Dongqi Liu
Disco-RAG: Discourse-Aware Retrieval-Augmented Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) has emerged as an important means of enhancing the performance of large language models (LLMs) in knowledge-intensive tasks. However, most existing RAG strategies treat retrieved passages in a flat and unstructured way, which prevents the model from capturing structural cues and constrains its ability to synthesize knowledge from dispersed evidence across documents. To overcome these limitations, we propose Disco-RAG, a discourse-aware framework that explicitly injects discourse signals into the generation process. Our method constructs intra-chunk discourse trees to capture local hierarchies and builds inter-chunk rhetorical graphs to model cross-passage coherence. These structures are jointly integrated into a planning blueprint that conditions the generation. Experiments on question answering and long-document summarization benchmarks show the efficacy of our approach. Disco-RAG achieves state-of-the-art results on the benchmarks without fine-tuning. These findings underscore the important role of discourse structure in advancing RAG systems.
RoleRMBench & RoleRM: Towards Reward Modeling for Profile-Based Role Play in Dialogue Systems
Dec 11, 2025Abstract:Reward modeling has become a cornerstone of aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences. Yet, when extended to subjective and open-ended domains such as role play, existing reward models exhibit severe degradation, struggling to capture nuanced and persona-grounded human judgments. To address this gap, we introduce RoleRMBench, the first systematic benchmark for reward modeling in role-playing dialogue, covering seven fine-grained capabilities from narrative management to role consistency and engagement. Evaluation on RoleRMBench reveals large and consistent gaps between general-purpose reward models and human judgment, particularly in narrative and stylistic dimensions. We further propose RoleRM, a reward model trained with Continuous Implicit Preferences (CIP), which reformulates subjective evaluation as continuous consistent pairwise supervision under multiple structuring strategies. Comprehensive experiments show that RoleRM surpasses strong open- and closed-source reward models by over 24% on average, demonstrating substantial gains in narrative coherence and stylistic fidelity. Our findings highlight the importance of continuous preference representation and annotation consistency, establishing a foundation for subjective alignment in human-centered dialogue systems.
Explanatory Summarization with Discourse-Driven Planning
Apr 27, 2025Abstract:Lay summaries for scientific documents typically include explanations to help readers grasp sophisticated concepts or arguments. However, current automatic summarization methods do not explicitly model explanations, which makes it difficult to align the proportion of explanatory content with human-written summaries. In this paper, we present a plan-based approach that leverages discourse frameworks to organize summary generation and guide explanatory sentences by prompting responses to the plan. Specifically, we propose two discourse-driven planning strategies, where the plan is conditioned as part of the input or part of the output prefix, respectively. Empirical experiments on three lay summarization datasets show that our approach outperforms existing state-of-the-art methods in terms of summary quality, and it enhances model robustness, controllability, and mitigates hallucination.
What Is That Talk About? A Video-to-Text Summarization Dataset for Scientific Presentations
Feb 12, 2025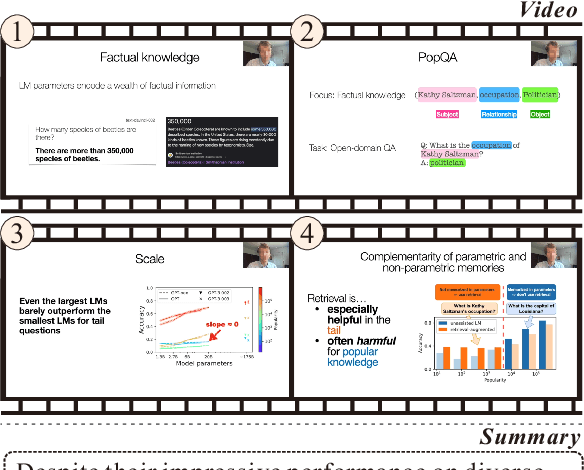
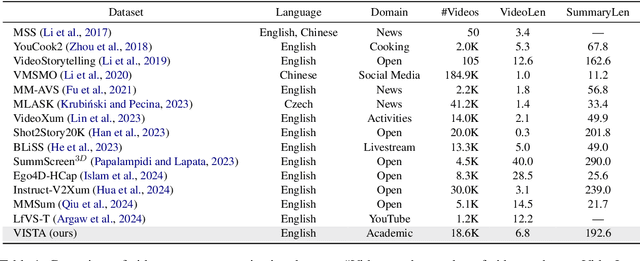

Abstract:Transforming recorded videos into concise and accurate textual summaries is a growing challenge in multimodal learning. This paper introduces VISTA, a dataset specifically designed for video-to-text summarization in scientific domains. VISTA contains 18,599 recorded AI conference presentations paired with their corresponding paper abstracts. We benchmark the performance of state-of-the-art large models and apply a plan-based framework to better capture the structured nature of abstracts. Both human and automated evaluations confirm that explicit planning enhances summary quality and factual consistency. However, a considerable gap remains between models and human performance, highlighting the challenges of scientific video summarization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge