Victor Dibia
Magentic-UI: Towards Human-in-the-loop Agentic Systems
Jul 30, 2025Abstract:AI agents powered by large language models are increasingly capable of autonomously completing complex, multi-step tasks using external tools. Yet, they still fall short of human-level performance in most domains including computer use, software development, and research. Their growing autonomy and ability to interact with the outside world, also introduces safety and security risks including potentially misaligned actions and adversarial manipulation. We argue that human-in-the-loop agentic systems offer a promising path forward, combining human oversight and control with AI efficiency to unlock productivity from imperfect systems. We introduce Magentic-UI, an open-source web interface for developing and studying human-agent interaction. Built on a flexible multi-agent architecture, Magentic-UI supports web browsing, code execution, and file manipulation, and can be extended with diverse tools via Model Context Protocol (MCP). Moreover, Magentic-UI presents six interaction mechanisms for enabling effective, low-cost human involvement: co-planning, co-tasking, multi-tasking, action guards, and long-term memory. We evaluate Magentic-UI across four dimensions: autonomous task completion on agentic benchmarks, simulated user testing of its interaction capabilities, qualitative studies with real users, and targeted safety assessments. Our findings highlight Magentic-UI's potential to advance safe and efficient human-agent collaboration.
Interactive Debugging and Steering of Multi-Agent AI Systems
Mar 03, 2025Abstract:Fully autonomous teams of LLM-powered AI agents are emerging that collaborate to perform complex tasks for users. What challenges do developers face when trying to build and debug these AI agent teams? In formative interviews with five AI agent developers, we identify core challenges: difficulty reviewing long agent conversations to localize errors, lack of support in current tools for interactive debugging, and the need for tool support to iterate on agent configuration. Based on these needs, we developed an interactive multi-agent debugging tool, AGDebugger, with a UI for browsing and sending messages, the ability to edit and reset prior agent messages, and an overview visualization for navigating complex message histories. In a two-part user study with 14 participants, we identify common user strategies for steering agents and highlight the importance of interactive message resets for debugging. Our studies deepen understanding of interfaces for debugging increasingly important agentic workflows.
Magentic-One: A Generalist Multi-Agent System for Solving Complex Tasks
Nov 07, 2024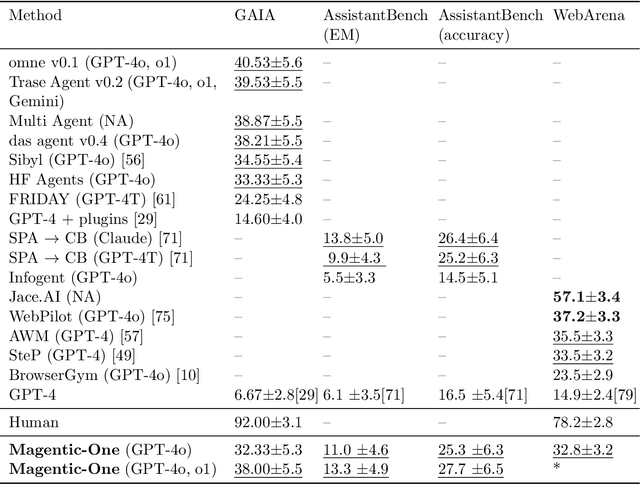
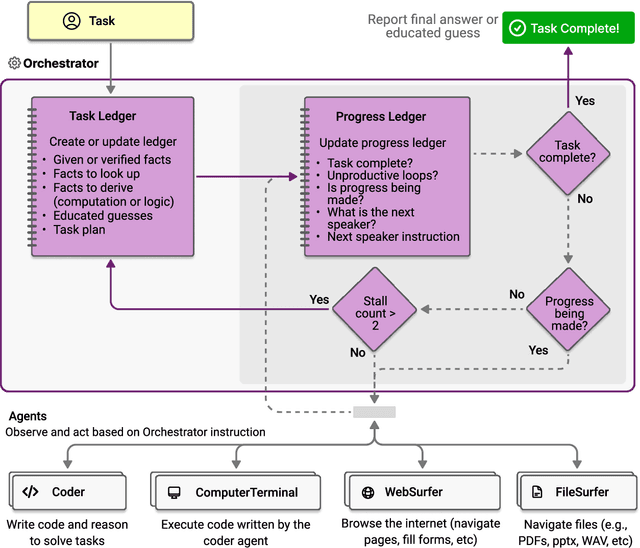
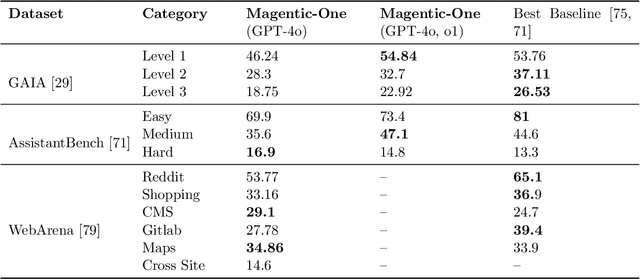
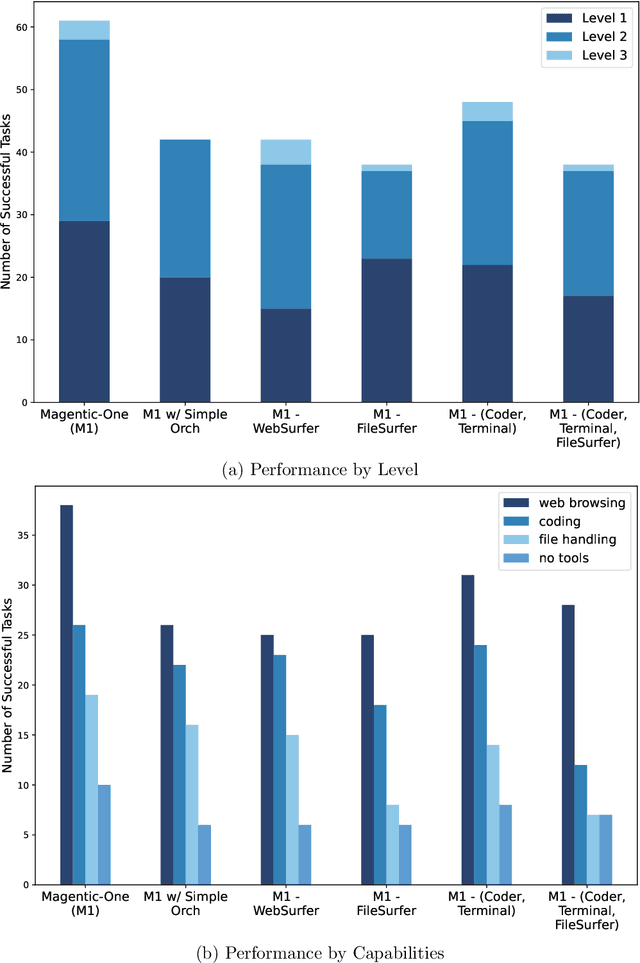
Abstract:Modern AI agents, driven by advances in large foundation models, promise to enhance our productivity and transform our lives by augmenting our knowledge and capabilities. To achieve this vision, AI agents must effectively plan, perform multi-step reasoning and actions, respond to novel observations, and recover from errors, to successfully complete complex tasks across a wide range of scenarios. In this work, we introduce Magentic-One, a high-performing open-source agentic system for solving such tasks. Magentic-One uses a multi-agent architecture where a lead agent, the Orchestrator, plans, tracks progress, and re-plans to recover from errors. Throughout task execution, the Orchestrator directs other specialized agents to perform tasks as needed, such as operating a web browser, navigating local files, or writing and executing Python code. We show that Magentic-One achieves statistically competitive performance to the state-of-the-art on three diverse and challenging agentic benchmarks: GAIA, AssistantBench, and WebArena. Magentic-One achieves these results without modification to core agent capabilities or to how they collaborate, demonstrating progress towards generalist agentic systems. Moreover, Magentic-One's modular design allows agents to be added or removed from the team without additional prompt tuning or training, easing development and making it extensible to future scenarios. We provide an open-source implementation of Magentic-One, and we include AutoGenBench, a standalone tool for agentic evaluation. AutoGenBench provides built-in controls for repetition and isolation to run agentic benchmarks in a rigorous and contained manner -- which is important when agents' actions have side-effects. Magentic-One, AutoGenBench and detailed empirical performance evaluations of Magentic-One, including ablations and error analysis are available at https://aka.ms/magentic-one
Data Analysis in the Era of Generative AI
Sep 27, 2024



Abstract:This paper explores the potential of AI-powered tools to reshape data analysis, focusing on design considerations and challenges. We explore how the emergence of large language and multimodal models offers new opportunities to enhance various stages of data analysis workflow by translating high-level user intentions into executable code, charts, and insights. We then examine human-centered design principles that facilitate intuitive interactions, build user trust, and streamline the AI-assisted analysis workflow across multiple apps. Finally, we discuss the research challenges that impede the development of these AI-based systems such as enhancing model capabilities, evaluating and benchmarking, and understanding end-user needs.
Concept Distillation from Strong to Weak Models via Hypotheses-to-Theories Prompting
Aug 18, 2024



Abstract:Hand-crafting high quality prompts to optimize the performance of language models is a complicated and labor-intensive process. Furthermore, when migrating to newer, smaller, or weaker models (possibly due to latency or cost gains), prompts need to be updated to re-optimize the task performance. We propose Concept Distillation (CD), an automatic prompt optimization technique for enhancing weaker models on complex tasks. CD involves: (1) collecting mistakes made by weak models with a base prompt (initialization), (2) using a strong model to generate reasons for these mistakes and create rules/concepts for weak models (induction), and (3) filtering these rules based on validation set performance and integrating them into the base prompt (deduction/verification). We evaluated CD on NL2Code and mathematical reasoning tasks, observing significant performance boosts for small and weaker language models. Notably, Mistral-7B's accuracy on Multi-Arith increased by 20%, and Phi-3-mini-3.8B's accuracy on HumanEval rose by 34%. Compared to other automated methods, CD offers an effective, cost-efficient strategy for improving weak models' performance on complex tasks and enables seamless workload migration across different language models without compromising performance.
Towards better Human-Agent Alignment: Assessing Task Utility in LLM-Powered Applications
Feb 22, 2024Abstract:The rapid development in the field of Large Language Models (LLMs) has led to a surge in applications that facilitate collaboration among multiple agents to assist humans in their daily tasks. However, a significant gap remains in assessing whether LLM-powered applications genuinely enhance user experience and task execution efficiency. This highlights the pressing need for methods to verify utility of LLM-powered applications, particularly by ensuring alignment between the application's functionality and end-user needs. We introduce AgentEval provides an implementation for the math problems, a novel framework designed to simplify the utility verification process by automatically proposing a set of criteria tailored to the unique purpose of any given application. This allows for a comprehensive assessment, quantifying the utility of an application against the suggested criteria. We present a comprehensive analysis of the robustness of quantifier's work.
Axiomatic Preference Modeling for Longform Question Answering
Dec 02, 2023



Abstract:The remarkable abilities of large language models (LLMs) like GPT-4 partially stem from post-training processes like Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback (RLHF) involving human preferences encoded in a reward model. However, these reward models (RMs) often lack direct knowledge of why, or under what principles, the preferences annotations were made. In this study, we identify principles that guide RMs to better align with human preferences, and then develop an axiomatic framework to generate a rich variety of preference signals to uphold them. We use these axiomatic signals to train a model for scoring answers to longform questions. Our approach yields a Preference Model with only about 220M parameters that agrees with gold human-annotated preference labels more often than GPT-4. The contributions of this work include: training a standalone preference model that can score human- and LLM-generated answers on the same scale; developing an axiomatic framework for generating training data pairs tailored to certain principles; and showing that a small amount of axiomatic signals can help small models outperform GPT-4 in preference scoring. We release our model on huggingface: https://huggingface.co/corbyrosset/axiomatic_preference_model
LIDA: A Tool for Automatic Generation of Grammar-Agnostic Visualizations and Infographics using Large Language Models
Mar 06, 2023



Abstract:Systems that support users in the automatic creation of visualizations must address several subtasks - understand the semantics of data, enumerate relevant visualization goals and generate visualization specifications. In this work, we pose visualization generation as a multi-stage generation problem and argue that well-orchestrated pipelines based on large language models (LLMs) and image generation models (IGMs) are suitable to addressing these tasks. We present LIDA, a novel tool for generating grammar-agnostic visualizations and infographics. LIDA comprises of 4 modules - A SUMMARIZER that converts data into a rich but compact natural language summary, a GOAL EXPLORER that enumerates visualization goals given the data, a VISGENERATOR that generates, refines, executes and filters visualization code and an INFOGRAPHER module that yields data-faithful stylized graphics using IGMs. LIDA provides a python api, and a hybrid user interface (direct manipulation and natural language) for interactive chart, infographics and data story generation.
Aligning Offline Metrics and Human Judgments of Value of AI-Pair Programmers
Oct 29, 2022Abstract:Large language models trained on massive amounts of natural language data and code have shown impressive capabilities in automatic code generation scenarios. Development and evaluation of these models has largely been driven by offline functional correctness metrics, which consider a task to be solved if the generated code passes corresponding unit tests. While functional correctness is clearly an important property of a code generation model, we argue that it may not fully capture what programmers value when collaborating with their AI pair programmers. For example, while a nearly correct suggestion that does not consider edge cases may fail a unit test, it may still provide a substantial starting point or hint to the programmer, thereby reducing total needed effort to complete a coding task. To investigate this, we conduct a user study with (N=49) experienced programmers, and find that while both correctness and effort correlate with value, the association is strongest for effort. We argue that effort should be considered as an important dimension of evaluation in code generation scenarios. We also find that functional correctness remains better at identifying the highest-value generations; but participants still saw considerable value in code that failed unit tests. Conversely, similarity-based metrics are very good at identifying the lowest-value generations among those that fail unit tests. Based on these findings, we propose a simple hybrid metric, which combines functional correctness and similarity-based metrics to capture different dimensions of what programmers might value and show that this hybrid metric more strongly correlates with both value and effort. Our findings emphasize the importance of designing human-centered metrics that capture what programmers need from and value in their AI pair programmers.
NeuralQA: A Usable Library for Question Answering (Contextual Query Expansion + BERT) on Large Datasets
Jul 30, 2020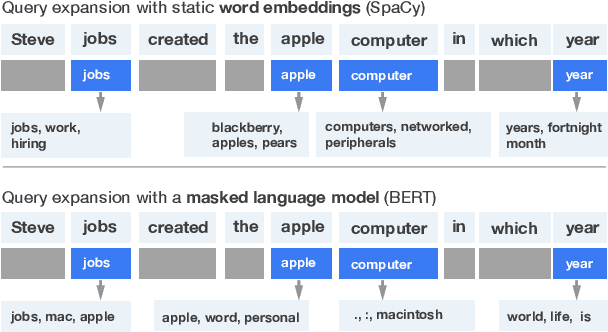


Abstract:Existing tools for Question Answering (QA) have challenges that limit their use in practice. They can be complex to set up or integrate with existing infrastructure, do not offer configurable interactive interfaces, and do not cover the full set of subtasks that frequently comprise the QA pipeline (query expansion, retrieval, reading, and explanation/sensemaking). To help address these issues, we introduce NeuralQA - a usable library for QA on large datasets. NeuralQA integrates well with existing infrastructure (e.g., ElasticSearch instances and reader models trained with the HuggingFace Transformers API) and offers helpful defaults for QA subtasks. It introduces and implements contextual query expansion (CQE) using a masked language model (MLM) as well as relevant snippets (RelSnip) - a method for condensing large documents into smaller passages that can be speedily processed by a document reader model. Finally, it offers a flexible user interface to support workflows for research explorations (e.g., visualization of gradient-based explanations to support qualitative inspection of model behaviour) and large scale search deployment. Code and documentation for NeuralQA is available as open source on Github.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge