Ryan McKenna
Privately Fine-Tuned LLMs Preserve Temporal Dynamics in Tabular Data
Feb 02, 2026Abstract:Research on differentially private synthetic tabular data has largely focused on independent and identically distributed rows where each record corresponds to a unique individual. This perspective neglects the temporal complexity in longitudinal datasets, such as electronic health records, where a user contributes an entire (sub) table of sequential events. While practitioners might attempt to model such data by flattening user histories into high-dimensional vectors for use with standard marginal-based mechanisms, we demonstrate that this strategy is insufficient. Flattening fails to preserve temporal coherence even when it maintains valid marginal distributions. We introduce PATH, a novel generative framework that treats the full table as the unit of synthesis and leverages the autoregressive capabilities of privately fine-tuned large language models. Extensive evaluations show that PATH effectively captures long-range dependencies that traditional methods miss. Empirically, our method reduces the distributional distance to real trajectories by over 60% and reduces state transition errors by nearly 50% compared to leading marginal mechanisms while achieving similar marginal fidelity.
DP-$λ$CGD: Efficient Noise Correlation for Differentially Private Model Training
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Differentially private stochastic gradient descent (DP-SGD) is the gold standard for training machine learning models with formal differential privacy guarantees. Several recent extensions improve its accuracy by introducing correlated noise across training iterations. Matrix factorization mechanisms are a prominent example, but they correlate noise across many iterations and require storing previously added noise vectors, leading to substantial memory overhead in some settings. In this work, we propose a new noise correlation strategy that correlates noise only with the immediately preceding iteration and cancels a controlled portion of it. Our method relies on noise regeneration using a pseudorandom noise generator, eliminating the need to store past noise. As a result, it requires no additional memory beyond standard DP-SGD. We show that the computational overhead is minimal and empirically demonstrate improved accuracy over DP-SGD.
Correlated Noise Mechanisms for Differentially Private Learning
Jun 09, 2025
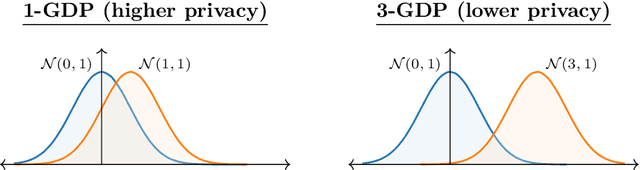
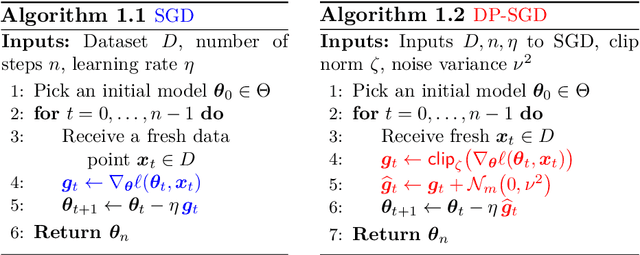
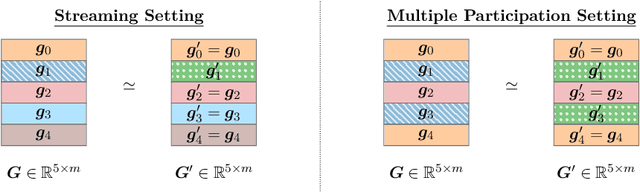
Abstract:This monograph explores the design and analysis of correlated noise mechanisms for differential privacy (DP), focusing on their application to private training of AI and machine learning models via the core primitive of estimation of weighted prefix sums. While typical DP mechanisms inject independent noise into each step of a stochastic gradient (SGD) learning algorithm in order to protect the privacy of the training data, a growing body of recent research demonstrates that introducing (anti-)correlations in the noise can significantly improve privacy-utility trade-offs by carefully canceling out some of the noise added on earlier steps in subsequent steps. Such correlated noise mechanisms, known variously as matrix mechanisms, factorization mechanisms, and DP-Follow-the-Regularized-Leader (DP-FTRL) when applied to learning algorithms, have also been influential in practice, with industrial deployment at a global scale.
Back to Square Roots: An Optimal Bound on the Matrix Factorization Error for Multi-Epoch Differentially Private SGD
May 17, 2025Abstract:Matrix factorization mechanisms for differentially private training have emerged as a promising approach to improve model utility under privacy constraints. In practical settings, models are typically trained over multiple epochs, requiring matrix factorizations that account for repeated participation. Existing theoretical upper and lower bounds on multi-epoch factorization error leave a significant gap. In this work, we introduce a new explicit factorization method, Banded Inverse Square Root (BISR), which imposes a banded structure on the inverse correlation matrix. This factorization enables us to derive an explicit and tight characterization of the multi-epoch error. We further prove that BISR achieves asymptotically optimal error by matching the upper and lower bounds. Empirically, BISR performs on par with state-of-the-art factorization methods, while being simpler to implement, computationally efficient, and easier to analyze.
It's My Data Too: Private ML for Datasets with Multi-User Training Examples
Mar 05, 2025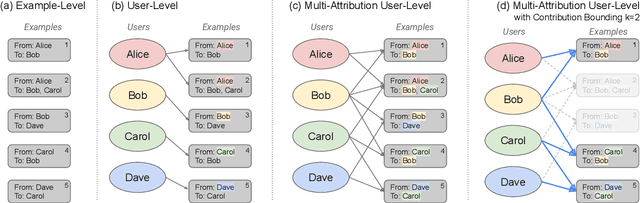
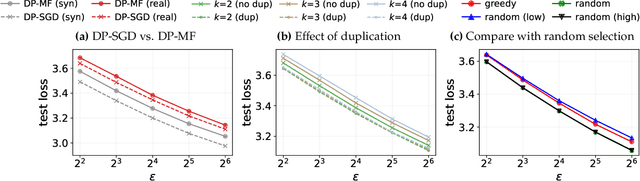
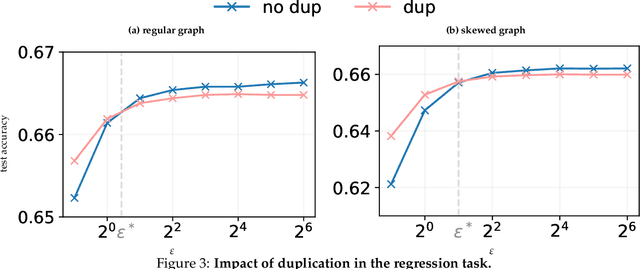
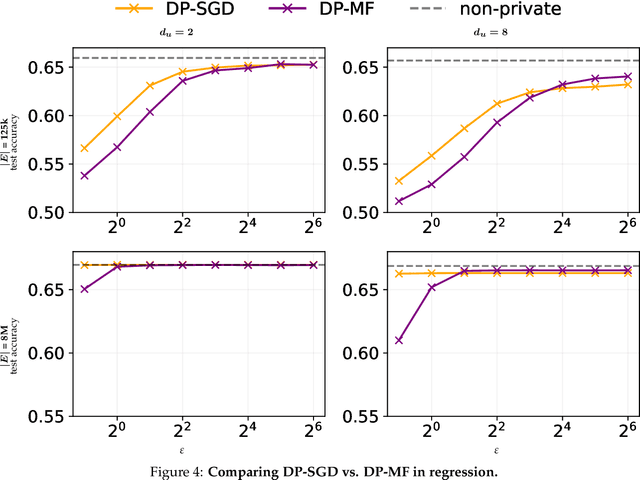
Abstract:We initiate a study of algorithms for model training with user-level differential privacy (DP), where each example may be attributed to multiple users, which we call the multi-attribution model. We first provide a carefully chosen definition of user-level DP under the multi-attribution model. Training in the multi-attribution model is facilitated by solving the contribution bounding problem, i.e. the problem of selecting a subset of the dataset for which each user is associated with a limited number of examples. We propose a greedy baseline algorithm for the contribution bounding problem. We then empirically study this algorithm for a synthetic logistic regression task and a transformer training task, including studying variants of this baseline algorithm that optimize the subset chosen using different techniques and criteria. We find that the baseline algorithm remains competitive with its variants in most settings, and build a better understanding of the practical importance of a bias-variance tradeoff inherent in solutions to the contribution bounding problem.
Is API Access to LLMs Useful for Generating Private Synthetic Tabular Data?
Feb 10, 2025

Abstract:Differentially private (DP) synthetic data is a versatile tool for enabling the analysis of private data. Recent advancements in large language models (LLMs) have inspired a number of algorithm techniques for improving DP synthetic data generation. One family of approaches uses DP finetuning on the foundation model weights; however, the model weights for state-of-the-art models may not be public. In this work we propose two DP synthetic tabular data algorithms that only require API access to the foundation model. We adapt the Private Evolution algorithm (Lin et al., 2023; Xie et al., 2024) -- which was designed for image and text data -- to the tabular data domain. In our extension of Private Evolution, we define a query workload-based distance measure, which may be of independent interest. We propose a family of algorithms that use one-shot API access to LLMs, rather than adaptive queries to the LLM. Our findings reveal that API-access to powerful LLMs does not always improve the quality of DP synthetic data compared to established baselines that operate without such access. We provide insights into the underlying reasons and propose improvements to LLMs that could make them more effective for this application.
Scaling Laws for Differentially Private Language Models
Jan 31, 2025Abstract:Scaling laws have emerged as important components of large language model (LLM) training as they can predict performance gains through scale, and provide guidance on important hyper-parameter choices that would otherwise be expensive. LLMs also rely on large, high-quality training datasets, like those sourced from (sometimes sensitive) user data. Training models on this sensitive user data requires careful privacy protections like differential privacy (DP). However, the dynamics of DP training are significantly different, and consequently their scaling laws are not yet fully understood. In this work, we establish scaling laws that accurately model the intricacies of DP LLM training, providing a complete picture of the compute-privacy-utility tradeoffs and the optimal training configurations in many settings.
Fine-Tuning Large Language Models with User-Level Differential Privacy
Jul 10, 2024Abstract:We investigate practical and scalable algorithms for training large language models (LLMs) with user-level differential privacy (DP) in order to provably safeguard all the examples contributed by each user. We study two variants of DP-SGD with: (1) example-level sampling (ELS) and per-example gradient clipping, and (2) user-level sampling (ULS) and per-user gradient clipping. We derive a novel user-level DP accountant that allows us to compute provably tight privacy guarantees for ELS. Using this, we show that while ELS can outperform ULS in specific settings, ULS generally yields better results when each user has a diverse collection of examples. We validate our findings through experiments in synthetic mean estimation and LLM fine-tuning tasks under fixed compute budgets. We find that ULS is significantly better in settings where either (1) strong privacy guarantees are required, or (2) the compute budget is large. Notably, our focus on LLM-compatible training algorithms allows us to scale to models with hundreds of millions of parameters and datasets with hundreds of thousands of users.
Scaling up the Banded Matrix Factorization Mechanism for Differentially Private ML
May 24, 2024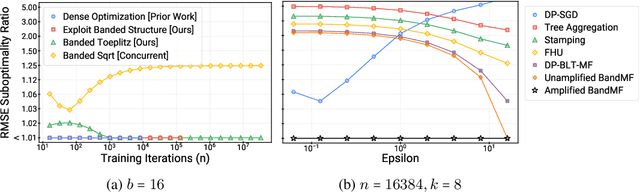
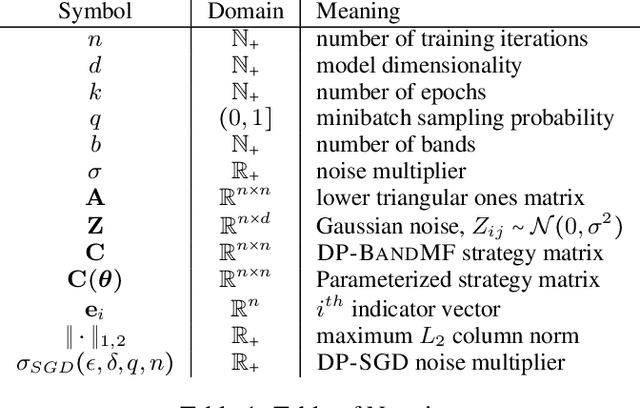
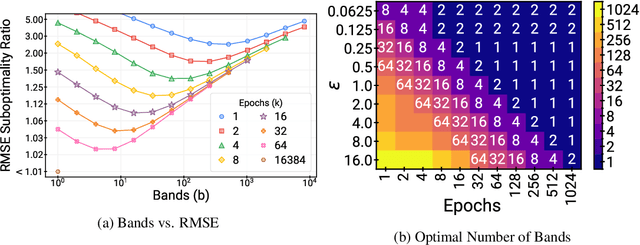
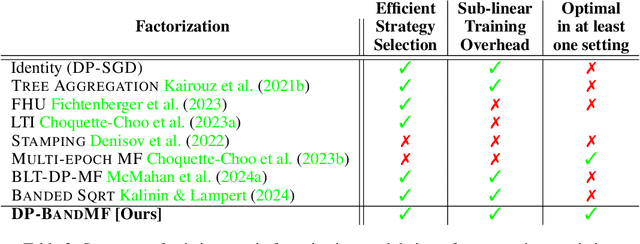
Abstract:DP-BandMF offers a powerful approach to differentially private machine learning, balancing privacy amplification with noise correlation for optimal noise reduction. However, its scalability has been limited to settings where the number of training iterations is less than $10^4$. In this work, we present techniques that significantly extend DP-BandMF's reach, enabling use in settings with and over $10^6$ training iterations. Our enhanced implementation, coupled with extensive experiments, provides clear guidelines on selecting the optimal number of bands. These insights offer practitioners a deeper understanding of DP-BandMF's performance and how to maximize its utility for privacy-preserving machine learning.
Joint Selection: Adaptively Incorporating Public Information for Private Synthetic Data
Mar 12, 2024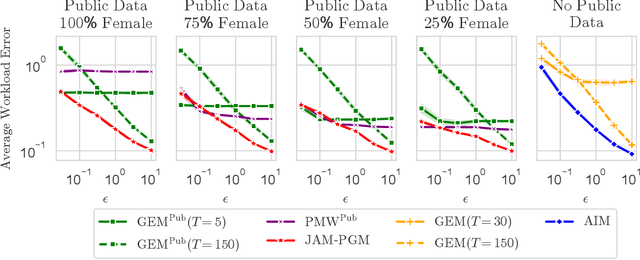
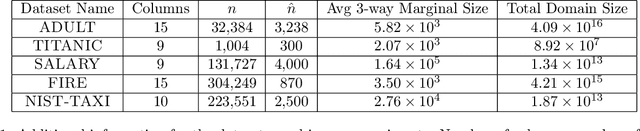
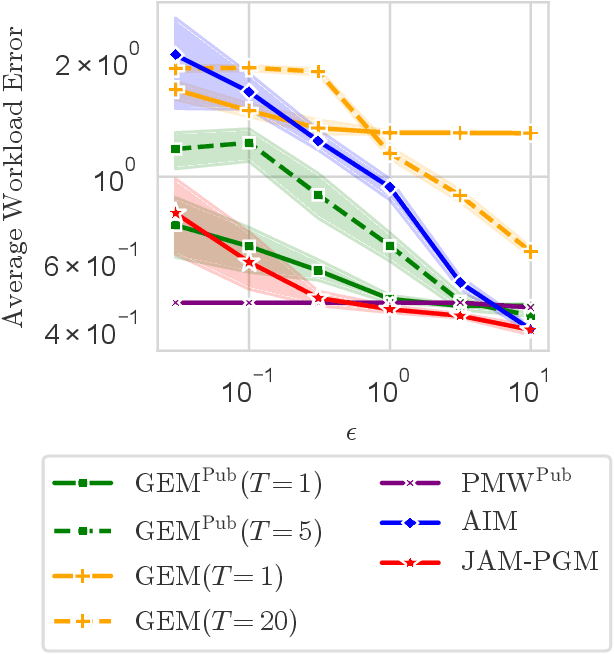
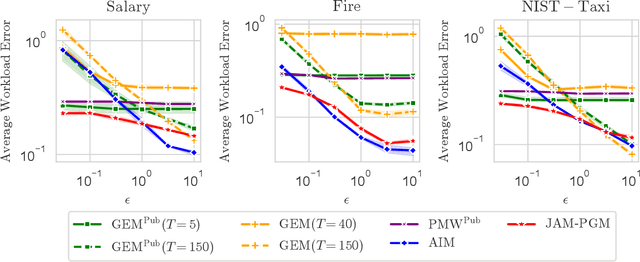
Abstract:Mechanisms for generating differentially private synthetic data based on marginals and graphical models have been successful in a wide range of settings. However, one limitation of these methods is their inability to incorporate public data. Initializing a data generating model by pre-training on public data has shown to improve the quality of synthetic data, but this technique is not applicable when model structure is not determined a priori. We develop the mechanism jam-pgm, which expands the adaptive measurements framework to jointly select between measuring public data and private data. This technique allows for public data to be included in a graphical-model-based mechanism. We show that jam-pgm is able to outperform both publicly assisted and non publicly assisted synthetic data generation mechanisms even when the public data distribution is biased.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge