Prateek Gupta
The Role of Social Learning and Collective Norm Formation in Fostering Cooperation in LLM Multi-Agent Systems
Oct 16, 2025Abstract:A growing body of multi-agent studies with Large Language Models (LLMs) explores how norms and cooperation emerge in mixed-motive scenarios, where pursuing individual gain can undermine the collective good. While prior work has explored these dynamics in both richly contextualized simulations and simplified game-theoretic environments, most LLM systems featuring common-pool resource (CPR) games provide agents with explicit reward functions directly tied to their actions. In contrast, human cooperation often emerges without full visibility into payoffs and population, relying instead on heuristics, communication, and punishment. We introduce a CPR simulation framework that removes explicit reward signals and embeds cultural-evolutionary mechanisms: social learning (adopting strategies and beliefs from successful peers) and norm-based punishment, grounded in Ostrom's principles of resource governance. Agents also individually learn from the consequences of harvesting, monitoring, and punishing via environmental feedback, enabling norms to emerge endogenously. We establish the validity of our simulation by reproducing key findings from existing studies on human behavior. Building on this, we examine norm evolution across a $2\times2$ grid of environmental and social initialisations (resource-rich vs. resource-scarce; altruistic vs. selfish) and benchmark how agentic societies comprised of different LLMs perform under these conditions. Our results reveal systematic model differences in sustaining cooperation and norm formation, positioning the framework as a rigorous testbed for studying emergent norms in mixed-motive LLM societies. Such analysis can inform the design of AI systems deployed in social and organizational contexts, where alignment with cooperative norms is critical for stability, fairness, and effective governance of AI-mediated environments.
OASIS: Open Agent Social Interaction Simulations with One Million Agents
Nov 26, 2024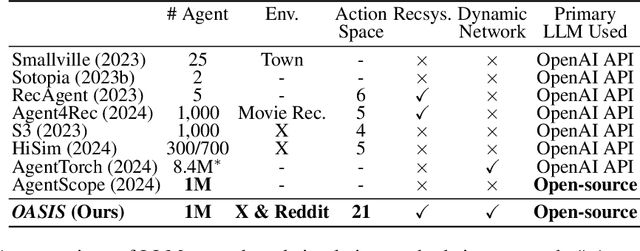
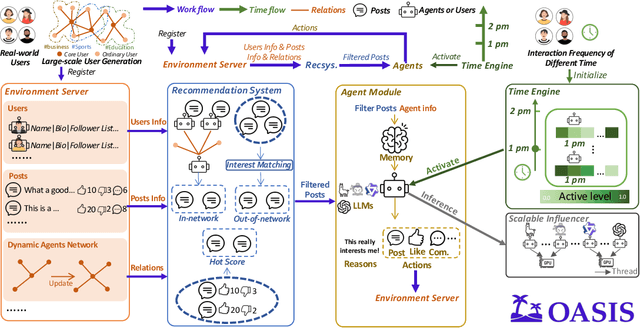

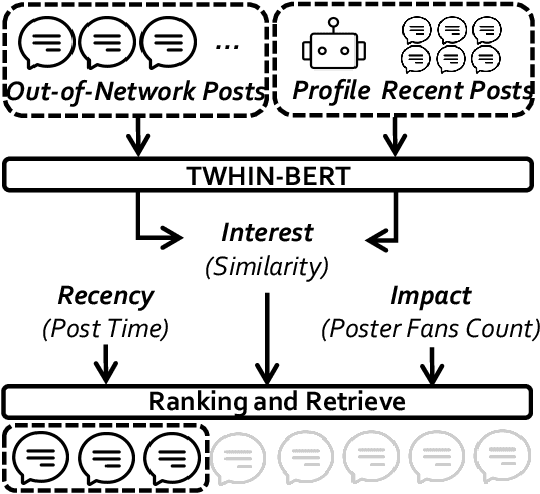
Abstract:There has been a growing interest in enhancing rule-based agent-based models (ABMs) for social media platforms (i.e., X, Reddit) with more realistic large language model (LLM) agents, thereby allowing for a more nuanced study of complex systems. As a result, several LLM-based ABMs have been proposed in the past year. While they hold promise, each simulator is specifically designed to study a particular scenario, making it time-consuming and resource-intensive to explore other phenomena using the same ABM. Additionally, these models simulate only a limited number of agents, whereas real-world social media platforms involve millions of users. To this end, we propose OASIS, a generalizable and scalable social media simulator. OASIS is designed based on real-world social media platforms, incorporating dynamically updated environments (i.e., dynamic social networks and post information), diverse action spaces (i.e., following, commenting), and recommendation systems (i.e., interest-based and hot-score-based). Additionally, OASIS supports large-scale user simulations, capable of modeling up to one million users. With these features, OASIS can be easily extended to different social media platforms to study large-scale group phenomena and behaviors. We replicate various social phenomena, including information spreading, group polarization, and herd effects across X and Reddit platforms. Moreover, we provide observations of social phenomena at different agent group scales. We observe that the larger agent group scale leads to more enhanced group dynamics and more diverse and helpful agents' opinions. These findings demonstrate OASIS's potential as a powerful tool for studying complex systems in digital environments.
OASIS: Open Agents Social Interaction Simulations on One Million Agents
Nov 21, 2024



Abstract:There has been a growing interest in enhancing rule-based agent-based models (ABMs) for social media platforms (i.e., X, Reddit) with more realistic large language model (LLM) agents, thereby allowing for a more nuanced study of complex systems. As a result, several LLM-based ABMs have been proposed in the past year. While they hold promise, each simulator is specifically designed to study a particular scenario, making it time-consuming and resource-intensive to explore other phenomena using the same ABM. Additionally, these models simulate only a limited number of agents, whereas real-world social media platforms involve millions of users. To this end, we propose OASIS, a generalizable and scalable social media simulator. OASIS is designed based on real-world social media platforms, incorporating dynamically updated environments (i.e., dynamic social networks and post information), diverse action spaces (i.e., following, commenting), and recommendation systems (i.e., interest-based and hot-score-based). Additionally, OASIS supports large-scale user simulations, capable of modeling up to one million users. With these features, OASIS can be easily extended to different social media platforms to study large-scale group phenomena and behaviors. We replicate various social phenomena, including information spreading, group polarization, and herd effects across X and Reddit platforms. Moreover, we provide observations of social phenomena at different agent group scales. We observe that the larger agent group scale leads to more enhanced group dynamics and more diverse and helpful agents' opinions. These findings demonstrate OASIS's potential as a powerful tool for studying complex systems in digital environments.
Machine learning and optimization-based approaches to duality in statistical physics
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:The notion of duality -- that a given physical system can have two different mathematical descriptions -- is a key idea in modern theoretical physics. Establishing a duality in lattice statistical mechanics models requires the construction of a dual Hamiltonian and a map from the original to the dual observables. By using simple neural networks to parameterize these maps and introducing a loss function that penalises the difference between correlation functions in original and dual models, we formulate the process of duality discovery as an optimization problem. We numerically solve this problem and show that our framework can rediscover the celebrated Kramers-Wannier duality for the 2d Ising model, reconstructing the known mapping of temperatures. We also discuss an alternative approach which uses known features of the mapping of topological lines to reduce the problem to optimizing the couplings in a dual Hamiltonian, and explore next-to-nearest neighbour deformations of the 2d Ising duality. We discuss future directions and prospects for discovering new dualities within this framework.
Empirical evidence of Large Language Model's influence on human spoken communication
Sep 03, 2024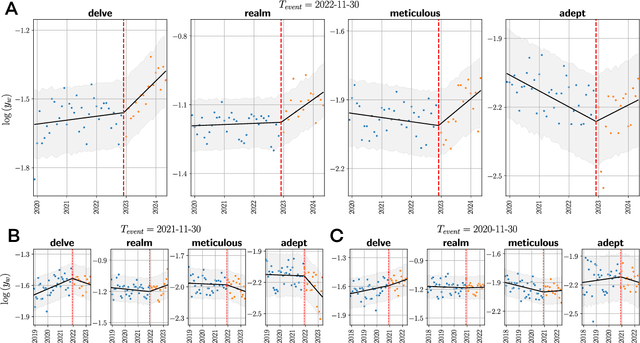
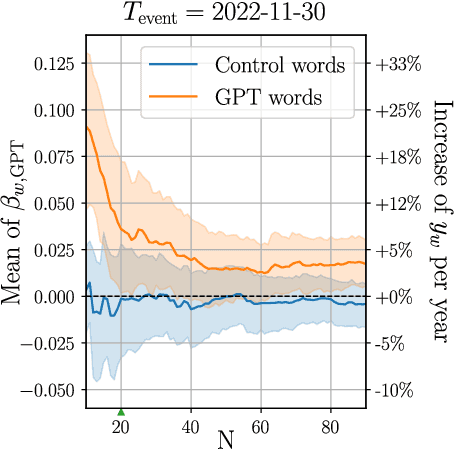
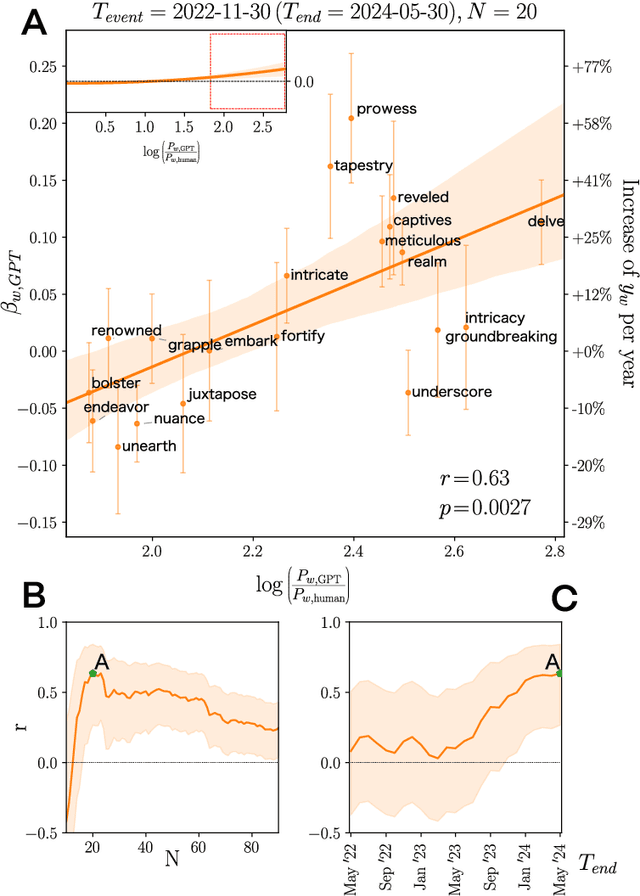

Abstract:Artificial Intelligence (AI) agents now interact with billions of humans in natural language, thanks to advances in Large Language Models (LLMs) like ChatGPT. This raises the question of whether AI has the potential to shape a fundamental aspect of human culture: the way we speak. Recent analyses revealed that scientific publications already exhibit evidence of AI-specific language. But this evidence is inconclusive, since scientists may simply be using AI to copy-edit their writing. To explore whether AI has influenced human spoken communication, we transcribed and analyzed about 280,000 English-language videos of presentations, talks, and speeches from more than 20,000 YouTube channels of academic institutions. We find a significant shift in the trend of word usage specific to words distinctively associated with ChatGPT following its release. These findings provide the first empirical evidence that humans increasingly imitate LLMs in their spoken language. Our results raise societal and policy-relevant concerns about the potential of AI to unintentionally reduce linguistic diversity, or to be deliberately misused for mass manipulation. They also highlight the need for further investigation into the feedback loops between machine behavior and human culture.
Generative Active Learning for the Search of Small-molecule Protein Binders
May 02, 2024



Abstract:Despite substantial progress in machine learning for scientific discovery in recent years, truly de novo design of small molecules which exhibit a property of interest remains a significant challenge. We introduce LambdaZero, a generative active learning approach to search for synthesizable molecules. Powered by deep reinforcement learning, LambdaZero learns to search over the vast space of molecules to discover candidates with a desired property. We apply LambdaZero with molecular docking to design novel small molecules that inhibit the enzyme soluble Epoxide Hydrolase 2 (sEH), while enforcing constraints on synthesizability and drug-likeliness. LambdaZero provides an exponential speedup in terms of the number of calls to the expensive molecular docking oracle, and LambdaZero de novo designed molecules reach docking scores that would otherwise require the virtual screening of a hundred billion molecules. Importantly, LambdaZero discovers novel scaffolds of synthesizable, drug-like inhibitors for sEH. In in vitro experimental validation, a series of ligands from a generated quinazoline-based scaffold were synthesized, and the lead inhibitor N-(4,6-di(pyrrolidin-1-yl)quinazolin-2-yl)-N-methylbenzamide (UM0152893) displayed sub-micromolar enzyme inhibition of sEH.
AI For Global Climate Cooperation 2023 Competition Proceedings
Jul 10, 2023Abstract:The international community must collaborate to mitigate climate change and sustain economic growth. However, collaboration is hard to achieve, partly because no global authority can ensure compliance with international climate agreements. Combining AI with climate-economic simulations offers a promising solution to design international frameworks, including negotiation protocols and climate agreements, that promote and incentivize collaboration. In addition, these frameworks should also have policy goals fulfillment, and sustained commitment, taking into account climate-economic dynamics and strategic behaviors. These challenges require an interdisciplinary approach across machine learning, economics, climate science, law, policy, ethics, and other fields. Towards this objective, we organized AI for Global Climate Cooperation, a Mila competition in which teams submitted proposals and analyses of international frameworks, based on (modifications of) RICE-N, an AI-driven integrated assessment model (IAM). In particular, RICE-N supports modeling regional decision-making using AI agents. Furthermore, the IAM then models the climate-economic impact of those decisions into the future. Whereas the first track focused only on performance metrics, the proposals submitted to the second track were evaluated both quantitatively and qualitatively. The quantitative evaluation focused on a combination of (i) the degree of mitigation of global temperature rise and (ii) the increase in economic productivity. On the other hand, an interdisciplinary panel of human experts in law, policy, sociology, economics and environmental science, evaluated the solutions qualitatively. In particular, the panel considered the effectiveness, simplicity, feasibility, ethics, and notions of climate justice of the protocols. In the third track, the participants were asked to critique and improve RICE-N.
GNN-Assisted Phase Space Integration with Application to Atomistics
Mar 20, 2023



Abstract:Overcoming the time scale limitations of atomistics can be achieved by switching from the state-space representation of Molecular Dynamics (MD) to a statistical-mechanics-based representation in phase space, where approximations such as maximum-entropy or Gaussian phase packets (GPP) evolve the atomistic ensemble in a time-coarsened fashion. In practice, this requires the computation of expensive high-dimensional integrals over all of phase space of an atomistic ensemble. This, in turn, is commonly accomplished efficiently by low-order numerical quadrature. We show that numerical quadrature in this context, unfortunately, comes with a set of inherent problems, which corrupt the accuracy of simulations -- especially when dealing with crystal lattices with imperfections. As a remedy, we demonstrate that Graph Neural Networks, trained on Monte-Carlo data, can serve as a replacement for commonly used numerical quadrature rules, overcoming their deficiencies and significantly improving the accuracy. This is showcased by three benchmarks: the thermal expansion of copper, the martensitic phase transition of iron, and the energy of grain boundaries. We illustrate the benefits of the proposed technique over classically used third- and fifth-order Gaussian quadrature, we highlight the impact on time-coarsened atomistic predictions, and we discuss the computational efficiency. The latter is of general importance when performing frequent evaluation of phase space or other high-dimensional integrals, which is why the proposed framework promises applications beyond the scope of atomistics.
AI for Global Climate Cooperation: Modeling Global Climate Negotiations, Agreements, and Long-Term Cooperation in RICE-N
Aug 15, 2022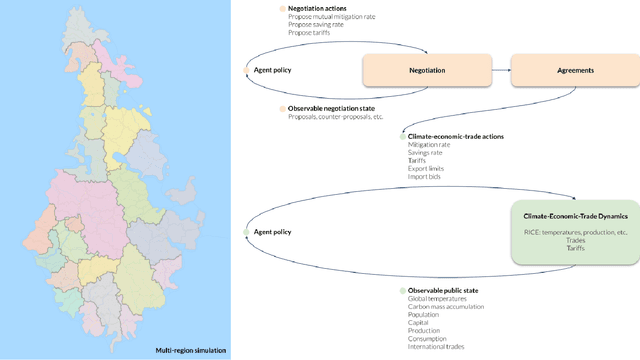
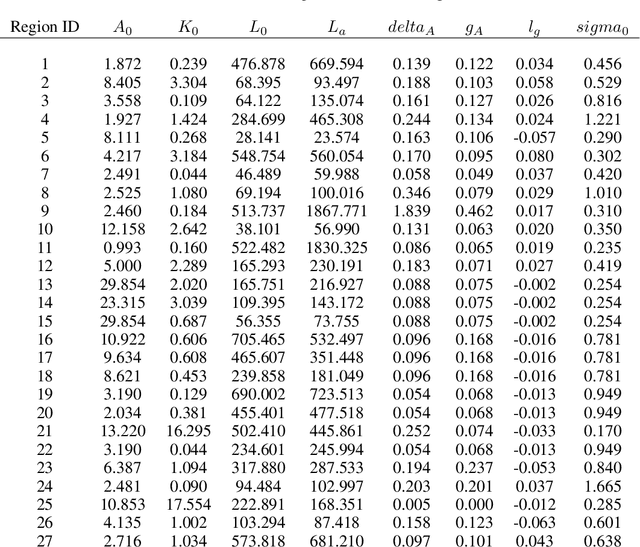
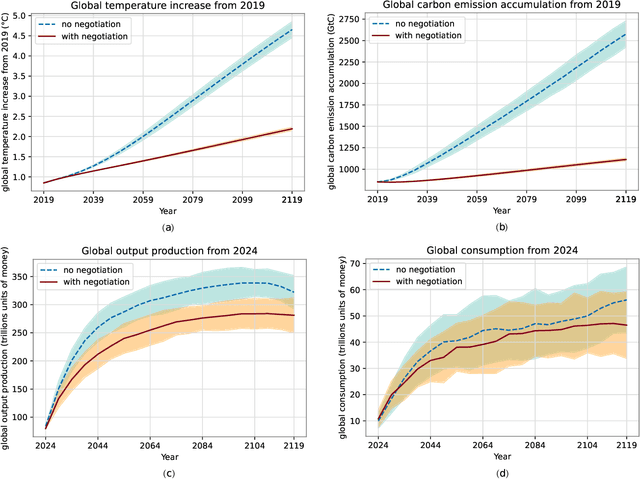
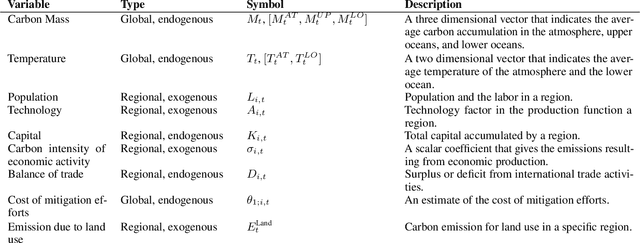
Abstract:Comprehensive global cooperation is essential to limit global temperature increases while continuing economic development, e.g., reducing severe inequality or achieving long-term economic growth. Achieving long-term cooperation on climate change mitigation with n strategic agents poses a complex game-theoretic problem. For example, agents may negotiate and reach climate agreements, but there is no central authority to enforce adherence to those agreements. Hence, it is critical to design negotiation and agreement frameworks that foster cooperation, allow all agents to meet their individual policy objectives, and incentivize long-term adherence. This is an interdisciplinary challenge that calls for collaboration between researchers in machine learning, economics, climate science, law, policy, ethics, and other fields. In particular, we argue that machine learning is a critical tool to address the complexity of this domain. To facilitate this research, here we introduce RICE-N, a multi-region integrated assessment model that simulates the global climate and economy, and which can be used to design and evaluate the strategic outcomes for different negotiation and agreement frameworks. We also describe how to use multi-agent reinforcement learning to train rational agents using RICE-N. This framework underpinsAI for Global Climate Cooperation, a working group collaboration and competition on climate negotiation and agreement design. Here, we invite the scientific community to design and evaluate their solutions using RICE-N, machine learning, economic intuition, and other domain knowledge. More information can be found on www.ai4climatecoop.org.
Lookback for Learning to Branch
Jun 30, 2022



Abstract:The expressive and computationally inexpensive bipartite Graph Neural Networks (GNN) have been shown to be an important component of deep learning based Mixed-Integer Linear Program (MILP) solvers. Recent works have demonstrated the effectiveness of such GNNs in replacing the branching (variable selection) heuristic in branch-and-bound (B&B) solvers. These GNNs are trained, offline and on a collection of MILPs, to imitate a very good but computationally expensive branching heuristic, strong branching. Given that B&B results in a tree of sub-MILPs, we ask (a) whether there are strong dependencies exhibited by the target heuristic among the neighboring nodes of the B&B tree, and (b) if so, whether we can incorporate them in our training procedure. Specifically, we find that with the strong branching heuristic, a child node's best choice was often the parent's second-best choice. We call this the "lookback" phenomenon. Surprisingly, the typical branching GNN of Gasse et al. (2019) often misses this simple "answer". To imitate the target behavior more closely by incorporating the lookback phenomenon in GNNs, we propose two methods: (a) target smoothing for the standard cross-entropy loss function, and (b) adding a Parent-as-Target (PAT) Lookback regularizer term. Finally, we propose a model selection framework to incorporate harder-to-formulate objectives such as solving time in the final models. Through extensive experimentation on standard benchmark instances, we show that our proposal results in up to 22% decrease in the size of the B&B tree and up to 15% improvement in the solving times.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge