Qingqing Zhao
CoT-VLA: Visual Chain-of-Thought Reasoning for Vision-Language-Action Models
Mar 27, 2025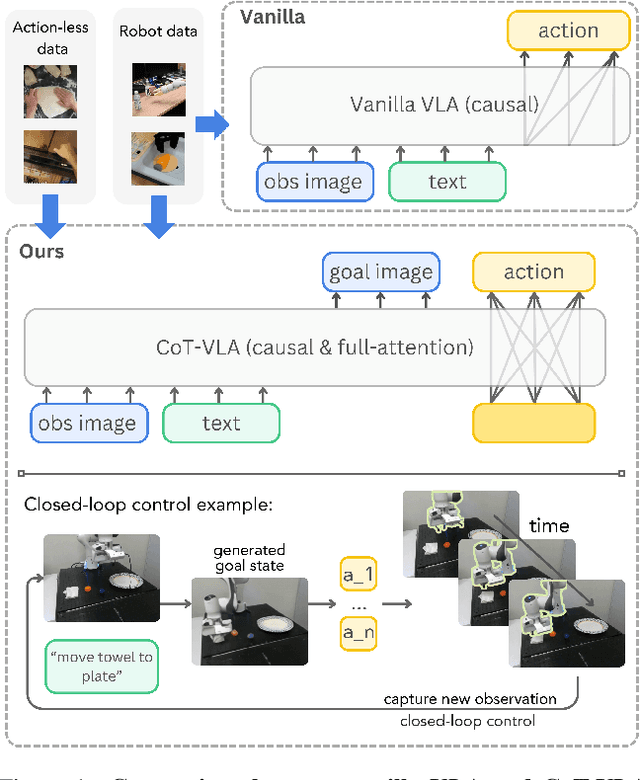
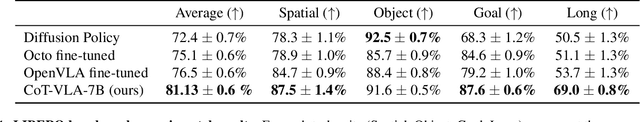
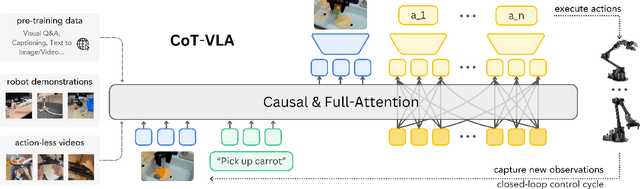
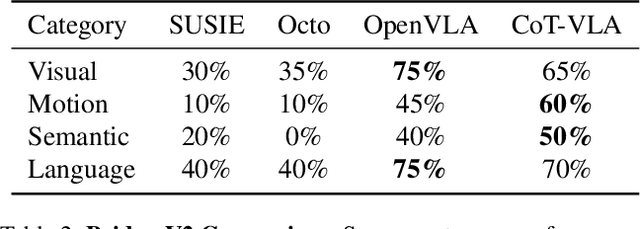
Abstract:Vision-language-action models (VLAs) have shown potential in leveraging pretrained vision-language models and diverse robot demonstrations for learning generalizable sensorimotor control. While this paradigm effectively utilizes large-scale data from both robotic and non-robotic sources, current VLAs primarily focus on direct input--output mappings, lacking the intermediate reasoning steps crucial for complex manipulation tasks. As a result, existing VLAs lack temporal planning or reasoning capabilities. In this paper, we introduce a method that incorporates explicit visual chain-of-thought (CoT) reasoning into vision-language-action models (VLAs) by predicting future image frames autoregressively as visual goals before generating a short action sequence to achieve these goals. We introduce CoT-VLA, a state-of-the-art 7B VLA that can understand and generate visual and action tokens. Our experimental results demonstrate that CoT-VLA achieves strong performance, outperforming the state-of-the-art VLA model by 17% in real-world manipulation tasks and 6% in simulation benchmarks. Project website: https://cot-vla.github.io/
* Project website: https://cot-vla.github.io/
Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform for Physical AI
Jan 07, 2025



Abstract:Physical AI needs to be trained digitally first. It needs a digital twin of itself, the policy model, and a digital twin of the world, the world model. In this paper, we present the Cosmos World Foundation Model Platform to help developers build customized world models for their Physical AI setups. We position a world foundation model as a general-purpose world model that can be fine-tuned into customized world models for downstream applications. Our platform covers a video curation pipeline, pre-trained world foundation models, examples of post-training of pre-trained world foundation models, and video tokenizers. To help Physical AI builders solve the most critical problems of our society, we make our platform open-source and our models open-weight with permissive licenses available via https://github.com/NVIDIA/Cosmos.
HumanPlus: Humanoid Shadowing and Imitation from Humans
Jun 15, 2024Abstract:One of the key arguments for building robots that have similar form factors to human beings is that we can leverage the massive human data for training. Yet, doing so has remained challenging in practice due to the complexities in humanoid perception and control, lingering physical gaps between humanoids and humans in morphologies and actuation, and lack of a data pipeline for humanoids to learn autonomous skills from egocentric vision. In this paper, we introduce a full-stack system for humanoids to learn motion and autonomous skills from human data. We first train a low-level policy in simulation via reinforcement learning using existing 40-hour human motion datasets. This policy transfers to the real world and allows humanoid robots to follow human body and hand motion in real time using only a RGB camera, i.e. shadowing. Through shadowing, human operators can teleoperate humanoids to collect whole-body data for learning different tasks in the real world. Using the data collected, we then perform supervised behavior cloning to train skill policies using egocentric vision, allowing humanoids to complete different tasks autonomously by imitating human skills. We demonstrate the system on our customized 33-DoF 180cm humanoid, autonomously completing tasks such as wearing a shoe to stand up and walk, unloading objects from warehouse racks, folding a sweatshirt, rearranging objects, typing, and greeting another robot with 60-100% success rates using up to 40 demonstrations. Project website: https://humanoid-ai.github.io/
PhysAvatar: Learning the Physics of Dressed 3D Avatars from Visual Observations
Apr 09, 2024



Abstract:Modeling and rendering photorealistic avatars is of crucial importance in many applications. Existing methods that build a 3D avatar from visual observations, however, struggle to reconstruct clothed humans. We introduce PhysAvatar, a novel framework that combines inverse rendering with inverse physics to automatically estimate the shape and appearance of a human from multi-view video data along with the physical parameters of the fabric of their clothes. For this purpose, we adopt a mesh-aligned 4D Gaussian technique for spatio-temporal mesh tracking as well as a physically based inverse renderer to estimate the intrinsic material properties. PhysAvatar integrates a physics simulator to estimate the physical parameters of the garments using gradient-based optimization in a principled manner. These novel capabilities enable PhysAvatar to create high-quality novel-view renderings of avatars dressed in loose-fitting clothes under motions and lighting conditions not seen in the training data. This marks a significant advancement towards modeling photorealistic digital humans using physically based inverse rendering with physics in the loop. Our project website is at: https://qingqing-zhao.github.io/PhysAvatar
SensoryT5: Infusing Sensorimotor Norms into T5 for Enhanced Fine-grained Emotion Classification
Mar 22, 2024



Abstract:In traditional research approaches, sensory perception and emotion classification have traditionally been considered separate domains. Yet, the significant influence of sensory experiences on emotional responses is undeniable. The natural language processing (NLP) community has often missed the opportunity to merge sensory knowledge with emotion classification. To address this gap, we propose SensoryT5, a neuro-cognitive approach that integrates sensory information into the T5 (Text-to-Text Transfer Transformer) model, designed specifically for fine-grained emotion classification. This methodology incorporates sensory cues into the T5's attention mechanism, enabling a harmonious balance between contextual understanding and sensory awareness. The resulting model amplifies the richness of emotional representations. In rigorous tests across various detailed emotion classification datasets, SensoryT5 showcases improved performance, surpassing both the foundational T5 model and current state-of-the-art works. Notably, SensoryT5's success signifies a pivotal change in the NLP domain, highlighting the potential influence of neuro-cognitive data in refining machine learning models' emotional sensitivity.
Pose-to-Motion: Cross-Domain Motion Retargeting with Pose Prior
Oct 31, 2023



Abstract:Creating believable motions for various characters has long been a goal in computer graphics. Current learning-based motion synthesis methods depend on extensive motion datasets, which are often challenging, if not impossible, to obtain. On the other hand, pose data is more accessible, since static posed characters are easier to create and can even be extracted from images using recent advancements in computer vision. In this paper, we utilize this alternative data source and introduce a neural motion synthesis approach through retargeting. Our method generates plausible motions for characters that have only pose data by transferring motion from an existing motion capture dataset of another character, which can have drastically different skeletons. Our experiments show that our method effectively combines the motion features of the source character with the pose features of the target character, and performs robustly with small or noisy pose data sets, ranging from a few artist-created poses to noisy poses estimated directly from images. Additionally, a conducted user study indicated that a majority of participants found our retargeted motion to be more enjoyable to watch, more lifelike in appearance, and exhibiting fewer artifacts. Project page: https://cyanzhao42.github.io/pose2motion
Learning Controllable Adaptive Simulation for Multi-resolution Physics
May 01, 2023Abstract:Simulating the time evolution of physical systems is pivotal in many scientific and engineering problems. An open challenge in simulating such systems is their multi-resolution dynamics: a small fraction of the system is extremely dynamic, and requires very fine-grained resolution, while a majority of the system is changing slowly and can be modeled by coarser spatial scales. Typical learning-based surrogate models use a uniform spatial scale, which needs to resolve to the finest required scale and can waste a huge compute to achieve required accuracy. In this work, we introduce Learning controllable Adaptive simulation for Multi-resolution Physics (LAMP) as the first full deep learning-based surrogate model that jointly learns the evolution model and optimizes appropriate spatial resolutions that devote more compute to the highly dynamic regions. LAMP consists of a Graph Neural Network (GNN) for learning the forward evolution, and a GNN-based actor-critic for learning the policy of spatial refinement and coarsening. We introduce learning techniques that optimizes LAMP with weighted sum of error and computational cost as objective, allowing LAMP to adapt to varying relative importance of error vs. computation tradeoff at inference time. We evaluate our method in a 1D benchmark of nonlinear PDEs and a challenging 2D mesh-based simulation. We demonstrate that our LAMP outperforms state-of-the-art deep learning surrogate models, and can adaptively trade-off computation to improve long-term prediction error: it achieves an average of 33.7% error reduction for 1D nonlinear PDEs, and outperforms MeshGraphNets + classical Adaptive Mesh Refinement (AMR) in 2D mesh-based simulations. Project website with data and code can be found at: http://snap.stanford.edu/lamp.
Learning to Solve PDE-constrained Inverse Problems with Graph Networks
Jun 01, 2022



Abstract:Learned graph neural networks (GNNs) have recently been established as fast and accurate alternatives for principled solvers in simulating the dynamics of physical systems. In many application domains across science and engineering, however, we are not only interested in a forward simulation but also in solving inverse problems with constraints defined by a partial differential equation (PDE). Here we explore GNNs to solve such PDE-constrained inverse problems. Given a sparse set of measurements, we are interested in recovering the initial condition or parameters of the PDE. We demonstrate that GNNs combined with autodecoder-style priors are well-suited for these tasks, achieving more accurate estimates of initial conditions or physical parameters than other learned approaches when applied to the wave equation or Navier-Stokes equations. We also demonstrate computational speedups of up to 90x using GNNs compared to principled solvers. Project page: https://cyanzhao42.github.io/LearnInverseProblem
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge