Phuc Nguyen
Transform-Augmented GRPO Improves Pass@k
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Large language models trained via next-token prediction are fundamentally pattern-matchers: sensitive to superficial phrasing variations even when the underlying problem is identical. Group Relative Policy Optimization (GRPO) was designed to improve reasoning, but in fact it worsens this situation through two failure modes: diversity collapse, where training amplifies a single solution strategy while ignoring alternatives of gradient signal, and gradient diminishing, where a large portion of questions yield zero gradients because all rollouts receive identical rewards. We propose TA-GRPO (Transform-Augmented GRPO), which generates semantically equivalent transformed variants of each question (via paraphrasing, variable renaming, and format changes) and computes advantages by pooling rewards across the entire group. This pooled computation ensures mixed rewards even when the original question is too easy or too hard, while training on diverse phrasings promotes multiple solution strategies. We provide theoretical justification showing that TA-GRPO reduces zero-gradient probability and improves generalization via reduced train-test distribution shift. Experiments on mathematical reasoning benchmarks show consistent Pass@k improvements, with gains up to 9.84 points on competition math (AMC12, AIME24) and 5.05 points on out-of-distribution scientific reasoning (GPQA-Diamond).
BanditLP: Large-Scale Stochastic Optimization for Personalized Recommendations
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:We present BanditLP, a scalable multi-stakeholder contextual bandit framework that unifies neural Thompson Sampling for learning objective-specific outcomes with a large-scale linear program for constrained action selection at serving time. The methodology is application-agnostic, compatible with arbitrary neural architectures, and deployable at web scale, with an LP solver capable of handling billions of variables. Experiments on public benchmarks and synthetic data show consistent gains over strong baselines. We apply this approach in LinkedIn's email marketing system and demonstrate business win, illustrating the value of integrated exploration and constrained optimization in production.
Which Similarity-Sensitive Entropy?
Nov 10, 2025Abstract:A canonical step in quantifying a system is to measure its entropy. Shannon entropy and other traditional entropy measures capture only the information encoded in the frequencies of a system's elements. Recently, Leinster, Cobbold, and Reeve (LCR) introduced a method that also captures the rich information encoded in the similarities and differences among elements, yielding similarity-sensitive entropy. More recently, the Vendi score (VS) was introduced as an alternative, raising the question of how LCR and VS compare, and which is preferable. Here we address these questions conceptually, analytically, and experimentally, using 53 machine-learning datasets. We show that LCR and VS can differ by orders of magnitude and can capture complementary information about a system, except in limiting cases. We demonstrate that both LCR and VS depend on how similarities are scaled and introduce the concept of ``half distance'' to parameterize this dependence. We prove that VS provides an upper bound on LCR for several values of the Rényi-Hill order parameter and conjecture that this bound holds for all values. We conclude that VS is preferable only when interpreting elements as linear combinations of a more fundamental set of ``ur-elements'' or when the system or dataset possesses a quantum-mechanical character. In the broader circumstance where one seeks simply to capture the rich information encoded by similarity, LCR is favored; nevertheless, for certain half-distances the two methods can complement each other.
Beyond Basic A/B testing: Improving Statistical Efficiency for Business Growth
May 13, 2025Abstract:The standard A/B testing approaches are mostly based on t-test in large scale industry applications. These standard approaches however suffers from low statistical power in business settings, due to nature of small sample-size or non-Gaussian distribution or return-on-investment (ROI) consideration. In this paper, we propose several approaches to addresses these challenges: (i) regression adjustment, generalized estimating equation, Man-Whitney U and Zero-Trimmed U that addresses each of these issues separately, and (ii) a novel doubly robust generalized U that handles ROI consideration, distribution robustness and small samples in one framework. We provide theoretical results on asymptotic normality and efficiency bounds, together with insights on the efficiency gain from theoretical analysis. We further conduct comprehensive simulation studies and apply the methods to multiple real A/B tests.
Grade Inflation in Generative Models
Jan 05, 2025Abstract:Generative models hold great potential, but only if one can trust the evaluation of the data they generate. We show that many commonly used quality scores for comparing two-dimensional distributions of synthetic vs. ground-truth data give better results than they should, a phenomenon we call the "grade inflation problem." We show that the correlation score, Jaccard score, earth-mover's score, and Kullback-Leibler (relative-entropy) score all suffer grade inflation. We propose that any score that values all datapoints equally, as these do, will also exhibit grade inflation; we refer to such scores as "equipoint" scores. We introduce the concept of "equidensity" scores, and present the Eden score, to our knowledge the first example of such a score. We found that Eden avoids grade inflation and agrees better with human perception of goodness-of-fit than the equipoint scores above. We propose that any reasonable equidensity score will avoid grade inflation. We identify a connection between equidensity scores and R\'enyi entropy of negative order. We conclude that equidensity scores are likely to outperform equipoint scores for generative models, and for comparing low-dimensional distributions more generally.
QCResUNet: Joint Subject-level and Voxel-level Segmentation Quality Prediction
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:Deep learning has made significant strides in automated brain tumor segmentation from magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans in recent years. However, the reliability of these tools is hampered by the presence of poor-quality segmentation outliers, particularly in out-of-distribution samples, making their implementation in clinical practice difficult. Therefore, there is a need for quality control (QC) to screen the quality of the segmentation results. Although numerous automatic QC methods have been developed for segmentation quality screening, most were designed for cardiac MRI segmentation, which involves a single modality and a single tissue type. Furthermore, most prior works only provided subject-level predictions of segmentation quality and did not identify erroneous parts segmentation that may require refinement. To address these limitations, we proposed a novel multi-task deep learning architecture, termed QCResUNet, which produces subject-level segmentation-quality measures as well as voxel-level segmentation error maps for each available tissue class. To validate the effectiveness of the proposed method, we conducted experiments on assessing its performance on evaluating the quality of two distinct segmentation tasks. First, we aimed to assess the quality of brain tumor segmentation results. For this task, we performed experiments on one internal and two external datasets. Second, we aimed to evaluate the segmentation quality of cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) data from the Automated Cardiac Diagnosis Challenge. The proposed method achieved high performance in predicting subject-level segmentation-quality metrics and accurately identifying segmentation errors on a voxel basis. This has the potential to be used to guide human-in-the-loop feedback to improve segmentations in clinical settings.
Any3DIS: Class-Agnostic 3D Instance Segmentation by 2D Mask Tracking
Nov 25, 2024Abstract:Existing 3D instance segmentation methods frequently encounter issues with over-segmentation, leading to redundant and inaccurate 3D proposals that complicate downstream tasks. This challenge arises from their unsupervised merging approach, where dense 2D instance masks are lifted across frames into point clouds to form 3D candidate proposals without direct supervision. These candidates are then hierarchically merged based on heuristic criteria, often resulting in numerous redundant segments that fail to combine into precise 3D proposals. To overcome these limitations, we propose a 3D-Aware 2D Mask Tracking module that uses robust 3D priors from a 2D mask segmentation and tracking foundation model (SAM-2) to ensure consistent object masks across video frames. Rather than merging all visible superpoints across views to create a 3D mask, our 3D Mask Optimization module leverages a dynamic programming algorithm to select an optimal set of views, refining the superpoints to produce a final 3D proposal for each object. Our approach achieves comprehensive object coverage within the scene while reducing unnecessary proposals, which could otherwise impair downstream applications. Evaluations on ScanNet200 and ScanNet++ confirm the effectiveness of our method, with improvements across Class-Agnostic, Open-Vocabulary, and Open-Ended 3D Instance Segmentation tasks.
$\textit{lucie}$: An Improved Python Package for Loading Datasets from the UCI Machine Learning Repository
Oct 10, 2024Abstract:The University of California--Irvine (UCI) Machine Learning (ML) Repository (UCIMLR) is consistently cited as one of the most popular dataset repositories, hosting hundreds of high-impact datasets. However, a significant portion, including 28.4% of the top 250, cannot be imported via the $\textit{ucimlrepo}$ package that is provided and recommended by the UCIMLR website. Instead, they are hosted as .zip files, containing nonstandard formats that are difficult to import without additional ad hoc processing. To address this issue, here we present $\textit{lucie}$ -- $\underline{l}oad$ $\underline{U}niversity$ $\underline{C}alifornia$ $\underline{I}rvine$ $\underline{e}xamples$ -- a utility that automatically determines the data format and imports many of these previously non-importable datasets, while preserving as much of a tabular data structure as possible. $\textit{lucie}$ was designed using the top 100 most popular datasets and benchmarked on the next 130, where it resulted in a success rate of 95.4% vs. 73.1% for $\textit{ucimlrepo}$. $\textit{lucie}$ is available as a Python package on PyPI with 98% code coverage.
OpenSUN3D: 1st Workshop Challenge on Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding
Feb 23, 2024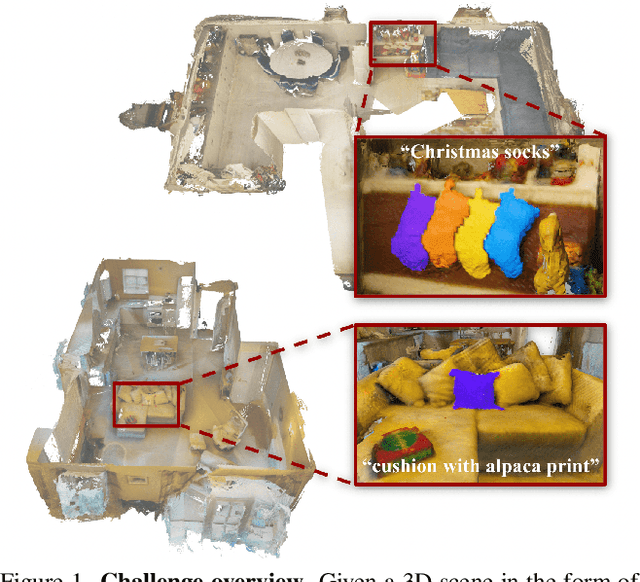

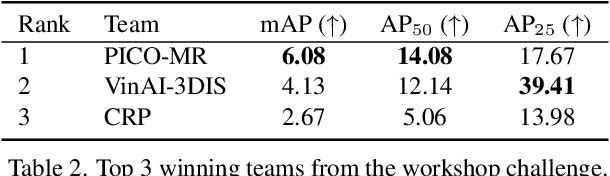
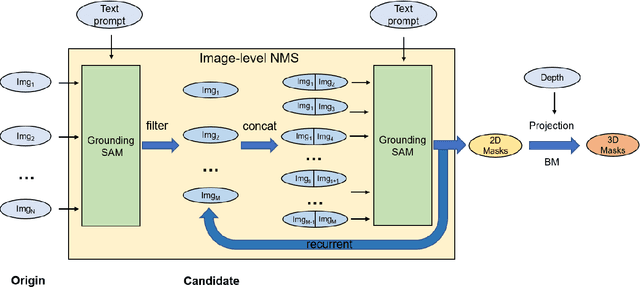
Abstract:This report provides an overview of the challenge hosted at the OpenSUN3D Workshop on Open-Vocabulary 3D Scene Understanding held in conjunction with ICCV 2023. The goal of this workshop series is to provide a platform for exploration and discussion of open-vocabulary 3D scene understanding tasks, including but not limited to segmentation, detection and mapping. We provide an overview of the challenge hosted at the workshop, present the challenge dataset, the evaluation methodology, and brief descriptions of the winning methods. For additional details, please see https://opensun3d.github.io/index_iccv23.html.
Real-Time Diagnostic Integrity Meets Efficiency: A Novel Platform-Agnostic Architecture for Physiological Signal Compression
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Head-based signals such as EEG, EMG, EOG, and ECG collected by wearable systems will play a pivotal role in clinical diagnosis, monitoring, and treatment of important brain disorder diseases. However, the real-time transmission of the significant corpus physiological signals over extended periods consumes substantial power and time, limiting the viability of battery-dependent physiological monitoring wearables. This paper presents a novel deep-learning framework employing a variational autoencoder (VAE) for physiological signal compression to reduce wearables' computational complexity and energy consumption. Our approach achieves an impressive compression ratio of 1:293 specifically for spectrogram data, surpassing state-of-the-art compression techniques such as JPEG2000, H.264, Direct Cosine Transform (DCT), and Huffman Encoding, which do not excel in handling physiological signals. We validate the efficacy of the compressed algorithms using collected physiological signals from real patients in the Hospital and deploy the solution on commonly used embedded AI chips (i.e., ARM Cortex V8 and Jetson Nano). The proposed framework achieves a 91% seizure detection accuracy using XGBoost, confirming the approach's reliability, practicality, and scalability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge