Rohit Saxena
Enhancing Long Document Long Form Summarisation with Self-Planning
Dec 19, 2025Abstract:We introduce a novel approach for long context summarisation, highlight-guided generation, that leverages sentence-level information as a content plan to improve the traceability and faithfulness of generated summaries. Our framework applies self-planning methods to identify important content and then generates a summary conditioned on the plan. We explore both an end-to-end and two-stage variants of the approach, finding that the two-stage pipeline performs better on long and information-dense documents. Experiments on long-form summarisation datasets demonstrate that our method consistently improves factual consistency while preserving relevance and overall quality. On GovReport, our best approach has improved ROUGE-L by 4.1 points and achieves about 35% gains in SummaC scores. Qualitative analysis shows that highlight-guided summarisation helps preserve important details, leading to more accurate and insightful summaries across domains.
MMLongBench: Benchmarking Long-Context Vision-Language Models Effectively and Thoroughly
May 15, 2025Abstract:The rapid extension of context windows in large vision-language models has given rise to long-context vision-language models (LCVLMs), which are capable of handling hundreds of images with interleaved text tokens in a single forward pass. In this work, we introduce MMLongBench, the first benchmark covering a diverse set of long-context vision-language tasks, to evaluate LCVLMs effectively and thoroughly. MMLongBench is composed of 13,331 examples spanning five different categories of downstream tasks, such as Visual RAG and Many-Shot ICL. It also provides broad coverage of image types, including various natural and synthetic images. To assess the robustness of the models to different input lengths, all examples are delivered at five standardized input lengths (8K-128K tokens) via a cross-modal tokenization scheme that combines vision patches and text tokens. Through a thorough benchmarking of 46 closed-source and open-source LCVLMs, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the current models' vision-language long-context ability. Our results show that: i) performance on a single task is a weak proxy for overall long-context capability; ii) both closed-source and open-source models face challenges in long-context vision-language tasks, indicating substantial room for future improvement; iii) models with stronger reasoning ability tend to exhibit better long-context performance. By offering wide task coverage, various image types, and rigorous length control, MMLongBench provides the missing foundation for diagnosing and advancing the next generation of LCVLMs.
PosterSum: A Multimodal Benchmark for Scientific Poster Summarization
Feb 24, 2025Abstract:Generating accurate and concise textual summaries from multimodal documents is challenging, especially when dealing with visually complex content like scientific posters. We introduce PosterSum, a novel benchmark to advance the development of vision-language models that can understand and summarize scientific posters into research paper abstracts. Our dataset contains 16,305 conference posters paired with their corresponding abstracts as summaries. Each poster is provided in image format and presents diverse visual understanding challenges, such as complex layouts, dense text regions, tables, and figures. We benchmark state-of-the-art Multimodal Large Language Models (MLLMs) on PosterSum and demonstrate that they struggle to accurately interpret and summarize scientific posters. We propose Segment & Summarize, a hierarchical method that outperforms current MLLMs on automated metrics, achieving a 3.14% gain in ROUGE-L. This will serve as a starting point for future research on poster summarization.
What Is That Talk About? A Video-to-Text Summarization Dataset for Scientific Presentations
Feb 12, 2025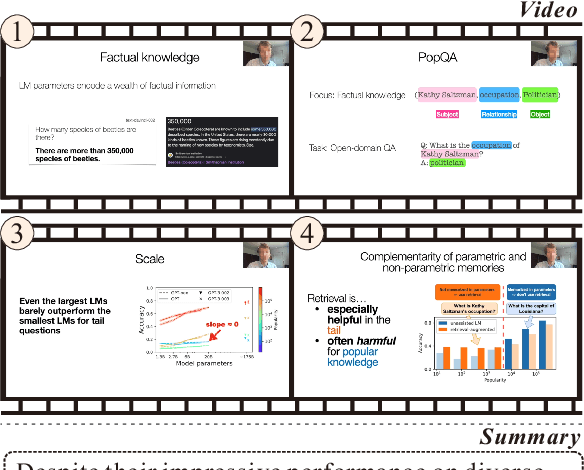
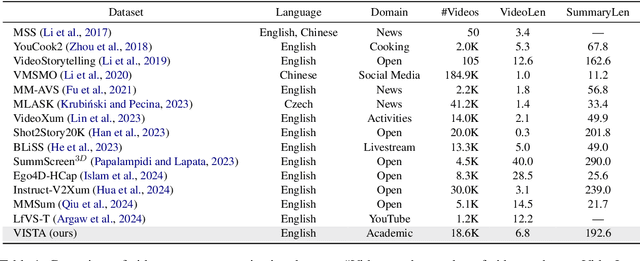

Abstract:Transforming recorded videos into concise and accurate textual summaries is a growing challenge in multimodal learning. This paper introduces VISTA, a dataset specifically designed for video-to-text summarization in scientific domains. VISTA contains 18,599 recorded AI conference presentations paired with their corresponding paper abstracts. We benchmark the performance of state-of-the-art large models and apply a plan-based framework to better capture the structured nature of abstracts. Both human and automated evaluations confirm that explicit planning enhances summary quality and factual consistency. However, a considerable gap remains between models and human performance, highlighting the challenges of scientific video summarization.
Lost in Time: Clock and Calendar Understanding Challenges in Multimodal LLMs
Feb 07, 2025Abstract:Understanding time from visual representations is a fundamental cognitive skill, yet it remains a challenge for multimodal large language models (MLLMs). In this work, we investigate the capabilities of MLLMs in interpreting time and date through analogue clocks and yearly calendars. To facilitate this, we curated a structured dataset comprising two subsets: 1) $\textit{ClockQA}$, which comprises various types of clock styles$-$standard, black-dial, no-second-hand, Roman numeral, and arrow-hand clocks$-$paired with time related questions; and 2) $\textit{CalendarQA}$, which consists of yearly calendar images with questions ranging from commonly known dates (e.g., Christmas, New Year's Day) to computationally derived ones (e.g., the 100th or 153rd day of the year). We aim to analyse how MLLMs can perform visual recognition, numerical reasoning, and temporal inference when presented with time-related visual data. Our evaluations show that despite recent advancements, reliably understanding time remains a significant challenge for MLLMs.
End-to-End Long Document Summarization using Gradient Caching
Jan 03, 2025



Abstract:Training transformer-based encoder-decoder models for long document summarization poses a significant challenge due to the quadratic memory consumption during training. Several approaches have been proposed to extend the input length at test time, but training with these approaches is still difficult, requiring truncation of input documents and causing a mismatch between training and test conditions. In this work, we propose CachED (Gradient $\textbf{Cach}$ing for $\textbf{E}$ncoder-$\textbf{D}$ecoder models), an approach that enables end-to-end training of existing transformer-based encoder-decoder models, using the entire document without truncation. Specifically, we apply non-overlapping sliding windows to input documents, followed by fusion in decoder. During backpropagation, the gradients are cached at the decoder and are passed through the encoder in chunks by re-computing the hidden vectors, similar to gradient checkpointing. In the experiments on long document summarization, we extend BART to CachED BART, processing more than 500K tokens during training and achieving superior performance without using any additional parameters.
MovieSum: An Abstractive Summarization Dataset for Movie Screenplays
Aug 12, 2024Abstract:Movie screenplay summarization is challenging, as it requires an understanding of long input contexts and various elements unique to movies. Large language models have shown significant advancements in document summarization, but they often struggle with processing long input contexts. Furthermore, while television transcripts have received attention in recent studies, movie screenplay summarization remains underexplored. To stimulate research in this area, we present a new dataset, MovieSum, for abstractive summarization of movie screenplays. This dataset comprises 2200 movie screenplays accompanied by their Wikipedia plot summaries. We manually formatted the movie screenplays to represent their structural elements. Compared to existing datasets, MovieSum possesses several distinctive features: (1) It includes movie screenplays, which are longer than scripts of TV episodes. (2) It is twice the size of previous movie screenplay datasets. (3) It provides metadata with IMDb IDs to facilitate access to additional external knowledge. We also show the results of recently released large language models applied to summarization on our dataset to provide a detailed baseline.
Are We Done with MMLU?
Jun 07, 2024



Abstract:Maybe not. We identify and analyse errors in the popular Massive Multitask Language Understanding (MMLU) benchmark. Even though MMLU is widely adopted, our analysis demonstrates numerous ground truth errors that obscure the true capabilities of LLMs. For example, we find that 57% of the analysed questions in the Virology subset contain errors. To address this issue, we introduce a comprehensive framework for identifying dataset errors using a novel error taxonomy. Then, we create MMLU-Redux, which is a subset of 3,000 manually re-annotated questions across 30 MMLU subjects. Using MMLU-Redux, we demonstrate significant discrepancies with the model performance metrics that were originally reported. Our results strongly advocate for revising MMLU's error-ridden questions to enhance its future utility and reliability as a benchmark. Therefore, we open up MMLU-Redux for additional annotation https://huggingface.co/datasets/edinburgh-dawg/mmlu-redux.
The Hallucinations Leaderboard -- An Open Effort to Measure Hallucinations in Large Language Models
Apr 08, 2024Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have transformed the Natural Language Processing (NLP) landscape with their remarkable ability to understand and generate human-like text. However, these models are prone to ``hallucinations'' -- outputs that do not align with factual reality or the input context. This paper introduces the Hallucinations Leaderboard, an open initiative to quantitatively measure and compare the tendency of each model to produce hallucinations. The leaderboard uses a comprehensive set of benchmarks focusing on different aspects of hallucinations, such as factuality and faithfulness, across various tasks, including question-answering, summarisation, and reading comprehension. Our analysis provides insights into the performance of different models, guiding researchers and practitioners in choosing the most reliable models for their applications.
Select and Summarize: Scene Saliency for Movie Script Summarization
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Abstractive summarization for long-form narrative texts such as movie scripts is challenging due to the computational and memory constraints of current language models. A movie script typically comprises a large number of scenes; however, only a fraction of these scenes are salient, i.e., important for understanding the overall narrative. The salience of a scene can be operationalized by considering it as salient if it is mentioned in the summary. Automatically identifying salient scenes is difficult due to the lack of suitable datasets. In this work, we introduce a scene saliency dataset that consists of human-annotated salient scenes for 100 movies. We propose a two-stage abstractive summarization approach which first identifies the salient scenes in script and then generates a summary using only those scenes. Using QA-based evaluation, we show that our model outperforms previous state-of-the-art summarization methods and reflects the information content of a movie more accurately than a model that takes the whole movie script as input.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge