to typographic noise, and linguistic hierarchy. SeeTok signals a shift from symbolic tokenization to human-like visual reading, and takes a step toward more natural and cognitively inspired language models.
Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization for Few-shot Action Recognition
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Few-shot action recognition (FSAR) aims to recognize novel action categories with few exemplars. Existing methods typically learn frame-level representations independently for each video by designing various inter-frame temporal modeling strategies. However, they neglect explicit relation modeling between videos and tasks, thus failing to capture shared temporal patterns across videos and reuse temporal knowledge from historical tasks. In light of this, we propose HR2G-shot, a Hierarchical Relation-augmented Representation Generalization framework for FSAR, which unifies three types of relation modeling (inter-frame, inter-video, and inter-task) to learn task-specific temporal patterns from a holistic view. In addition to conducting inter-frame temporal interactions, we further devise two components to respectively explore inter-video and inter-task relationships: i) Inter-video Semantic Correlation (ISC) performs cross-video frame-level interactions in a fine-grained manner, thereby capturing task-specific query features and learning intra- and inter-class temporal correlations among support features; ii) Inter-task Knowledge Transfer (IKT) retrieves and aggregates relevant temporal knowledge from the bank, which stores diverse temporal patterns from historical tasks. Extensive experiments on five benchmarks show that HR2G-shot outperforms current top-leading FSAR methods.
Learning Clustering-based Prototypes for Compositional Zero-shot Learning
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:Learning primitive (i.e., attribute and object) concepts from seen compositions is the primary challenge of Compositional Zero-Shot Learning (CZSL). Existing CZSL solutions typically rely on oversimplified data assumptions, e.g., modeling each primitive with a single centroid primitive representation, ignoring the natural diversities of the attribute (resp. object) when coupled with different objects (resp. attribute). In this work, we develop ClusPro, a robust clustering-based prototype mining framework for CZSL that defines the conceptual boundaries of primitives through a set of diversified prototypes. Specifically, ClusPro conducts within-primitive clustering on the embedding space for automatically discovering and dynamically updating prototypes. These representative prototypes are subsequently used to repaint a well-structured and independent primitive embedding space, ensuring intra-primitive separation and inter-primitive decorrelation through prototype-based contrastive learning and decorrelation learning. Moreover, ClusPro efficiently performs prototype clustering in a non-parametric fashion without the introduction of additional learnable parameters or computational budget during testing. Experiments on three benchmarks demonstrate ClusPro outperforms various top-leading CZSL solutions under both closed-world and open-world settings.
Locality-aware Cross-modal Correspondence Learning for Dense Audio-Visual Events Localization
Sep 12, 2024



Abstract:Dense-localization Audio-Visual Events (DAVE) aims to identify time boundaries and corresponding categories for events that can be heard and seen concurrently in an untrimmed video. Existing methods typically encode audio and visual representation separately without any explicit cross-modal alignment constraint. Then they adopt dense cross-modal attention to integrate multimodal information for DAVE. Thus these methods inevitably aggregate irrelevant noise and events, especially in complex and long videos, leading to imprecise detection. In this paper, we present LOCO, a Locality-aware cross-modal Correspondence learning framework for DAVE. The core idea is to explore local temporal continuity nature of audio-visual events, which serves as informative yet free supervision signals to guide the filtering of irrelevant information and inspire the extraction of complementary multimodal information during both unimodal and cross-modal learning stages. i) Specifically, LOCO applies Locality-aware Correspondence Correction (LCC) to uni-modal features via leveraging cross-modal local-correlated properties without any extra annotations. This enforces uni-modal encoders to highlight similar semantics shared by audio and visual features. ii) To better aggregate such audio and visual features, we further customize Cross-modal Dynamic Perception layer (CDP) in cross-modal feature pyramid to understand local temporal patterns of audio-visual events by imposing local consistency within multimodal features in a data-driven manner. By incorporating LCC and CDP, LOCO provides solid performance gains and outperforms existing methods for DAVE. The source code will be released.
MVP-Shot: Multi-Velocity Progressive-Alignment Framework for Few-Shot Action Recognition
May 03, 2024



Abstract:Recent few-shot action recognition (FSAR) methods achieve promising performance by performing semantic matching on learned discriminative features. However, most FSAR methods focus on single-scale (e.g., frame-level, segment-level, \etc) feature alignment, which ignores that human actions with the same semantic may appear at different velocities. To this end, we develop a novel Multi-Velocity Progressive-alignment (MVP-Shot) framework to progressively learn and align semantic-related action features at multi-velocity levels. Concretely, a Multi-Velocity Feature Alignment (MVFA) module is designed to measure the similarity between features from support and query videos with different velocity scales and then merge all similarity scores in a residual fashion. To avoid the multiple velocity features deviating from the underlying motion semantic, our proposed Progressive Semantic-Tailored Interaction (PSTI) module injects velocity-tailored text information into the video feature via feature interaction on channel and temporal domains at different velocities. The above two modules compensate for each other to predict query categories more accurately under the few-shot settings. Experimental results show our method outperforms current state-of-the-art methods on multiple standard few-shot benchmarks (i.e., HMDB51, UCF101, Kinetics, and SSv2-small).
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge